CLIP, as a BS2000 subsystem, uses the Syslog protocol to support external systems - such as SIEM solutions - in analyzing, consolidating, and storing events from multiple connected BS2000 systems. For this purpose, the CLIP subsystem must be active and properly configured on each monitored BS2000 system.
CLIP consists of two components:
TPR Component: The CLIP subsystem, managed via DSSM, is responsible for central processing of BS2000 events.
TU Component: A TU batch job that forwards BS2000 events to an external Syslog server using sockets.
TPR Component – CLIP Subsystem
CLIP is provided for the first time starting with BS2000 version V21.0B.
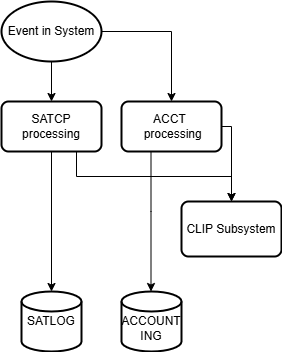
The following diagram illustrates the current CLIP integration with SAT and ACCOUNTING in schematic form.
The TPR component of CLIP receives SAT and ACCOUNTING data and passes it on to its TU component.
TU Component – CLIP Batch Job
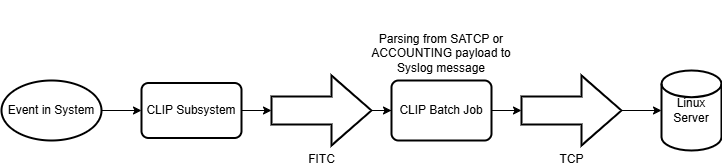
The CLIP batch job within the TU component establishes a TCP connection to the Syslog server, waits for events from the TPR component, analyzes them, and converts them into the Syslog format. After successful parsing, the events are transmitted via the socket interface to the external server configured in the CLIP configuration file.
A Syslog daemon must be running on the external server on the port configured in CLIP. This daemon receives and filters the incoming data and stores it in the server’s system logs.
The diagram provides a schematic representation of the current CLIP workflow in the TPR and TU components, using SAT and ACCOUNTING as examples.
If the connection to the Syslog server is lost, the batch job will, upon the next event to be sent (occurring at least one second after the connection loss), cyclically attempt to re-establish the connection. This process continues until either a timeout occurs or the internal buffer is full.