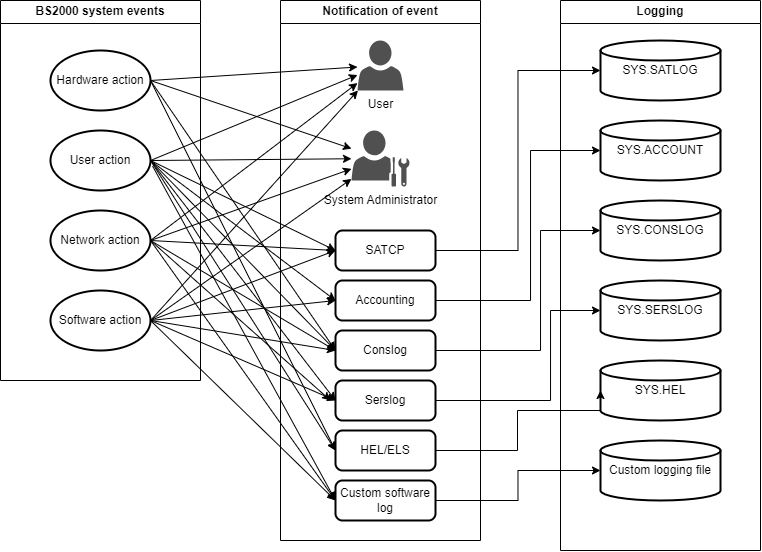
Every operating system should ensure that the System Administrator is aware of everything that occurs in the system. User actions, automated tasks, and hardware errors are all sources of actions and information that could be logged in the system. These logged activities will be referred to as events.
The diagram below illustrates the typical flow of information logging in the BS2000 operating system.
The quantity of events produced by an operating system during operation may be substantial. Therefore, filtration and pre-selection methods are utilized in specific logging tools. These methods are described in separate manuals that align with the relevant tool and will not be covered in this manual.
Several records are presented in a readable format for humans (like CONSLOG), whereas others may exist in a binary format and can only be accessed by particular applications (such as SATCP and SATUT).
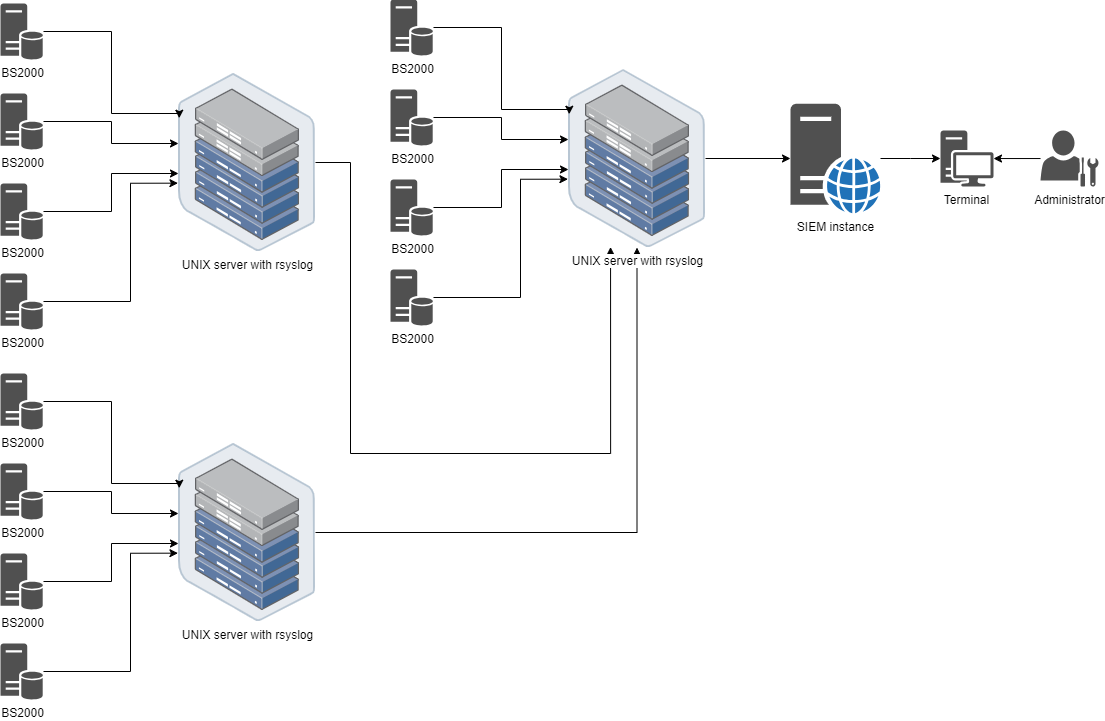
In complex systems that include several BS2000 server instances, managing a large number of logs can be challenging. Furthermore, certain logs are not accessible in real-time and may introduce a delay on the receiving end.
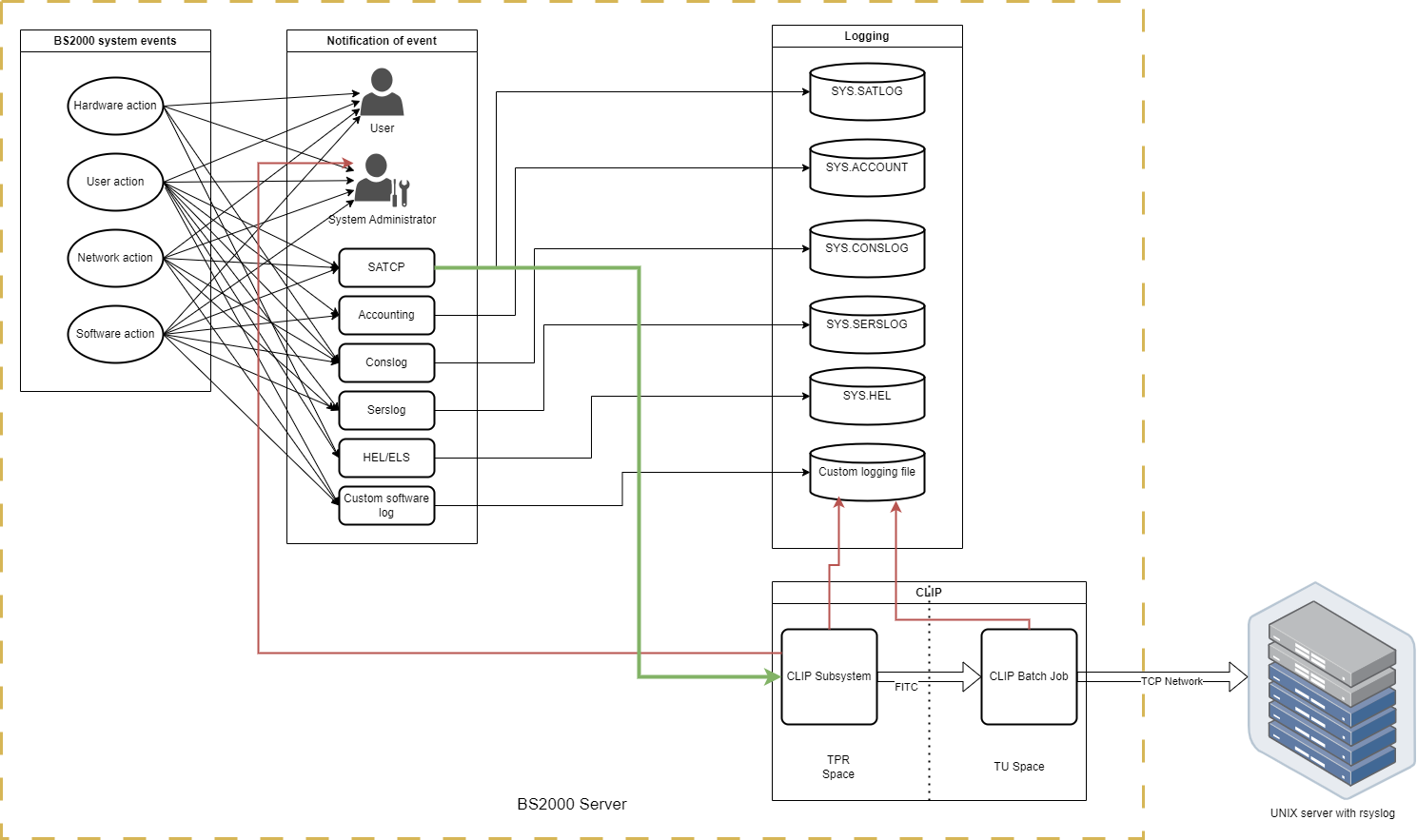
To enhance information flow, BS2000 has been updated in version 21.0B to not only store log records on but additionally send them to the CLIP Subsystem. The payload is then parsed and sent to the central rsyslog server. In the initial release, only support is provided for the SATCP subsystem. However, our plan is to extend the functionality to cover additional subsystems and event types in the future (e.g. ACCOUNTING, CONSLOG etc.)
Rsyslog is a UNIX-based open-source utility used for forwarding log messages over a network, extending the syslog protocol with content-based filtering, flexible configuration options, and other rich filtering capabilities.
The syslog protocol was initially defined in RFC 3164, but it has been unofficially extended, so a new standard, RFC 5424, has been released, replacing RFC 3164.
When records are received from SATCP in the CLIP Subsystem, the payload is processed by CLIP and sent to the rsyslog server via the syslog protocol.
Important Note:
HEADER and TRAILER record of a SAT file are written directly to the file. Therefore, the corresponding SAT events ZBG and ZND are not transferred to CLIP and cannot be logged there.
Typically, the CLIP configuration will resemble the diagram below.
The Rsyslog server stores logs, forwards them to another Rsyslog server, and collects logs from multiple machines to enhance the scalability of the entire infrastructure.