All permissible PRODAMP constructions can be determined with the aid of the syntax diagrams. On the other hand, not all constructions possible with the syntax diagrams are permissible, since type compatibility and possible restrictions with respect to names must also be taken into account. However, strictly speaking, these are not syntactical characteristics, since an expression which is illegal due, for example, to a type incompatibility can be made acceptable by choosing other designators.
In order to keep the size of the diagrams within reasonable limits, the following convention applies: connecting lines between boxes represent separators (see "Language elements"). A separator may be omitted only before or after a special character. Separators must not be used in diagrams whose headers are framed by double lines.
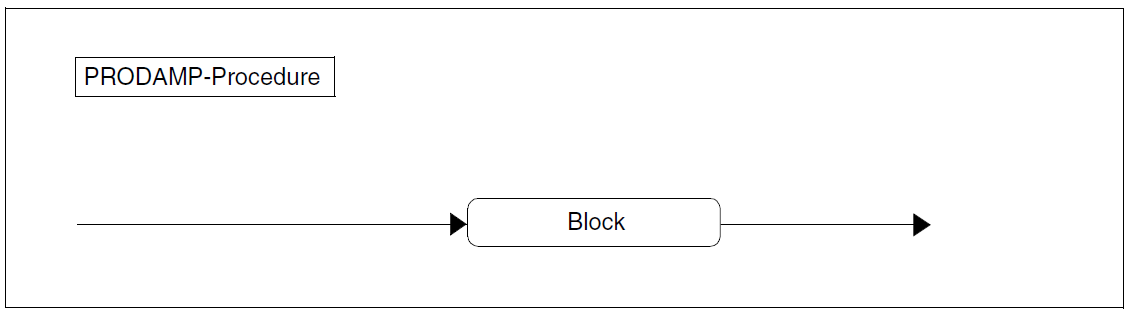
The entry point for the syntax diagrams is the term “PRODAMP procedure”. This is followed by an alphabetical list of all the terms used to define the “PRODAMP procedure”.
Figure 68: PRODAMP procedure
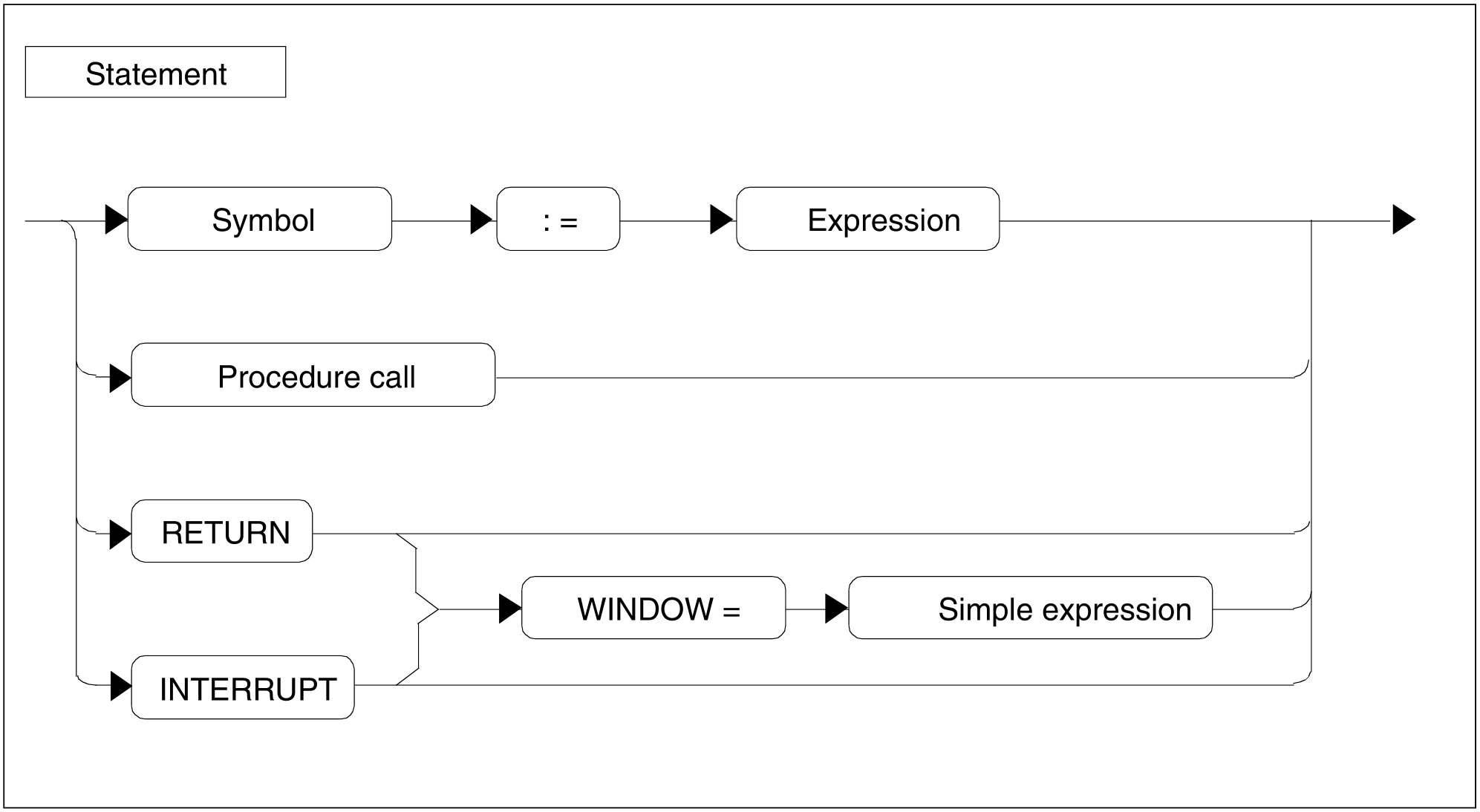
Figure 69: Statement
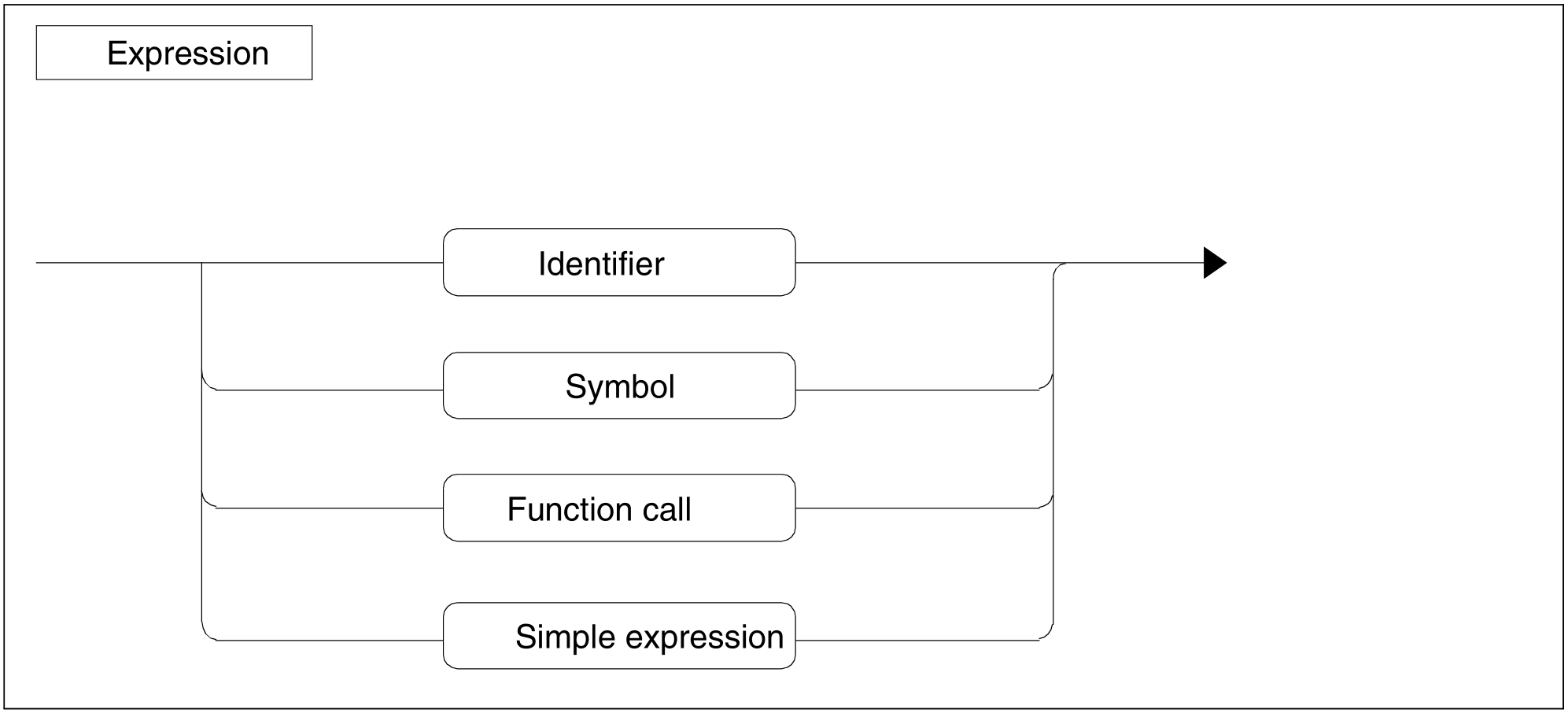
Figure 70: Expression
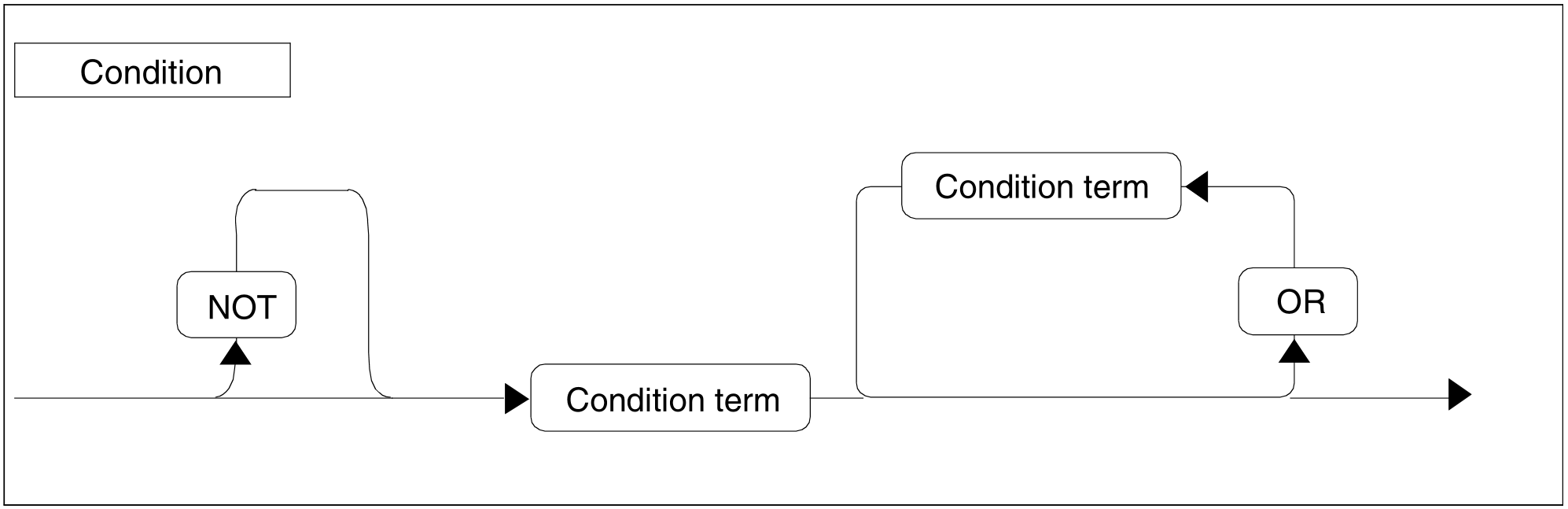
Figure 71: Condition
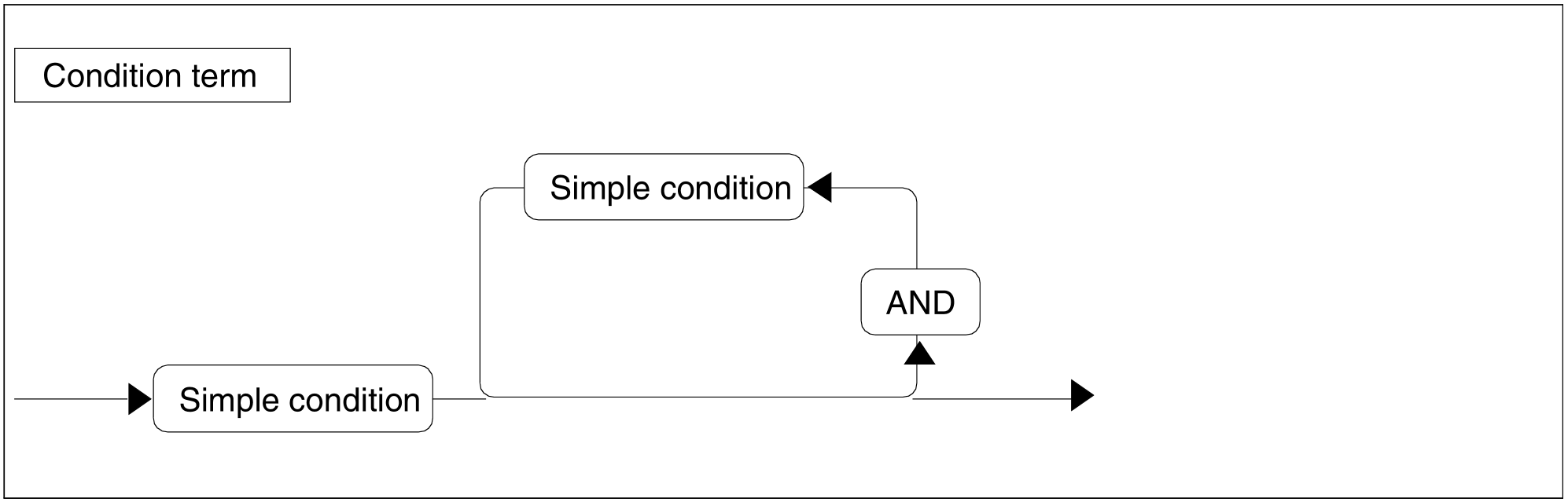
Figure 72: Condition term
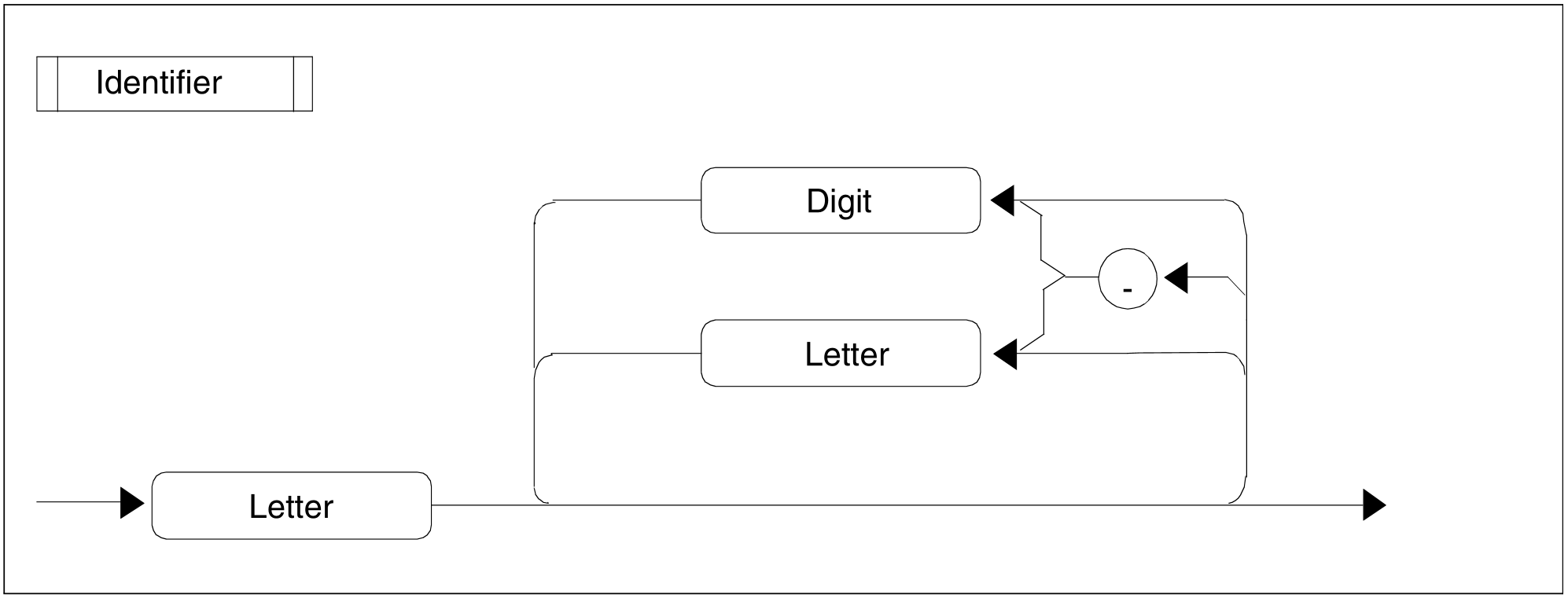
Figure 73: Identifier
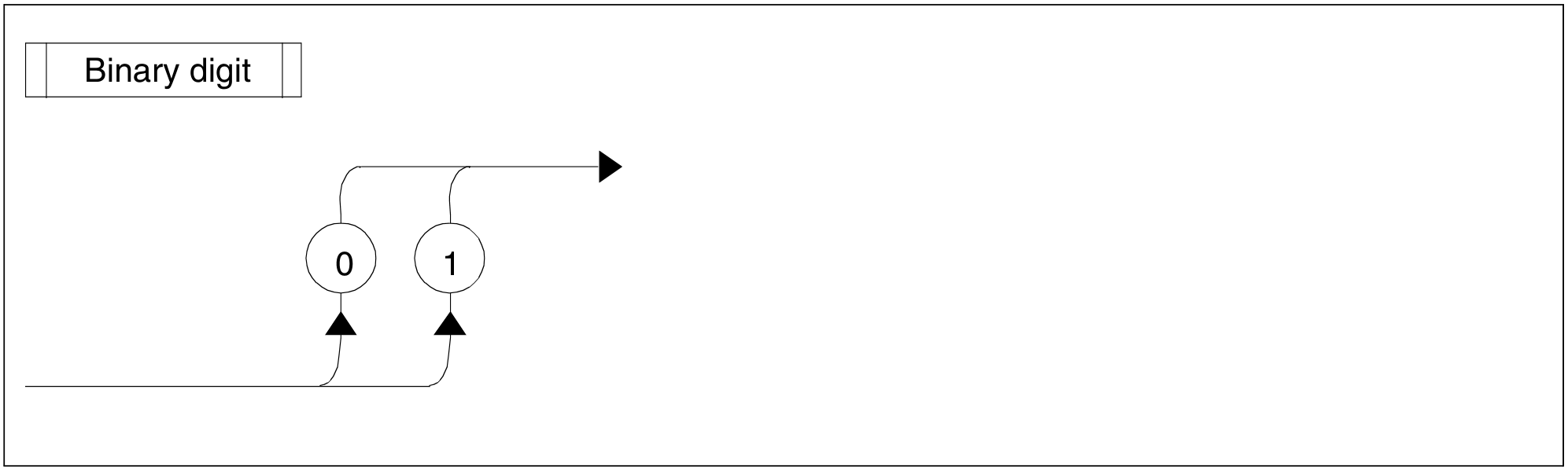
Figure 74: Binary digit
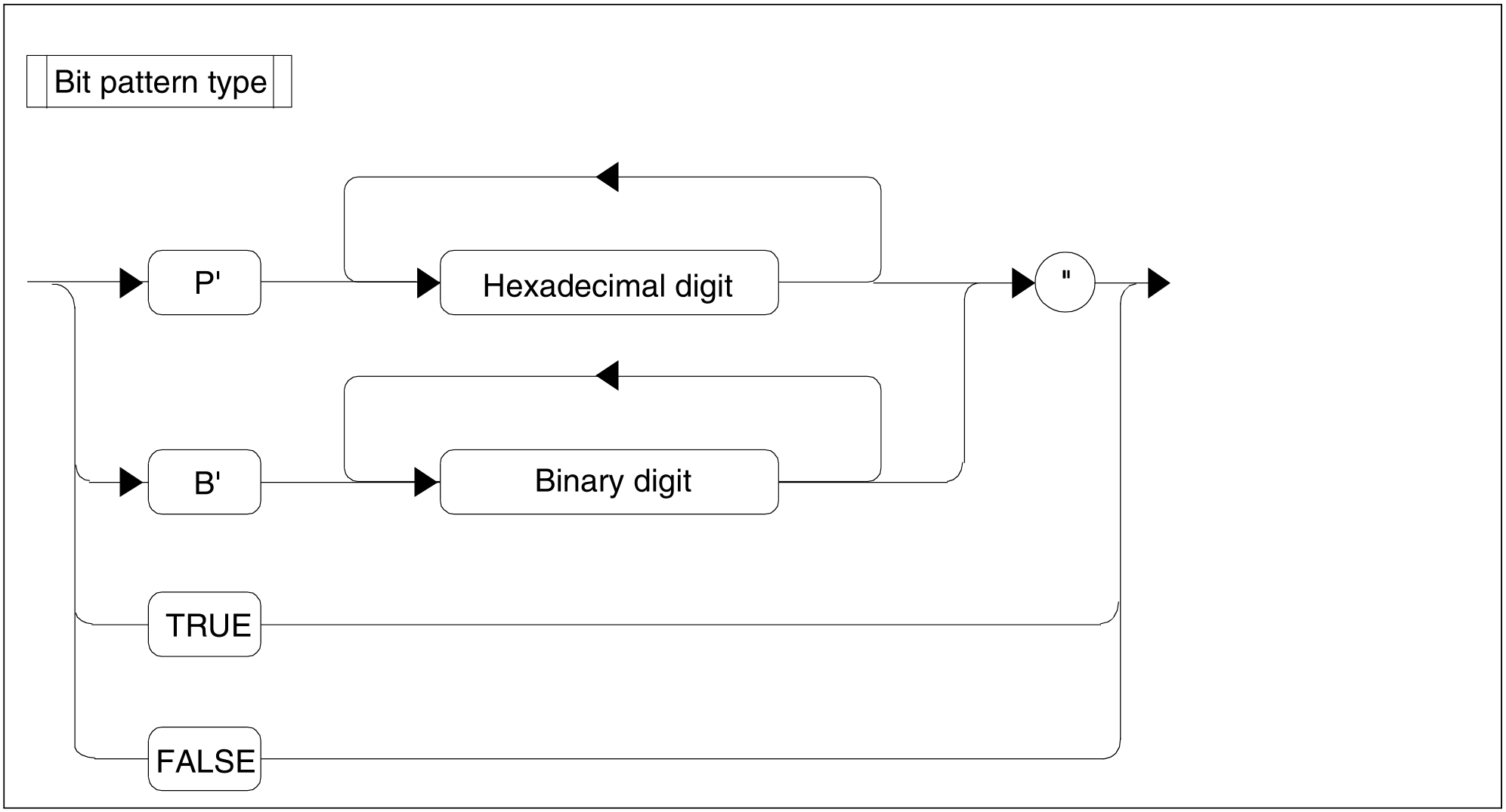
Figure 75: Bit pattern type
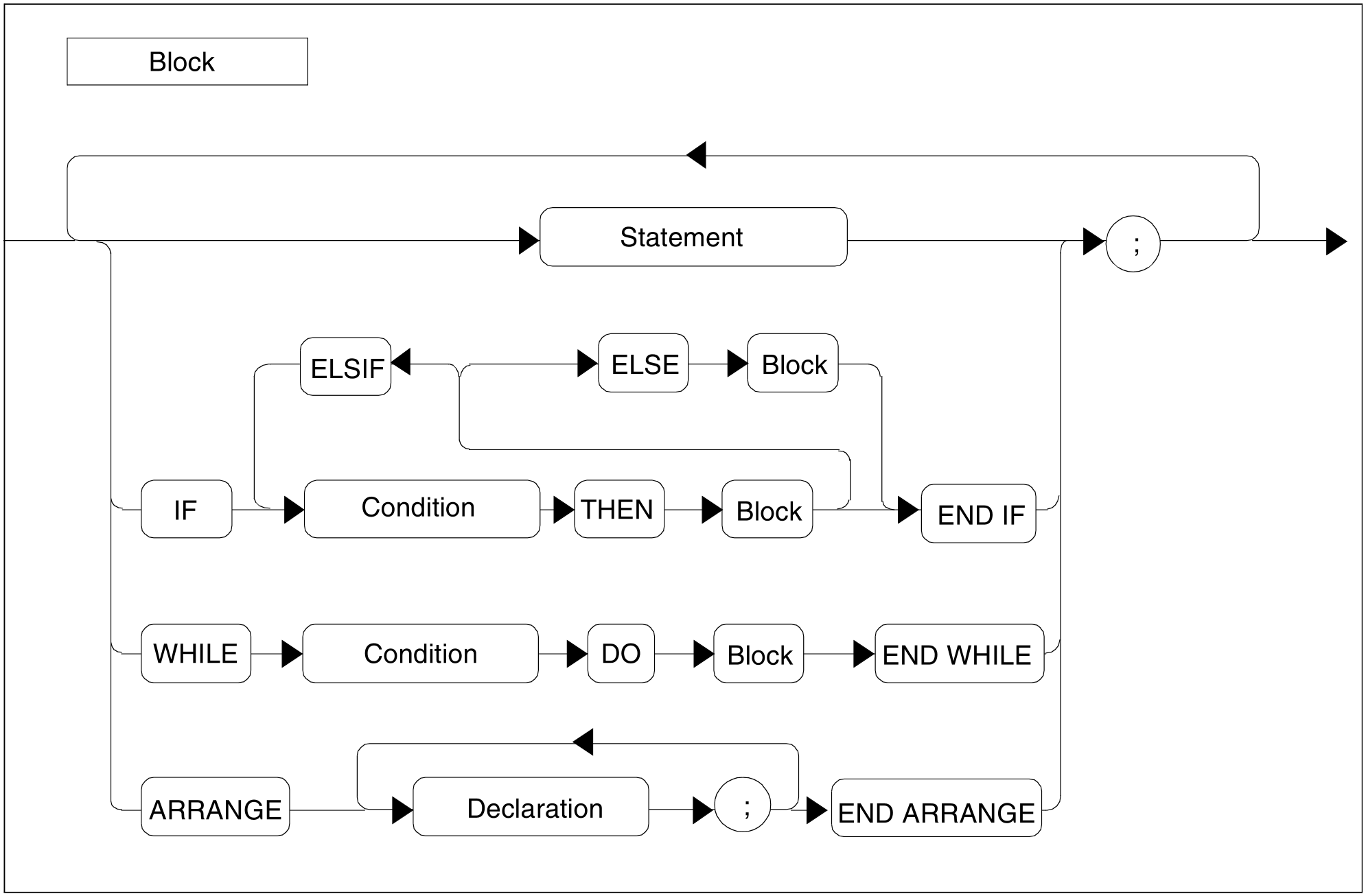
Figure 76: Block
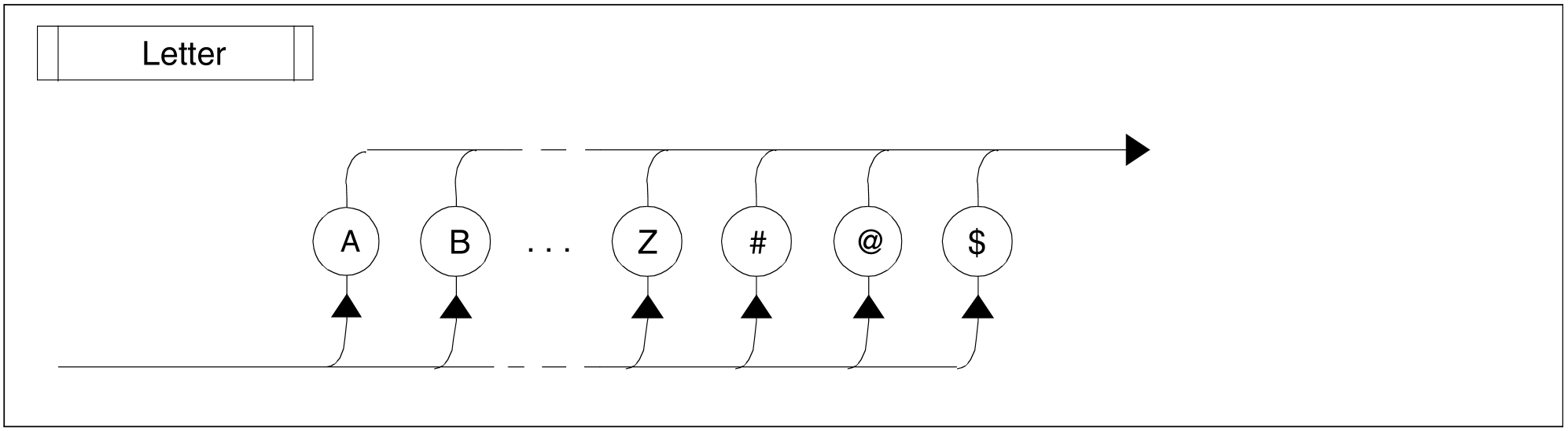
Figure 77: Letter
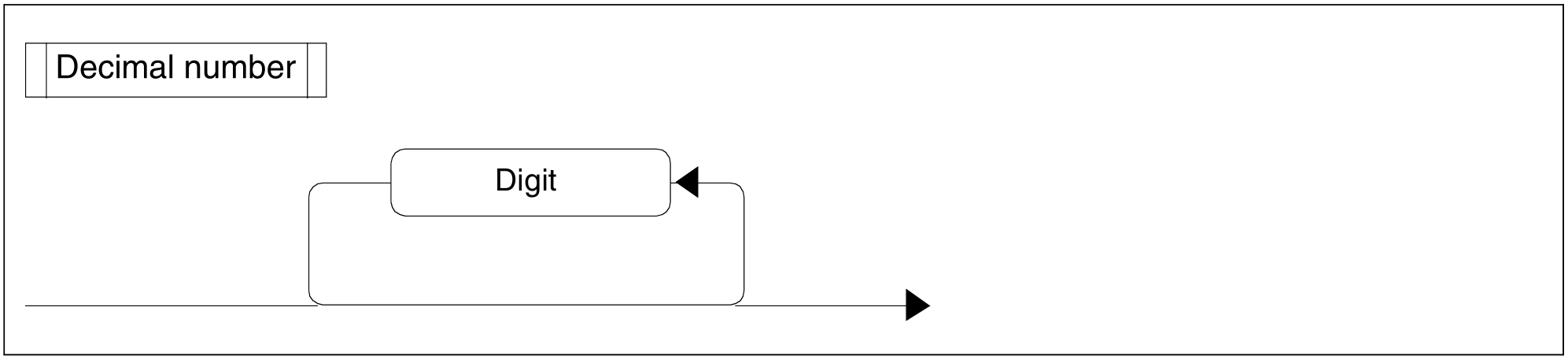
Figure 78: Decimal number
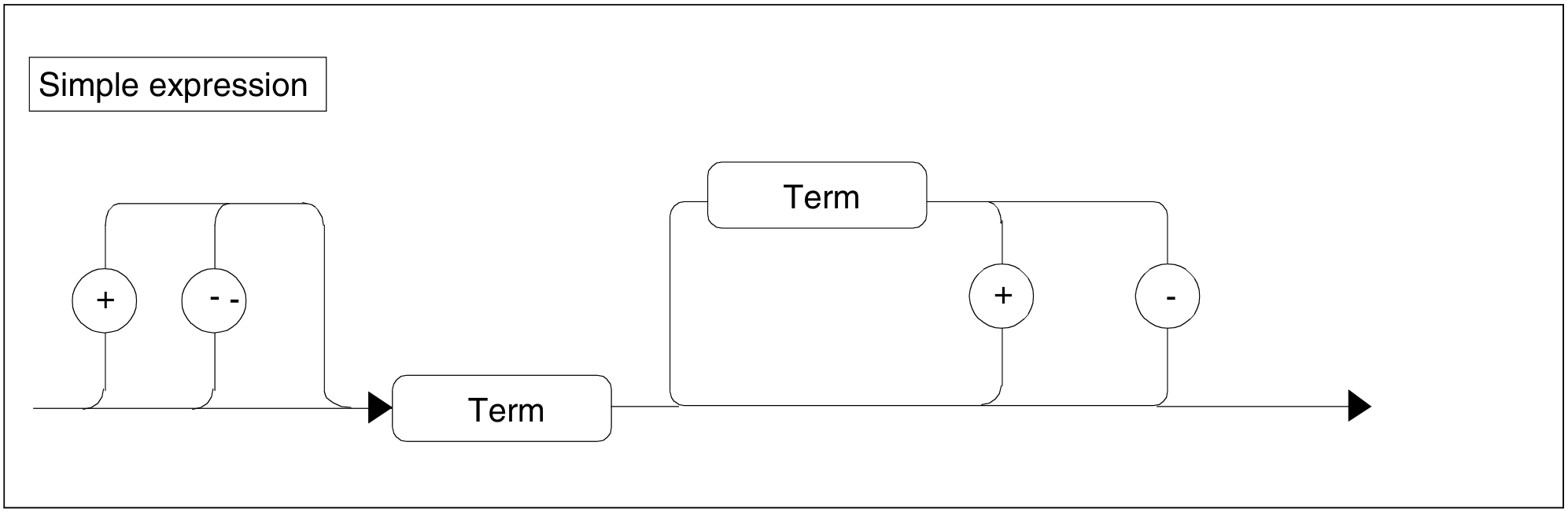
Figure 79: Simple expression
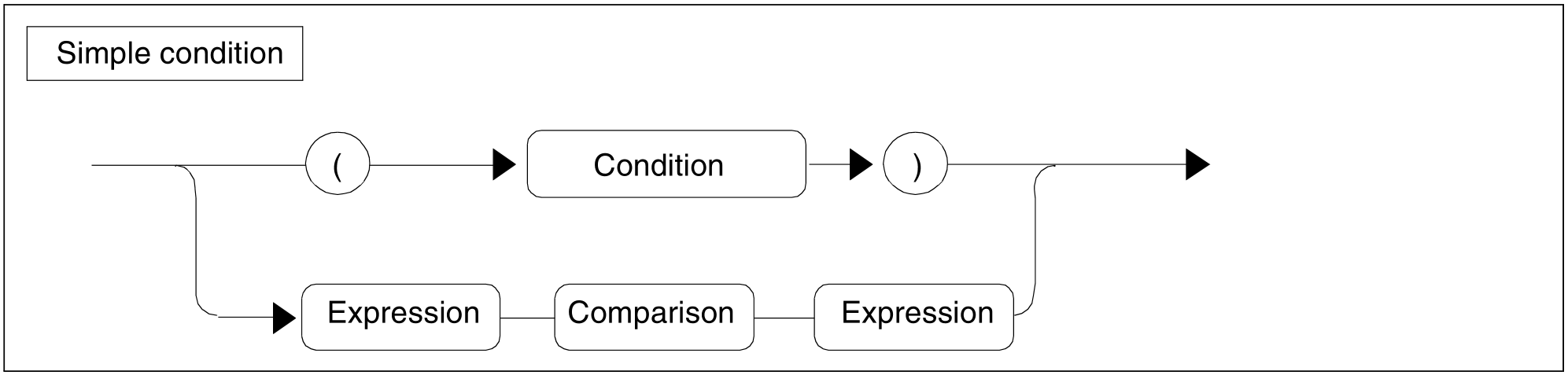
Figure 80: Simple condition
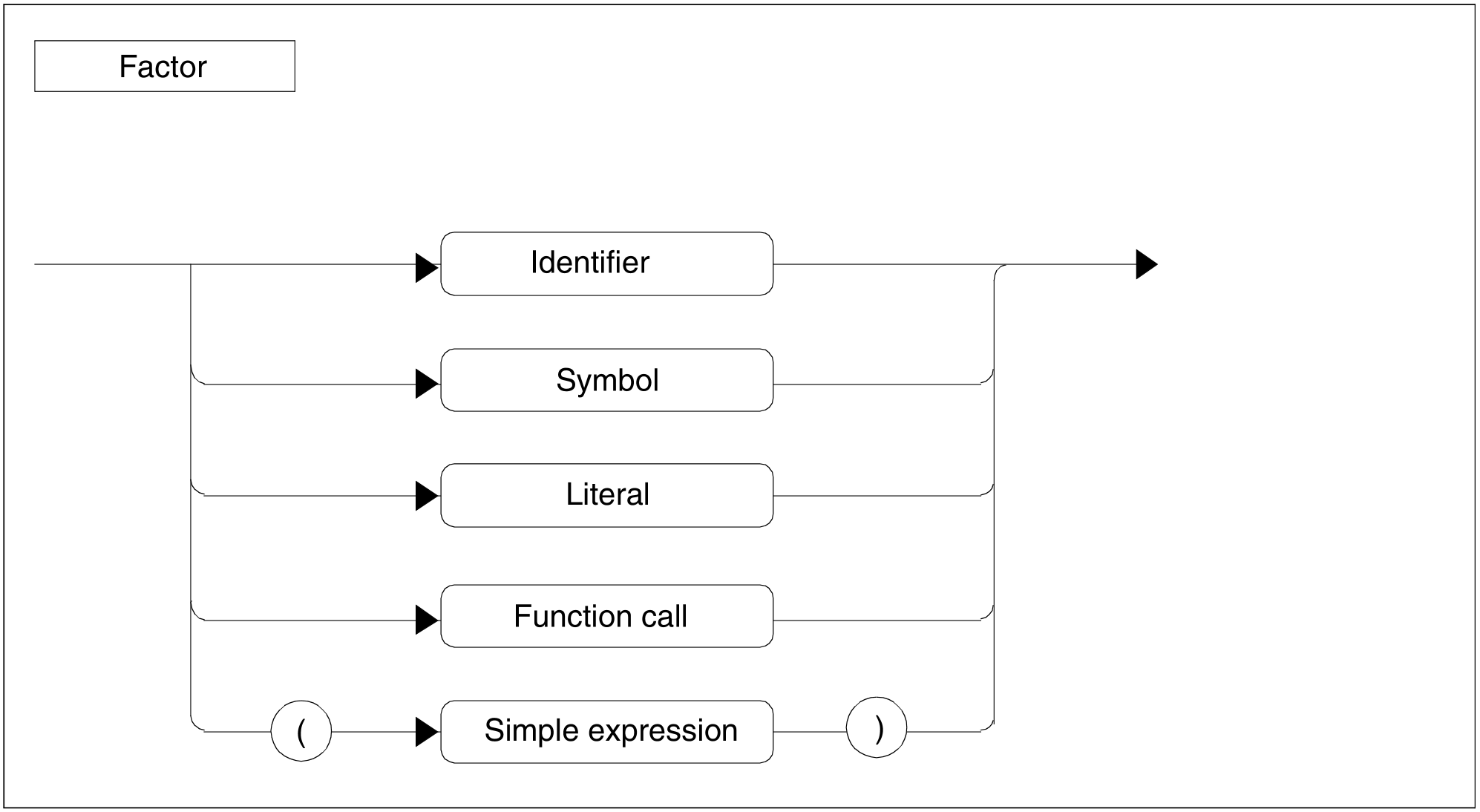
Figure 81: Factor
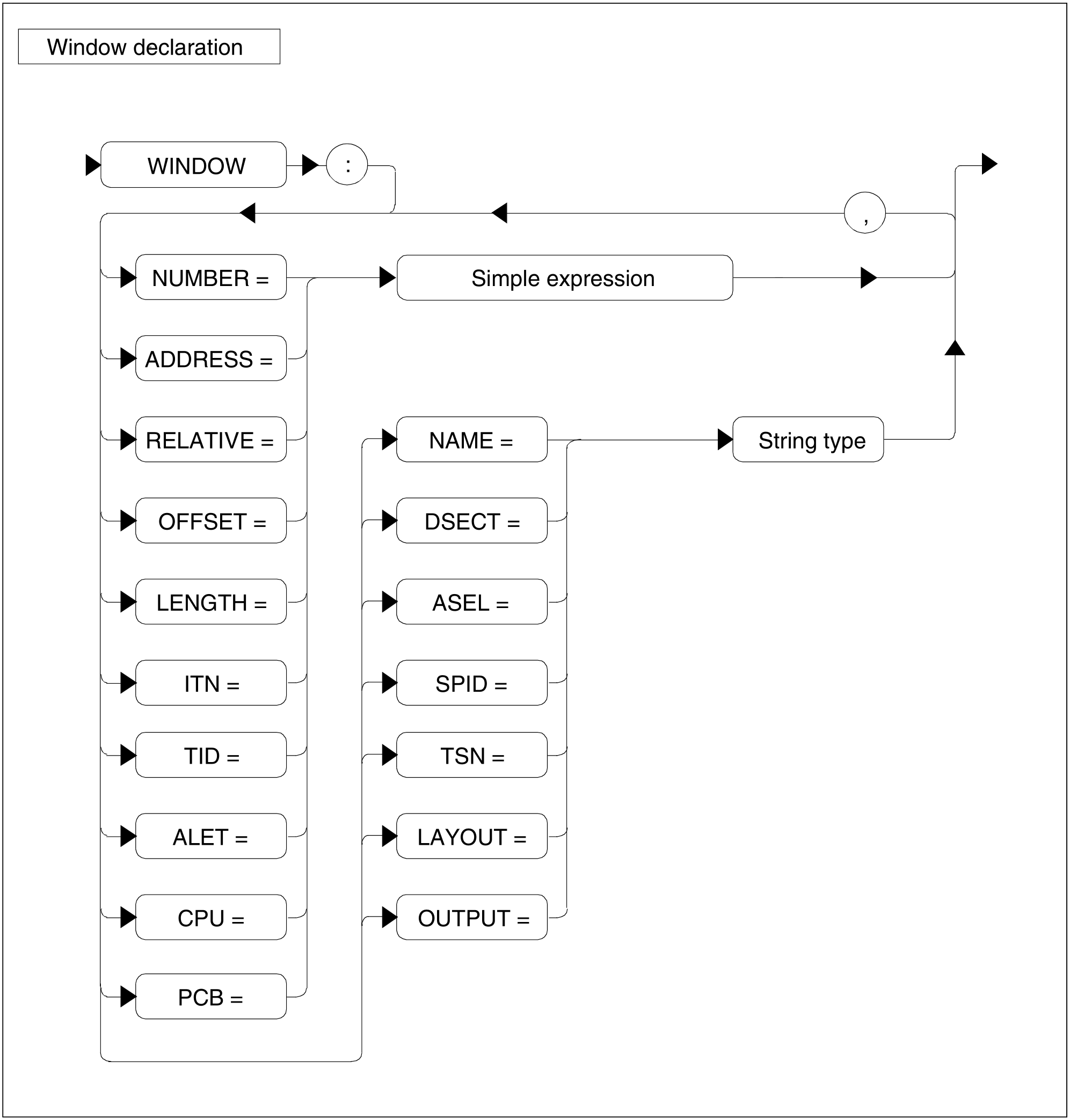
Figure 82: Window declaration
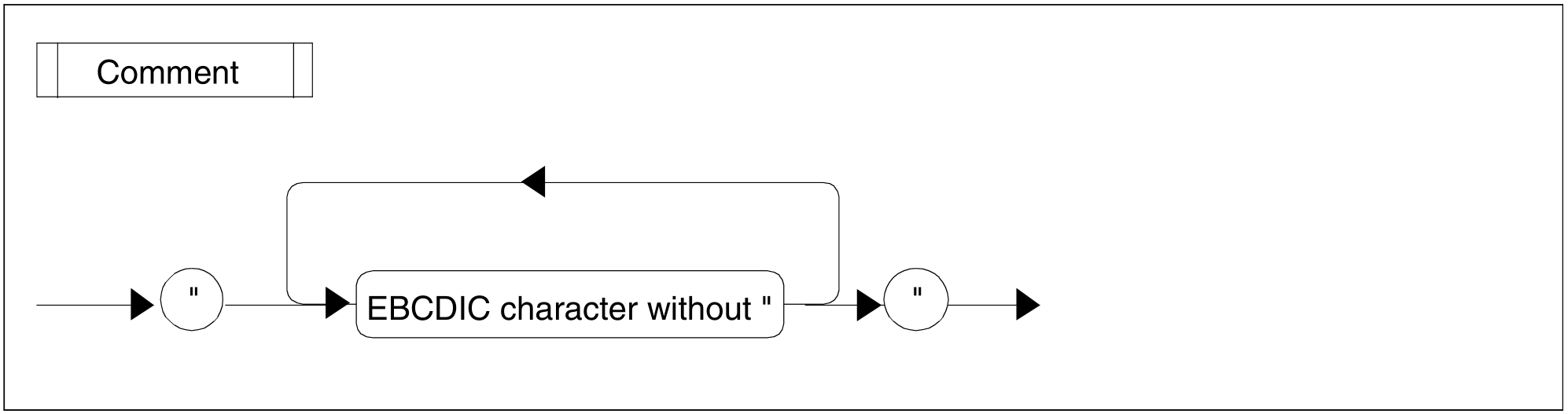
Figure 83: Comment
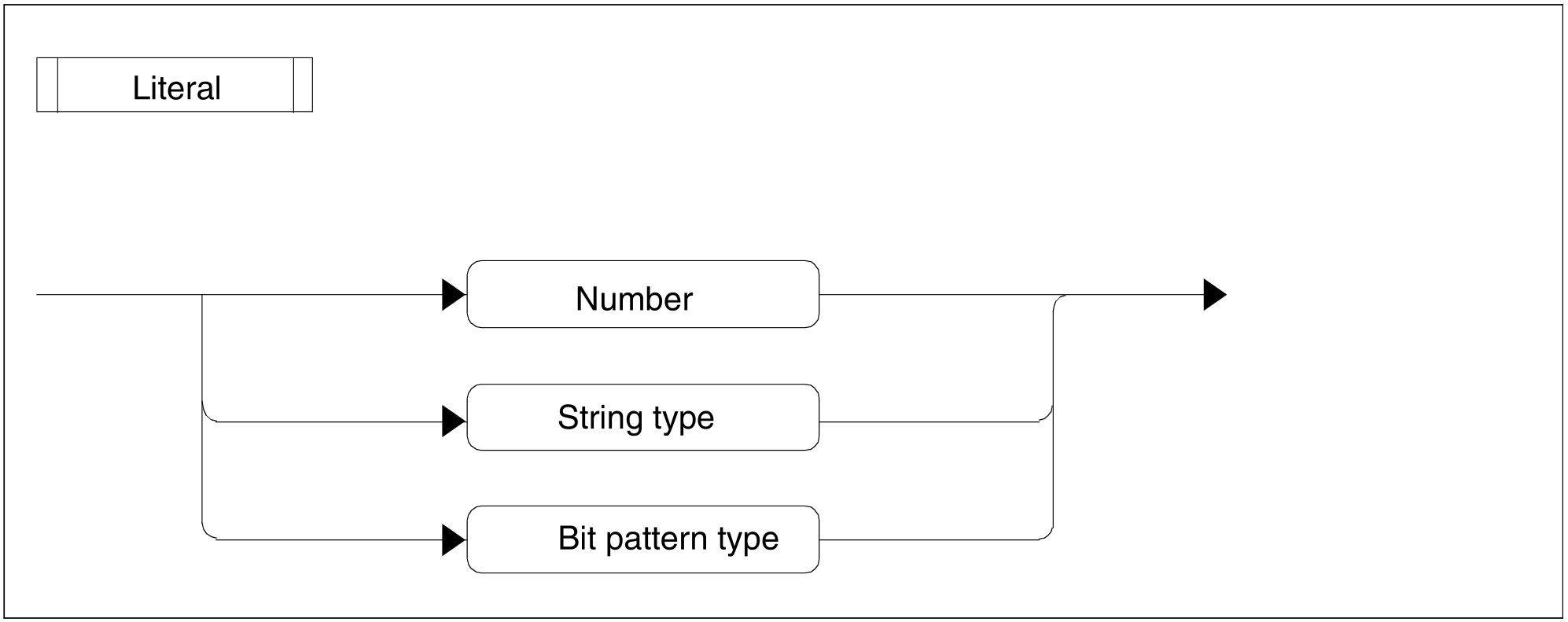
Figure 84: Literal
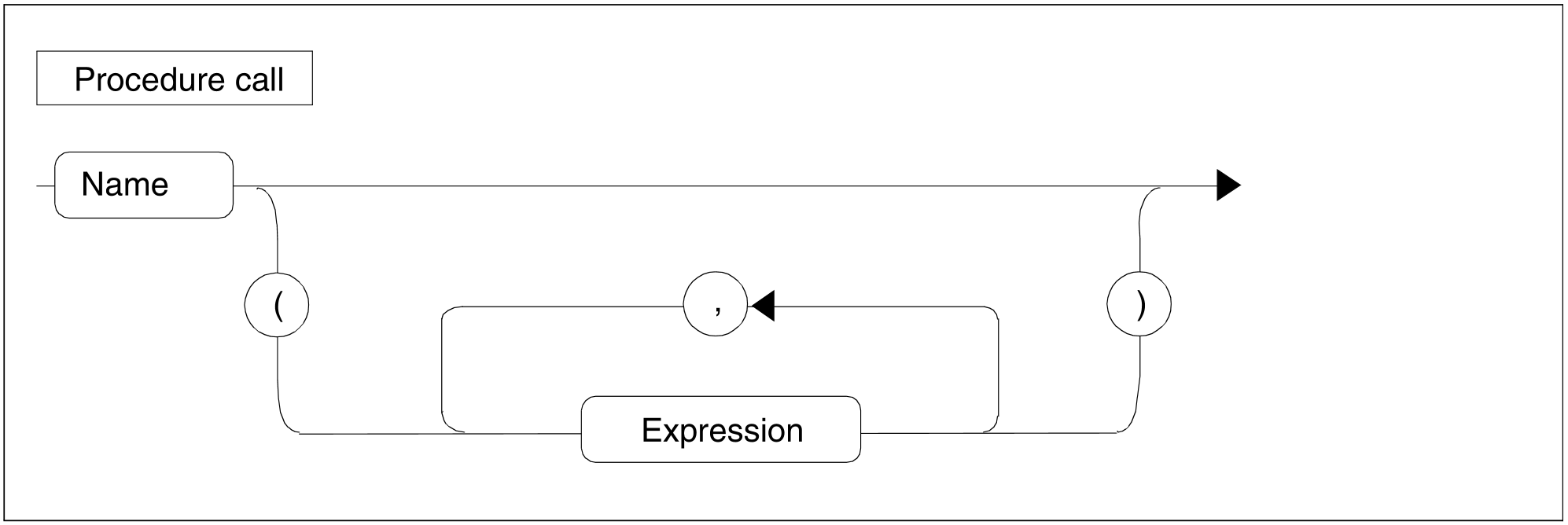
Figure 85: Procedure call
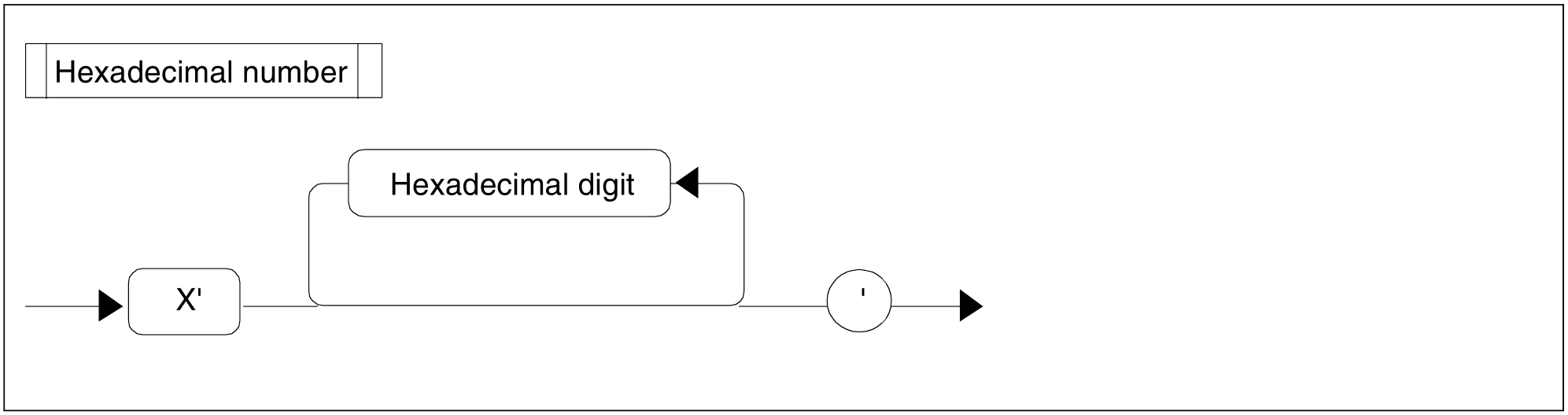
Figure 86: Hexadecimal number
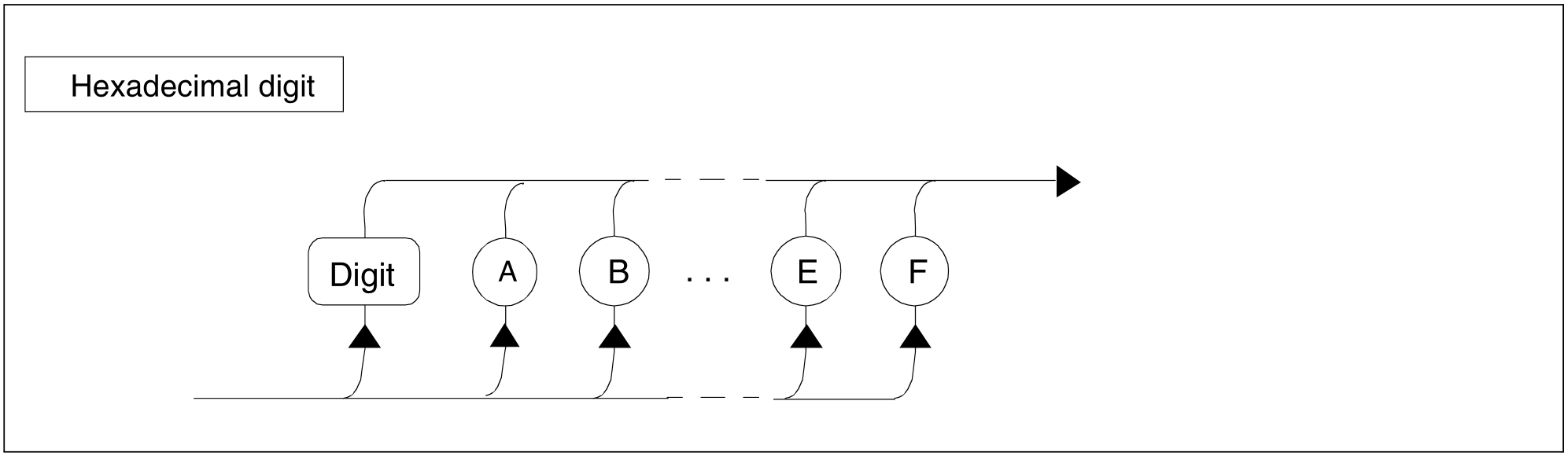
Figure 87: Hexadecimal digit
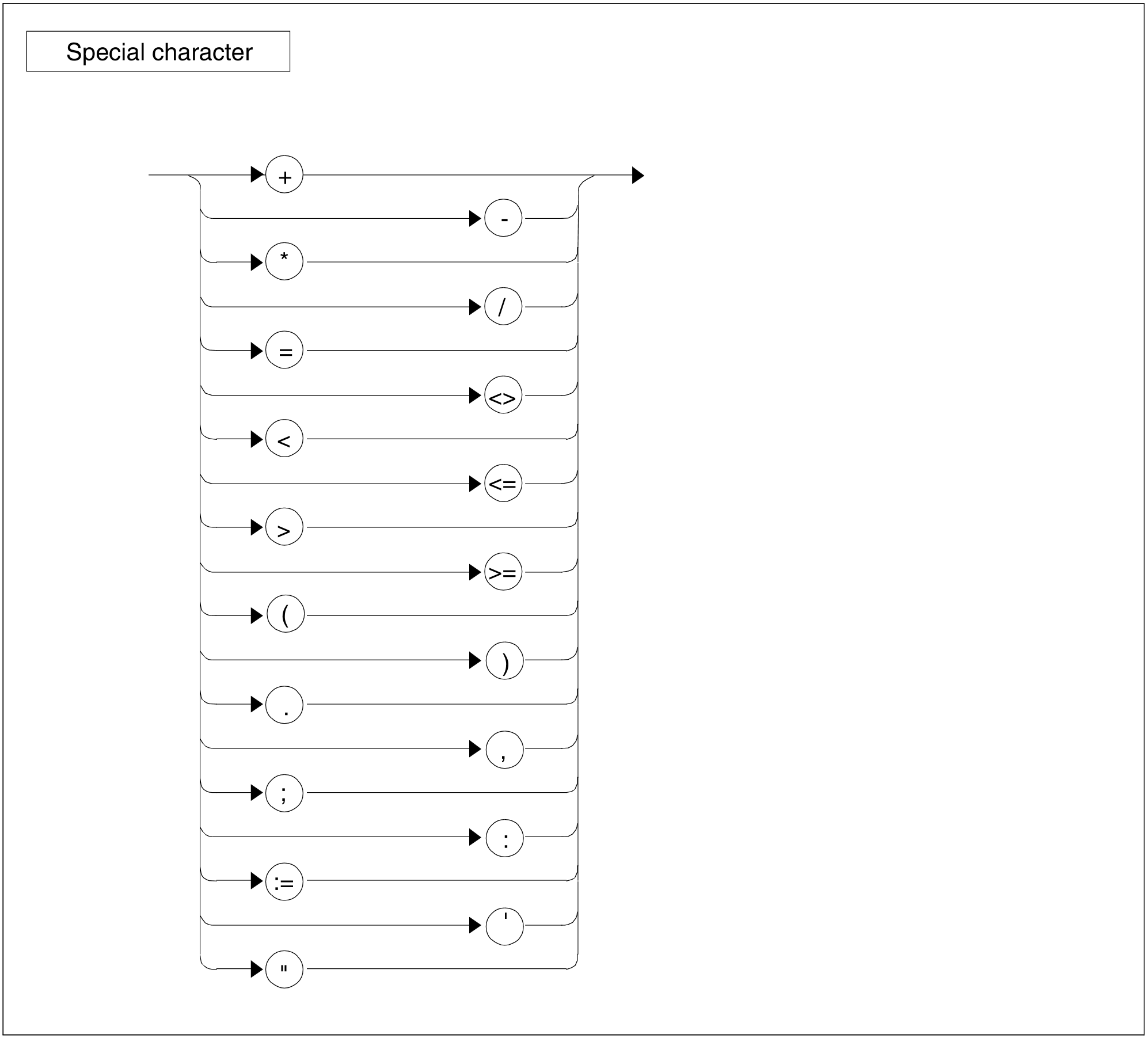
Figure 88: Special character
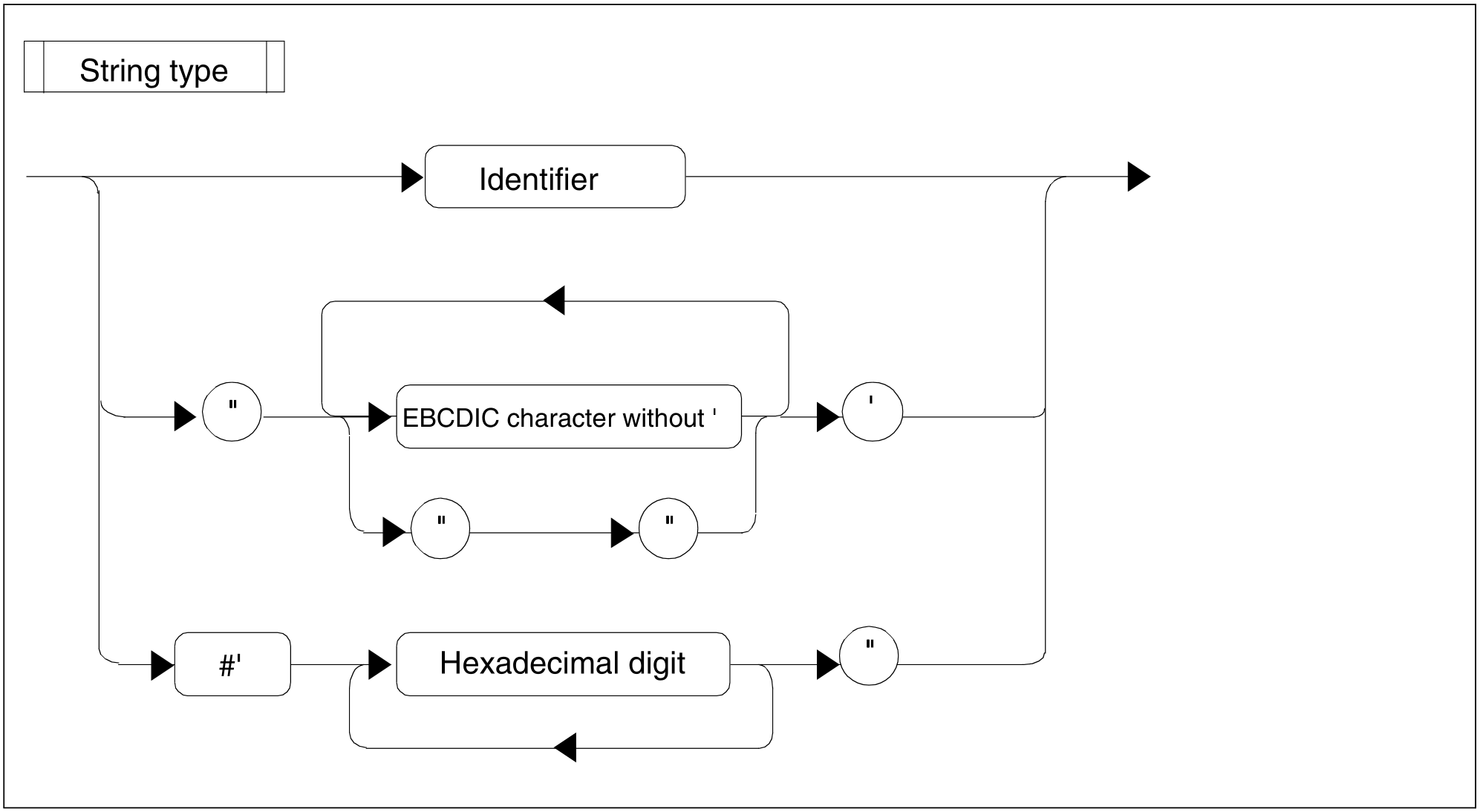
Figure 89: String type
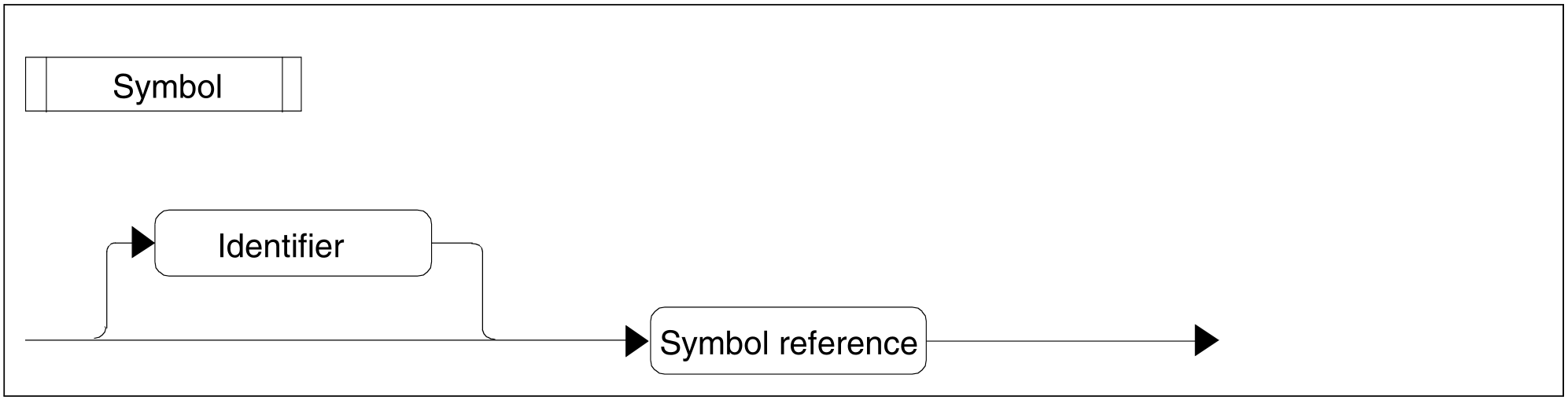
Figure 90: Symbol
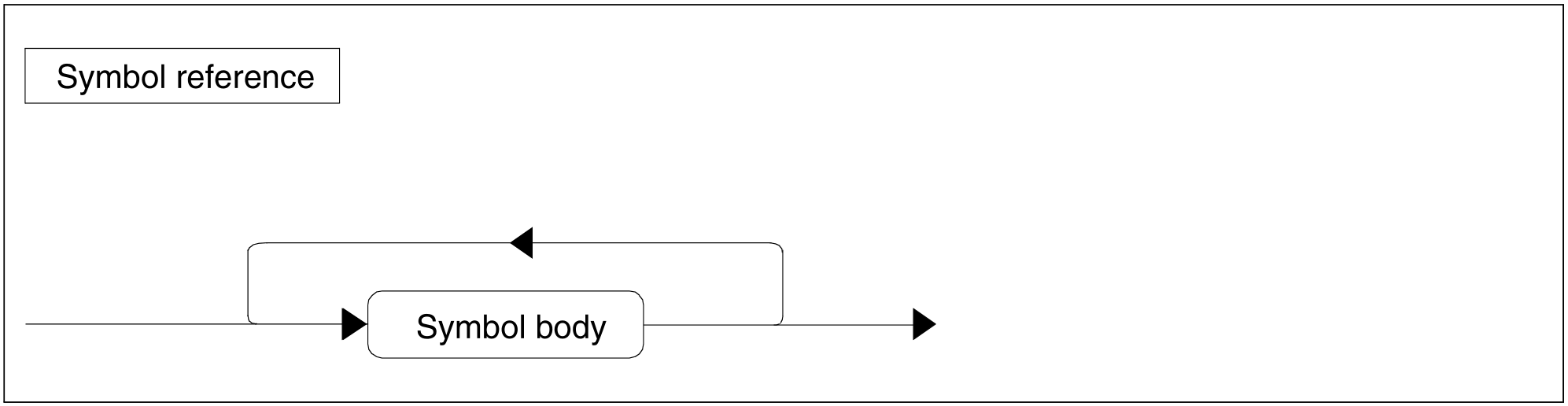
Figure 91: Symbol reference
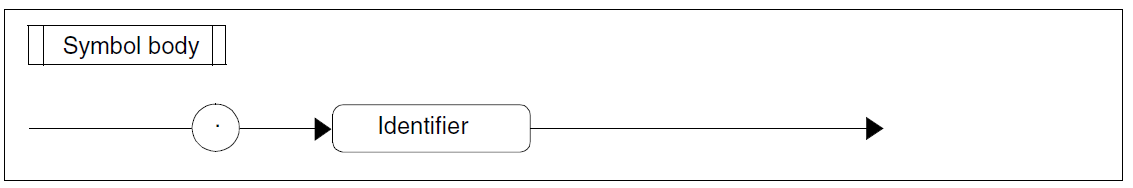
Figure 92: Symbol body
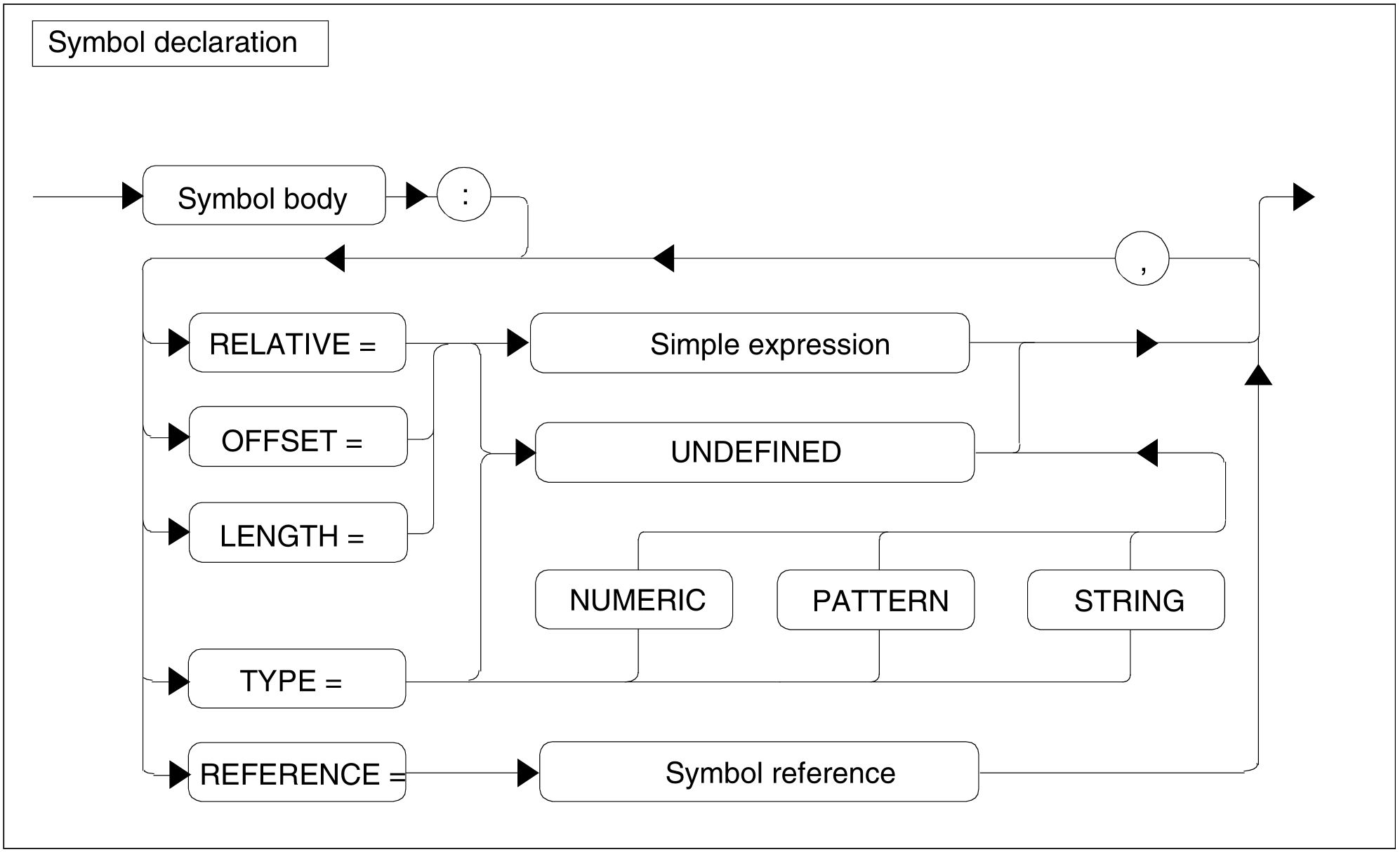
Figure 93: Symbol declaration
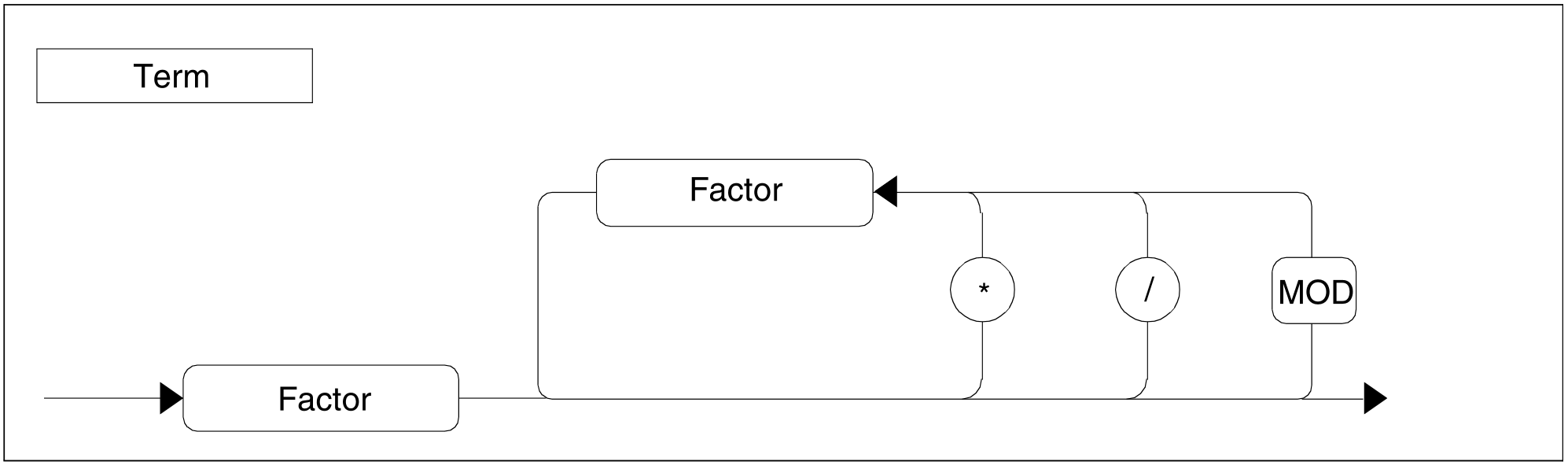
Figure 94: Term
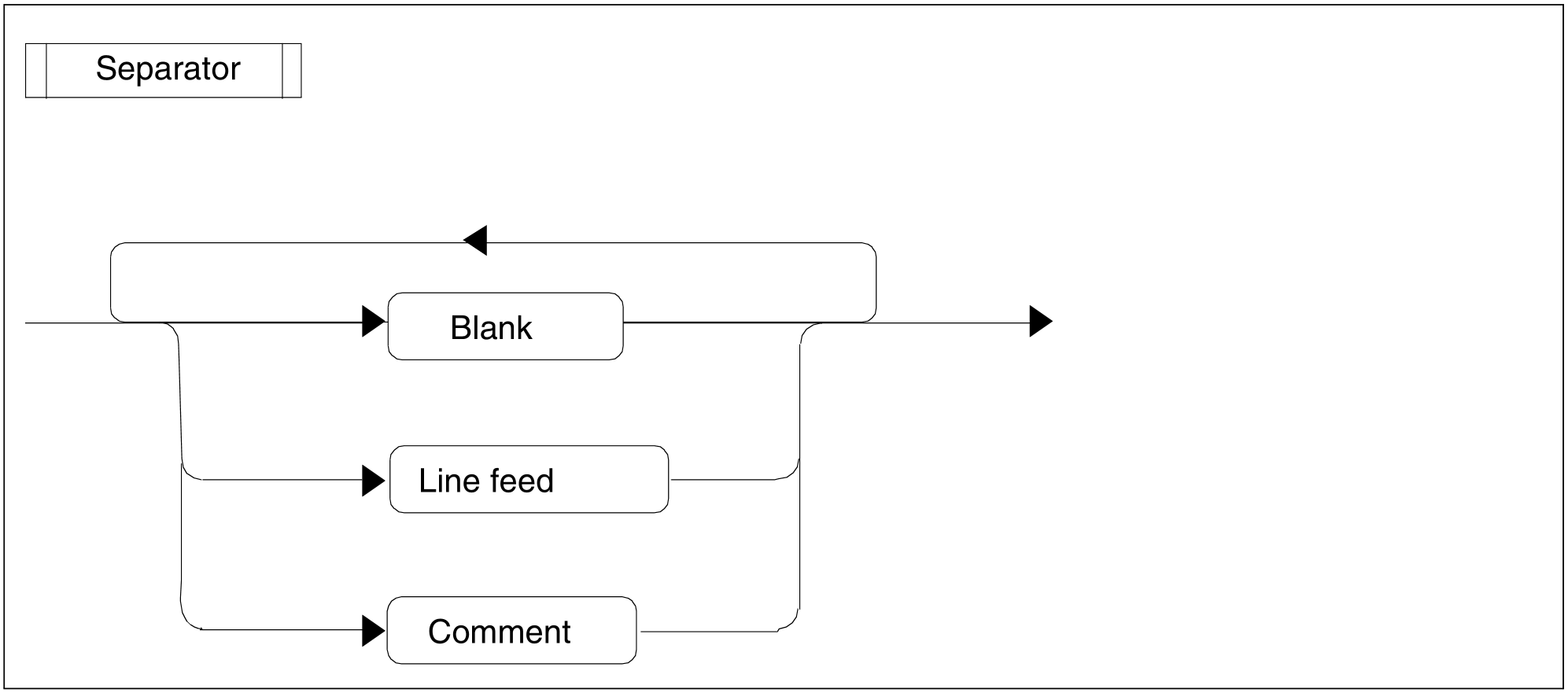
Figure 95: Separator
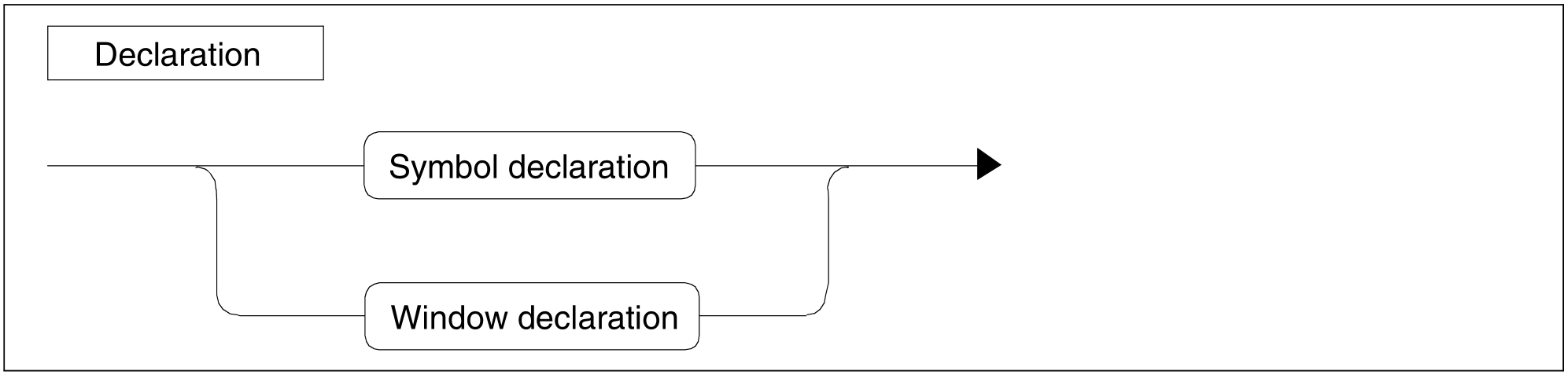
Figure 96: Declaration
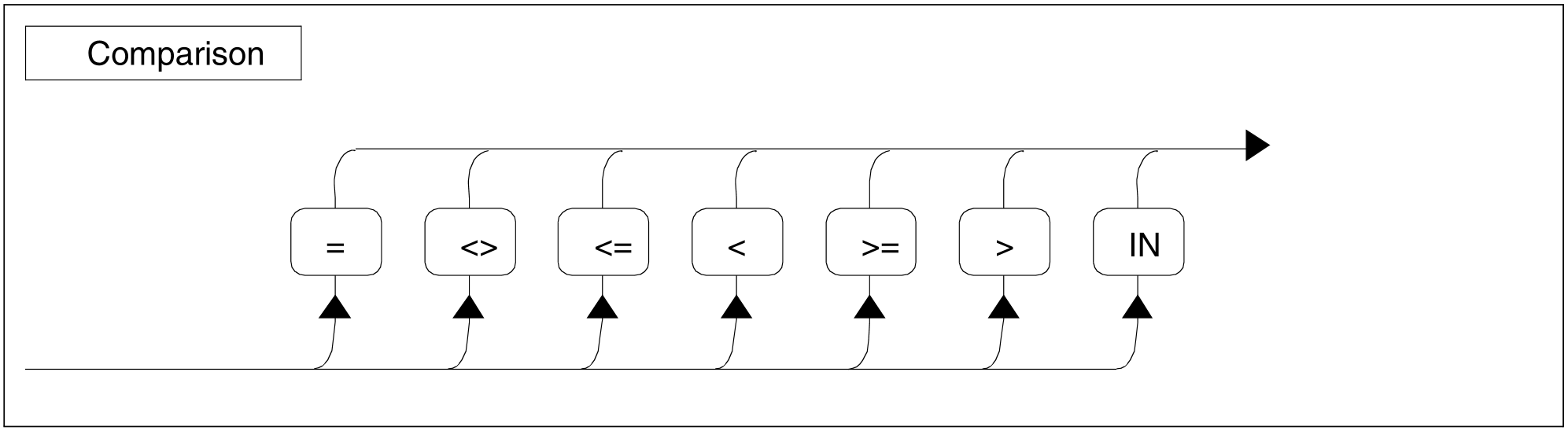
Figure 97: Comparison
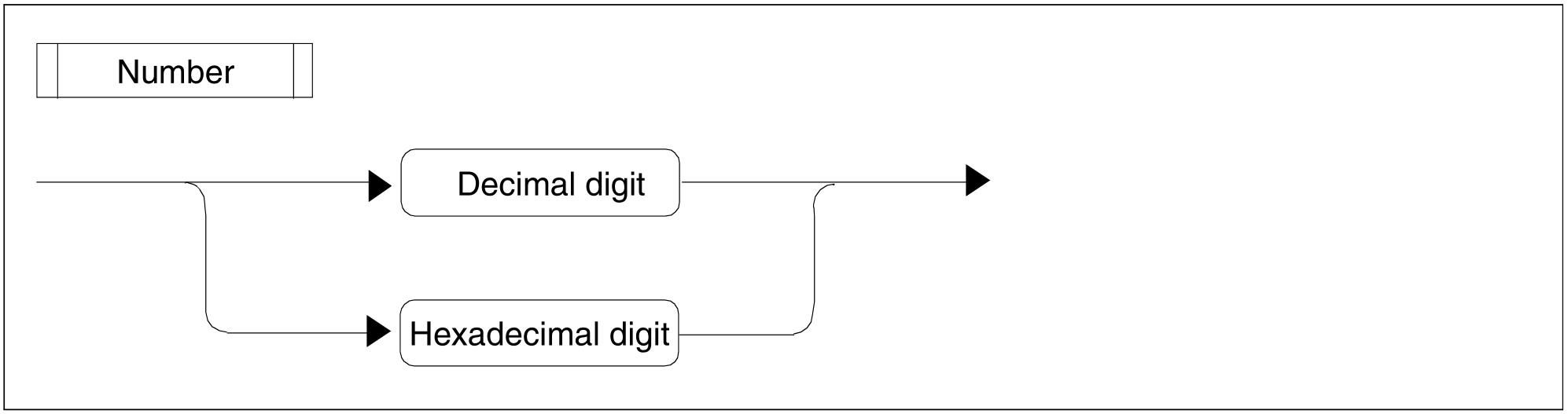
Figure 98: Number
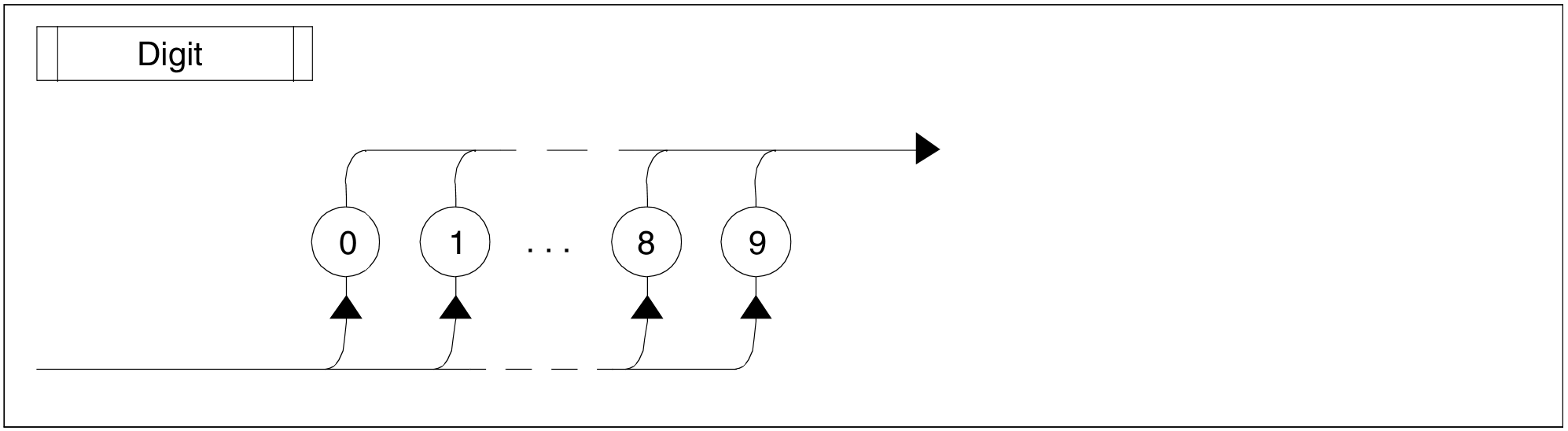
Figure 99: Digit