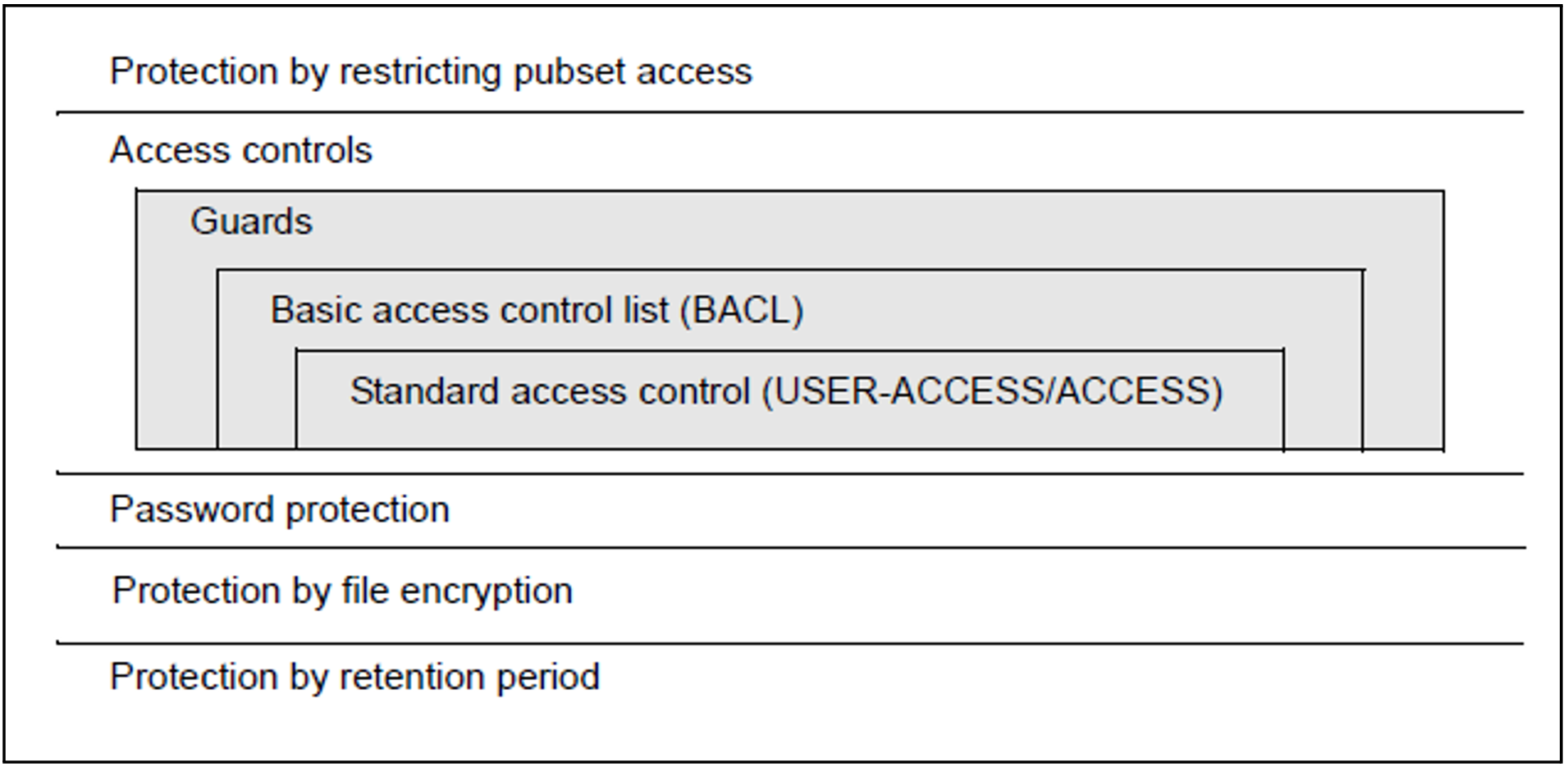
All files can be secured by one or more protection mechanisms.
If the ACCESS/USER-ACCESS, BACL and GUARDS protection mechanisms are all used for the same object then only one of them is effective in accordance with the following hierarchy:
Guards
If object protection is defined by means of Guards then only the access conditions defined in the Guards apply. Any BACL defined for the object is ignored as are the ACCESS/USER-ACCESS protection attributes.Basic Access Control List, BACL
If Guards protection is not defined for an object but a BACL is, then the protection settings specified in the BACL apply. The ACCESS and USER-ACCESS protection attributes are ignored.Standard access control (USER-ACCESS/SHARE and ACCESS)
If an object is not protected by Guards or by a BACL then the ACCESS and USER-ACCESS protection attributes are employed as the protection mechanism.
Restricted pubset access, password protection, file encryption and the retention period apply additionally in all cases.