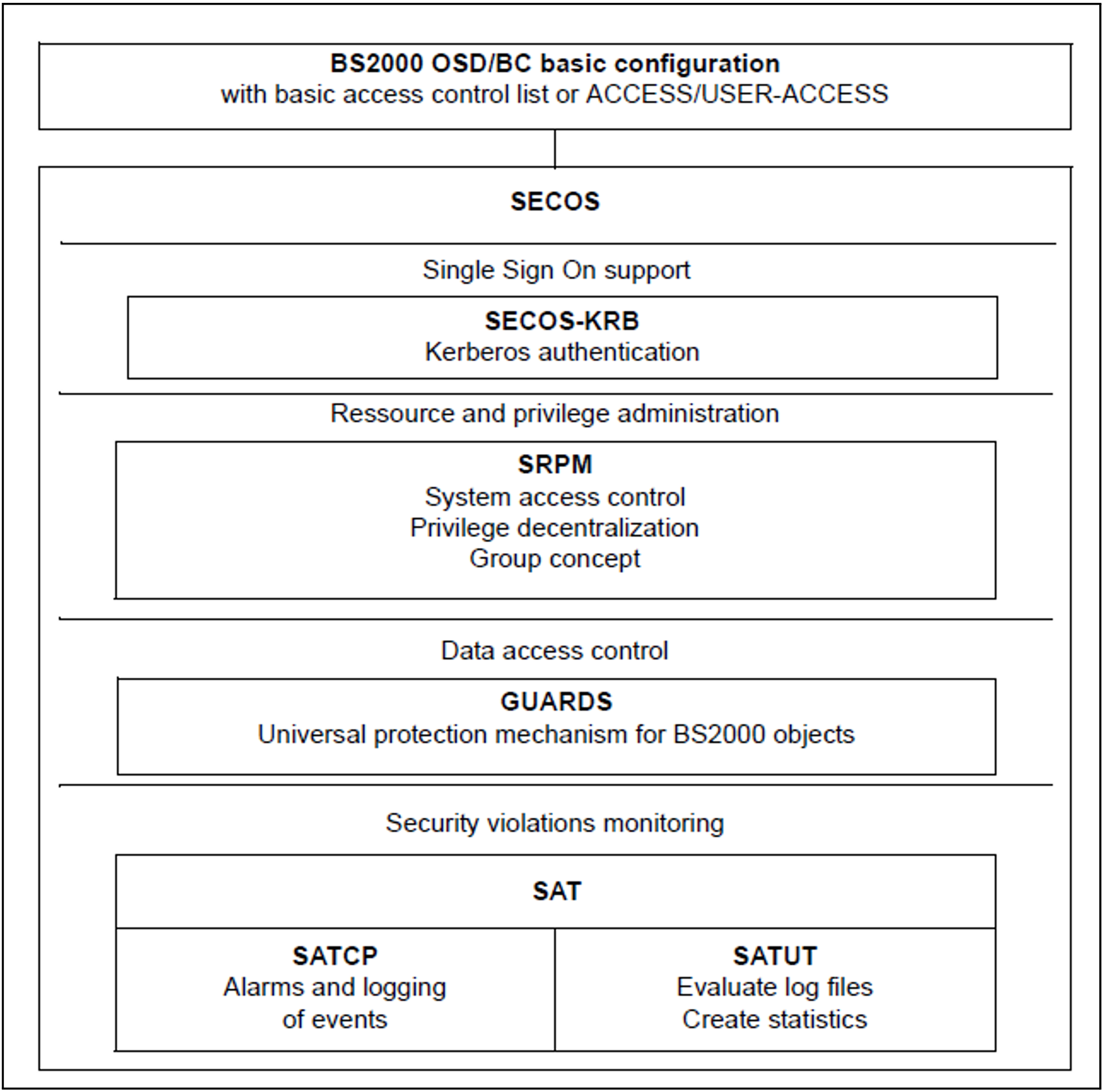
Use of the software product SECOS extends BS2000 OSD/BC by functions which guarantee secure operation in accordance with the required security criteria.
Figure 21: Functional units in the security package
Components of SECOS
SRPM (System Resources and Privileges Management) offers the following basic facilities:
Decentralization of systems support privileges. This makes it possible to bundle or unbundle systems support tasks, i.e. task assignments can be tailored to each individual data center. Privileges are assigned by the security administrator under a special user ID (see privilege SECURITY-ADMINISTRATION, in "Security administration" in section "Description of the privileges").
Identification and authentication of users by means of extended access protection (separation and control of access paths, terminal sets) and password protection (limited lifetime, minimum length and complexity).
Establishment of user groups, with the help of which differentiated access protection is possible. At the same time, administrative tasks can be carried out in decentralized form by group administrators. This means a reduction of trivial tasks for systems support.
GUARDS (Generally Usable Access Control Administration System) allows access to a user's data objects to be made dependent on “access conditions”. To prevent illegitimate access to the data objects, a user can specify access conditions which must be satisfied by any subject before it may access the data objects.
GUARDDEF (default protection) is used to assign default attribute values for files and job variables. Optionally, these values may be predefined for the creation or modification of objects. The settings may be made for the entire pubset by systems support (TSOS) or by individual users under their own user IDs for their own objects.
GUARDDEF uses GUARDS to store the settings.
GUARDCOO represents a refinement to the mechanism for co-owner protection (files and job variables can be created under a different user ID and this user ID is also able to administer them).
It is possible to assign co-owner rights for different name areas of the objects, remove them for the TSOS user ID and grant certain privileges to other user IDs or co-owners. GUARDCOO uses GUARDS to store the settings.
SAT (Security Audit Trail) permits auditing by logging security-relevant events in a specially protected file (SATLOG file). The security administrator has the exclusive right to activate/deactivate SAT logging and to switch auditing of user IDs and loggable events on and off.
With the help of the SATUT component, SATLOG files can be evaluated by a specially authorized user having the “SAT-FILE-MANAGEMENT” or “SAT-FILE-EVALUATION” privilege. Evaluation can be set in such a way, for example, that a trace of special processing steps or actions performed by certain user IDs is output. It is thus possible to detect misuse of the system or unauthorized access to secured data.
Kerberos can be used for SSO (Single Sign On) in BS2000.
SSO is implemented in BS2000 with SECOS-KRB (Kerberos authentication). Kerberos is an SSO (Single Sign On) security system based on cryptographic encryption methods. When authentication takes place with Kerberos, no passwords are sent over the network in plaintext. This prevents passwords from being intercepted on the network.
The software product SECOS, its individual components and their installation and integration in BS2000 are described in detail in the “SECOS” manuals [46] and [47].