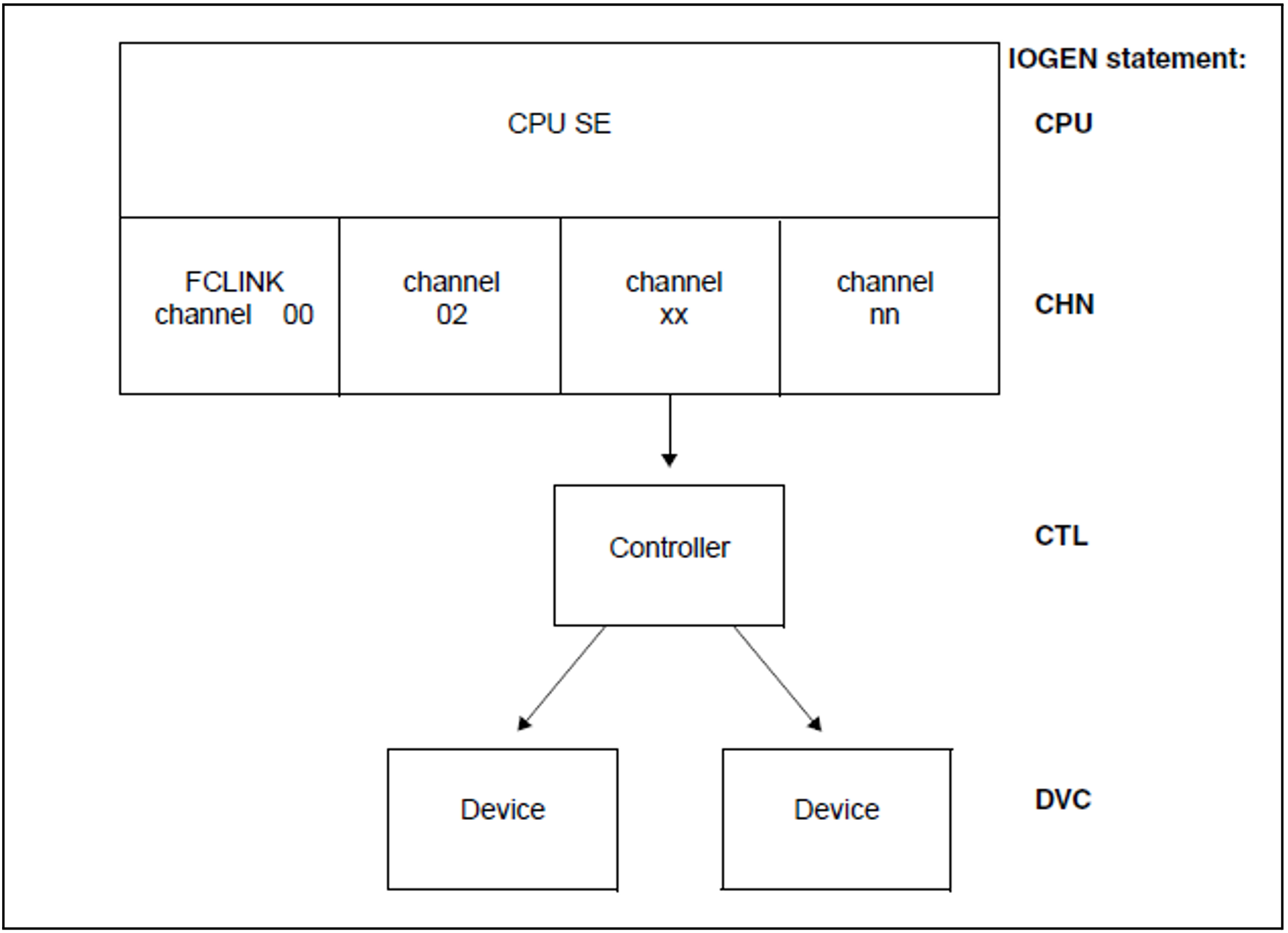
The I/O configuration of a Server Unit is defined by the statements for
CPU (CPU statement)
Channel (CHN statement)
Controller (CTL statement)
Device (DVC statement)
In figure 4 you are shown the structure of the I/O configuration for a Server Unit:
Hardware units supported
CPUs
The CPUs of Server Unit /390.
Channels
Channel type IBF (MODE=FCP) is supported, see section "Fibre Channel". When the channel type is generated, 02-FF must be specified as the channel path identifier in the MODE operand of the CHN statement.
FCLINK channel 00 is required for hardware tests, see section "Configuration for the hardware test"
Controllers
Controllers are regarded as connections between channels and devices.
Devices
See section "Device type table".
Dynamic modification of the I/O configuration
The I/O configuration of the Server Unit can be modified dynamically while BS2000 is operating. Channels, controllers and devices can be included in the I/O configuration or removed from it.
New units which are to be included must be defined in the IOCF. Space for up to 512 additional components (channel, controller, device, CCUC, CMPG) is provided in the IOCF. If it can be foreseen that more than 512 components will be added, these should be generated in advance. Your entries in the IOCF can then be modified later in accordance with the actual configuration.
The channels on boards which were present upon IMPL and are not yet used must also be generated in advance (without connected devices and controllers). It is otherwise not possible to place these channels in service dynamically.
Detailed information on dynamic modification of the I/O configuration is provided in the relevant sections of the manual “Introduction to System Administration” [4].
Disk controllers and devices can be replaced dynamically while BS2000 is operating, see the section "Disk device configuration".