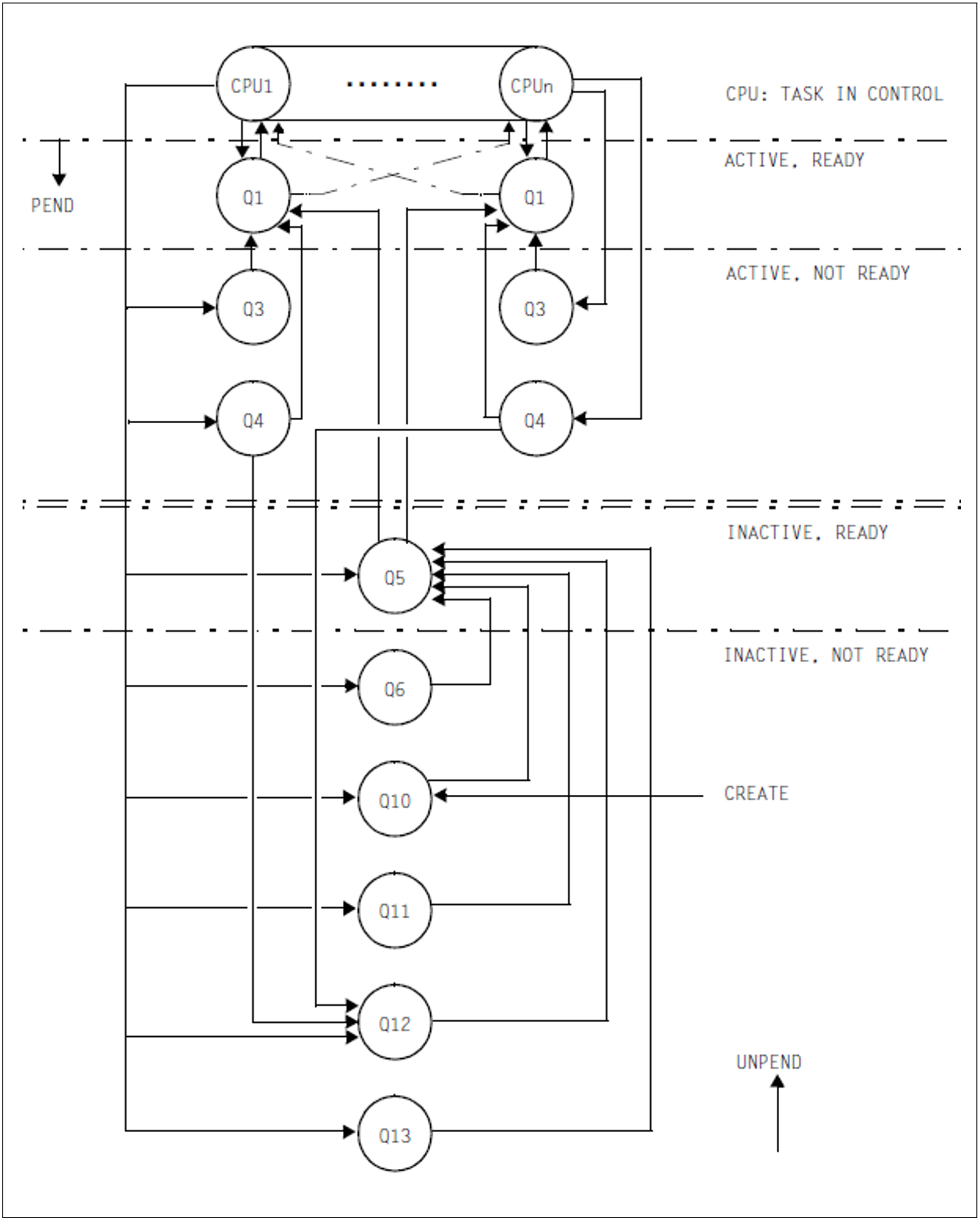
Tasks existing within an operating system can be in any of five different states:
TASK IN CONTROL
ACTIVE READY
ACTIVE NOT READY
INACTIVE READY
INACTIVE NOT READY
The number of tasks in the state TASK IN CONTROL can only be as great as the number of CPUs the server has.
The remaining 4 states are wait states. They can be divided into 2 groups, depending on whether they have already been allocated the right to use main memory (ACTIVE) or not (INACTIVE).
Tasks are assigned to the individual wait states with the aid of queues; for reasons of clarity the “NOT READY” states are further subdivided into events to show why the task is not executable.
In order to improve the MP factor for multiprocessors, the queues for the active space of each CPU are provided separately (locally for each CPU) and the remaining queues are common to all CPUs (see figure 7).
The PEND/UNPEND routines are used to change the state of a task (characterized by moving from one queue to another):
UNPEND routines move the task from its present waiting position towards use of the CPU.
PEND routines put the task in a wait state due to an intervening event.
Figure 7: Queue transfers
Overview of the individual queues
Queues Q0, Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 are provided once for each CPU.
TASK IN CONTROL
Q0
Task occupies CPU
ACTIVE, READY
Q1
CPU queue
contains active ready tasks waiting to use the CPU.ACTIVE, NOT READY
Q2
Special case (not shown in the diagram): monitoring system tasks
Q3 Waiting for termination of paging I/O Q4 Waiting for termination of DMS I/O (disk, tape)
Waiting for bourse events (“short wait”)
Waiting for termination of VPASS 0, VPASS MSEC=YINACTIVE, READY
Q5
Memory queue
contains inactive ready tasks waiting for authorization to use main memory.
This queue consists of 4 to 16 sub-queues corresponding to the following predefined categories:SYS
TP
DIALOG
BATCHand up to 12 further categories which can be defined by systems administration.
Q6
PCS-Not-Admitted queue
This queue contains inactive ready tasks which are not allowed to be activated by the Performance Control Subsystem.INACTIVE, NOT READY
Q10
HOLD queue
Contains newly generated tasks (call: $CREA)
Waiting for peripheral devices (/SECURE-RESOURCE-ALLOCATION)
Stopped by systems support (/HOLD-TASK)
Tasks cannot be terminated (serious errors)Q11
Inactive system tasks
Q12
Waiting for terminal input (WRTRD, RDATA)
Waiting for bourse events (“long wait”)
Waiting for an answer to a console messageQ13 Waiting for termination of PASS, VPASS calls
Waiting for ITC event