This chapter provides information about automatic caching (AutoDAB), DAB caching modes (read cache, write cache and read/write cache) and the main memory cache medium.
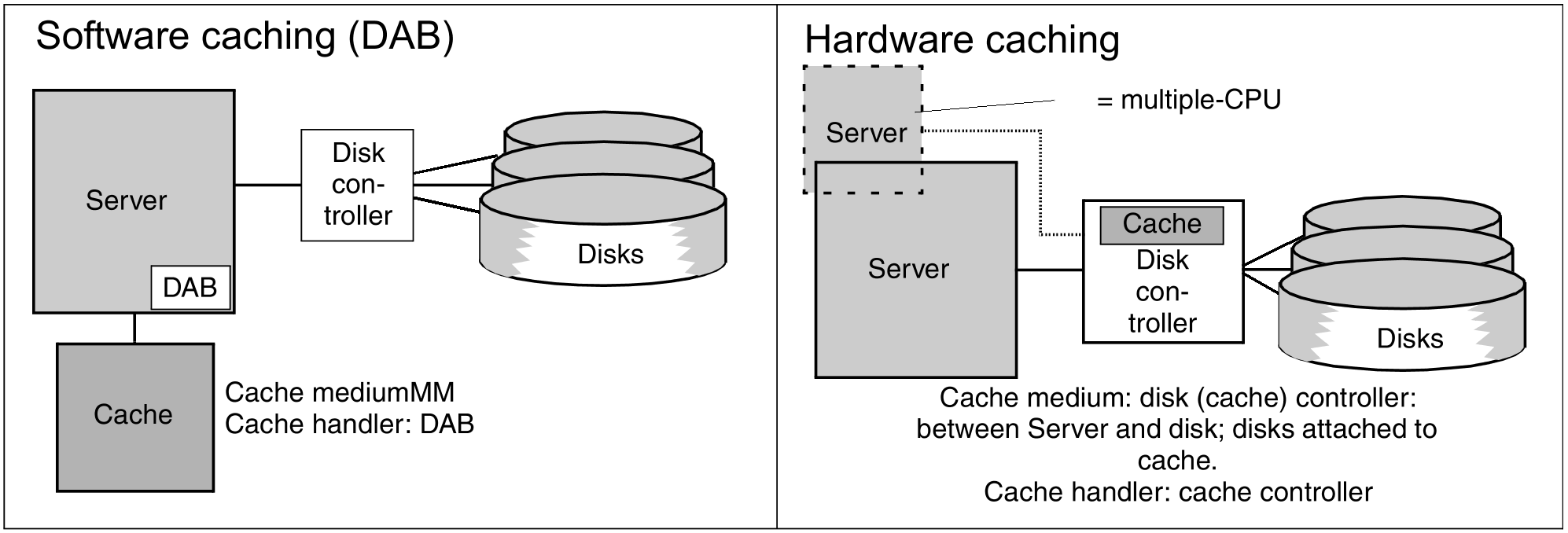
The subsystem DAB implements software caching in BS2000 with main memory (MM) as cache medium.
No additional software is required to control hardware caching for external disk storage systems. The cache is managed automatically by the external disk storage system in this case.
Figure 1: Comparison of software caching and hardware caching
Systems support defines cache usage by means of DAB commands and decides which data media are to be supported by automatic caching (DAB selects the files) or which manually selected files would profit from caching. The data areas to be cached may be located on shared disks (public volumes) or private disks.
Systems support can create new cache areas using the /START-DAB-CACHING command. Cache areas are independent cache units that are assigned, on the one hand, data areas to be served, and on the other hand, specific areas of cache storage. In addition, the following operating parameters are defined for each cache area:
cache size, which implicitly defines the caching technique (displacement according to LRU or resident buffering)
caching mode (read, write or read/write cache)
size of cache segments (4, 8, 16 or 32 KB)
saving of data to disk (controlled via a threshold value or not) for write and read/write
cachinglocation of the cache area and its management data
(resident below or non-resident above the minimum main memory size)
Files worth caching are selected automatically using AutoDAB. The cache segment size does not have to be selected since with automatic caching, DAB carries out the prefetch which matches the access profile of a file. With read/write caching, the data is also automatically saved to the disk.