The HIPLEX product family (HIPLEX® is a registered trademark of Fujitsu Technology Solutions GmbH) implements operational, capacity and availability networks for BS2000 servers.
As a member of this family, HIPLEX MSCF (HIPLEX = Highly Integrated System Complex, MSCF = Multiple System Control Facility) provides the necessary infrastructure for capacity and availability sharing, as well as the basic functions for distributed applications.
In HIPLEX MSCF a BS2000 processor (processor for short) is understood to be a BS2000 server with the BS2000 (native) operating system or a VM2000 guest system on a BS2000 server with VM2000.
In other literature the term “BS2000 system” (system for short) is also used.
Fundamental to an MSCF network is the communication of the processors in it based on BCAM transport links. Jobs involving the execution of functions and check messages for monitoring the network are exchanged between the processors.
Within the MSCF network, the shared pubset network is the most important network type. In addition to the communication link, in this type of network all the participating processors have access to shared disks, the shared pubset. The processors in the network monitor each other by means of two independent data routes, i.e. with the aid of the shared disks on the one hand and communication paths on the other, so that a processor crash can be reliably detected by the redundancy of the monitoring paths. If a processor crashes or a communication path fails, appropriate reconfiguration measures guarantee the continued functionality of the shared pubset network.
The XCS network is an extension of the shared pubset network. Synchronization mechanisms for all processors permit the management of globally available resources and the operation of distributed applications with data access to the shared data volumes.
Each processor in an MSCF network is autonomous. Systems support for each processor decides whether, when and for how long each processor will participate in the network. This ability to configure the network dynamically gives it a high degree of flexibility.
The mechanisms for detecting a processor failure are an integral part of the shared pubset and XCS network and also of the CCS network without shared pubsets. They allow the implementation of standby configurations which can be used to minimize application downtime.
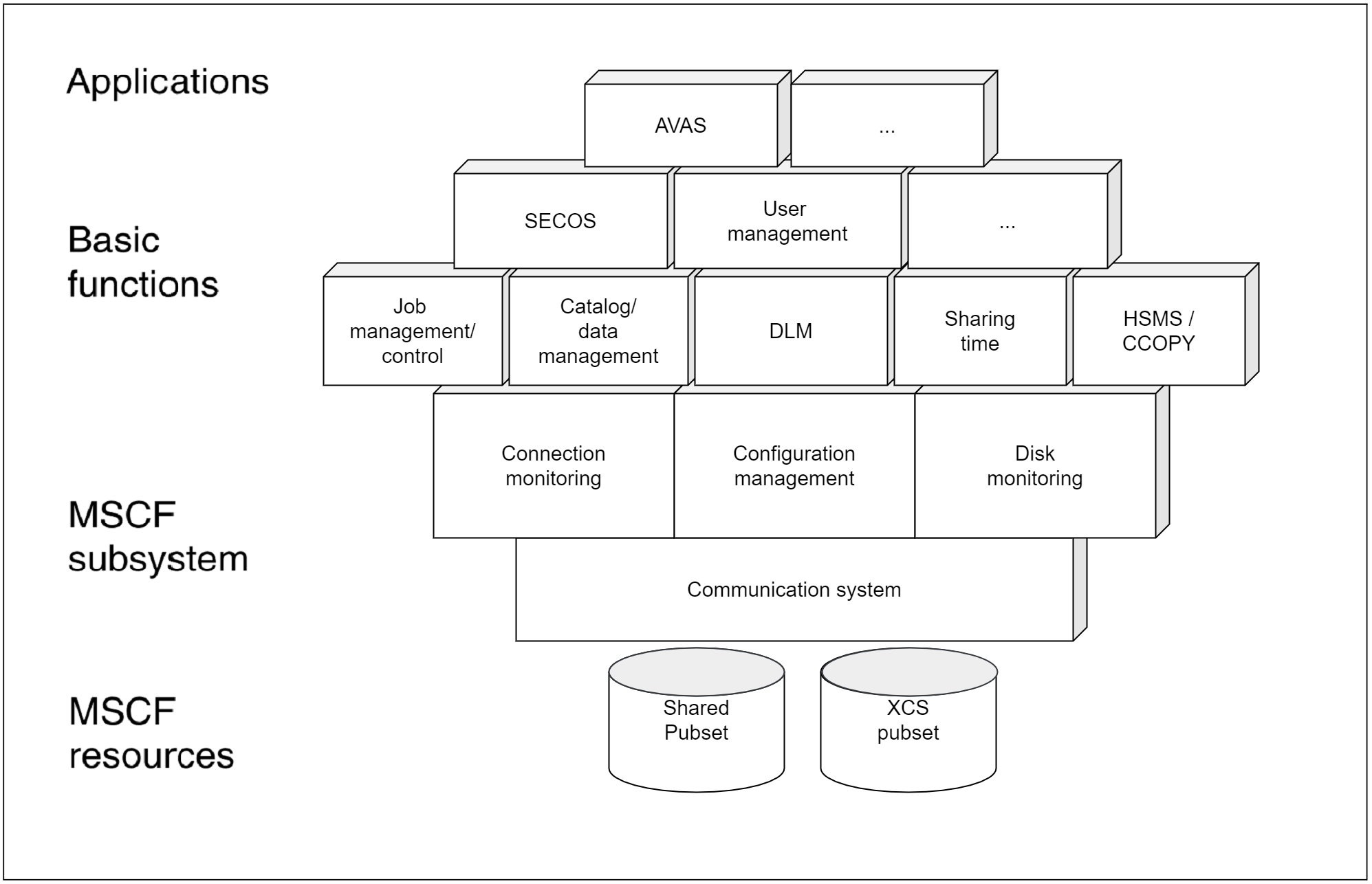
The HIPLEX MSCF architecture
The figure below provides an overview of the architecture of HIPLEX MSCF and the basic functions and applications that are based on it.
Figure 1: Architecture of the HIPLEX MSCF basic functions and applications
The product HIPLEX MSCF consists of the following DSSM subsystems:
MSCF, responsible for communication and configuration monitoring
NSM, DLM component (distributed lock management), implements the lock management across several systems
XCS-TIME, responsible for processor time.
The following basic functions are grouped together in the MSCF subsystem:
The communication system provides interfaces for starting and terminating the MSCF network on the local processor and for establishing and clearing down MSCF connections to partner processors. It also supports a communication interface to the partner processors.
The connection monitoring system checks that the communication between each local processor and its partners is functioning properly. If necessary, it implements measures to reestablish connections that have been interrupted.
The configuration management system manages the processors that are linked into an XCS network and coordinates any necessary reconfiguration measures. It also manages the shared pubset partners of the local processor.
The disk monitoring function monitors the processor’s shared pubset partners by means of their vital-sign messages written to the shared pubsets.
The following operating system functions an software products use the MSCF communication interface to extend their shared pubset and XCS network functionality:
job management and checking
catalog and data management
HSMS with CCOPY
user management (SRPM)
openSM2
SHC-OSD
SPACEOPT
MAREN
products of the SECOS security package
The XCS network offers the following functions:
distributed lock management (DLM)
time spent in the network
disk access buffer (DAB)
The basic functions are used by application systems to support network-wide applications, such as AVAS in the management of job networks within the processor network to support load distribution over several systems.