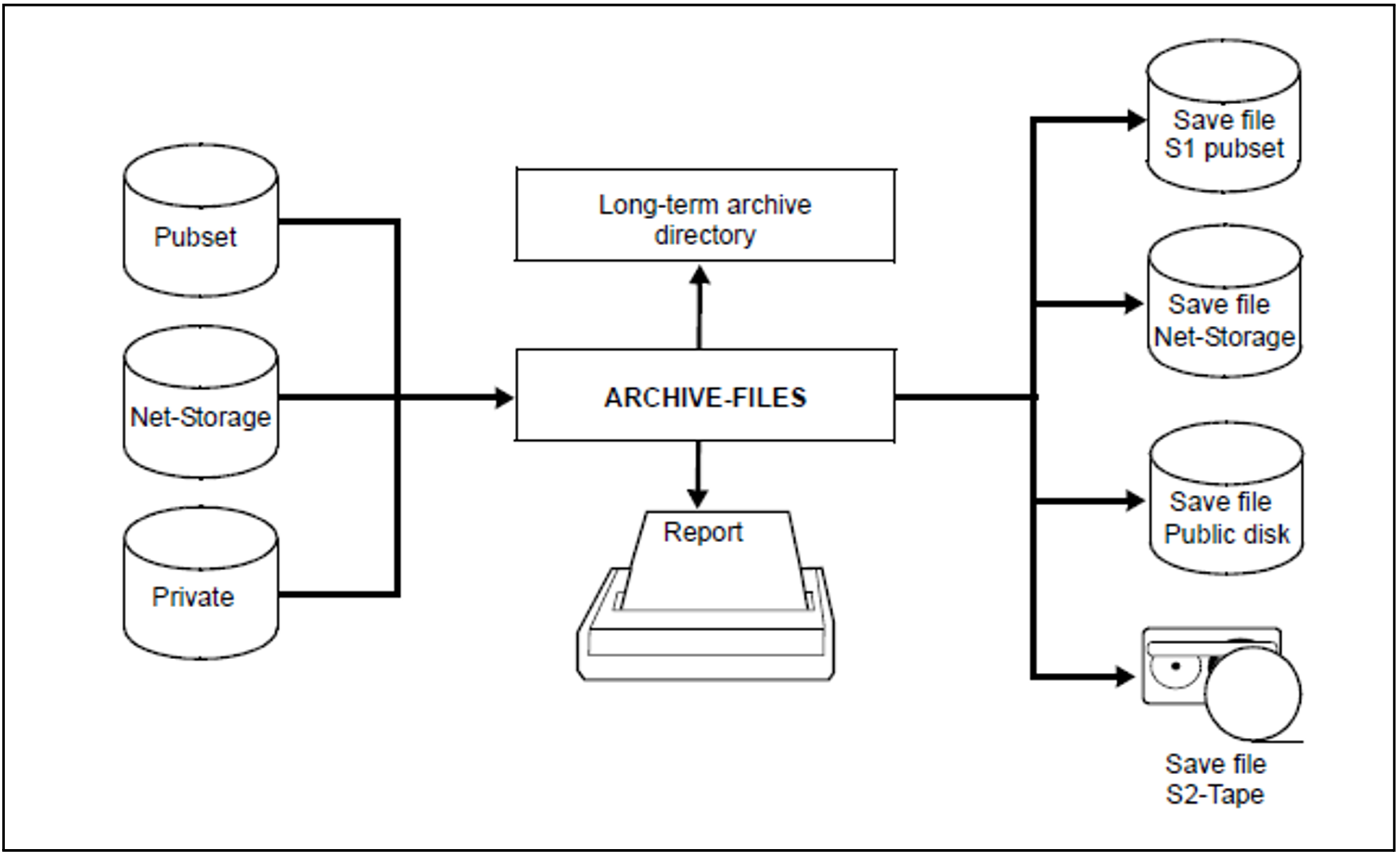
BS2000 files are archived by means of the HSMS statement ARCHIVE-FILES.
A global long-term archive that is defined in the SF environment can contain either SF files or SM files. A long-term archive that is local for the SM pubset can only contain SM files.
If the HSMS statement ARCHIVE-FILES refers to an archive that is defined in the central HSMS parameters, the files to be processed can be located either in the SF environment or in the SM environment. If the HSMS statement ARCHIVE-FILES refers to a local
SM pubset archive, the files to be edited can only be located in this SM environment.
A local SM pubset archive can only be stored at storage level S1 or S2. Other specifications in the TO-STORAGE operand are rejected.
The ARCHIVE-FILES statement offers the operands FILE-NAMES, EXCEPT-FILE-NAMES and SELECT-FILES for the selection of BS2000 files to be archived.
It is, of course, possible to specify a list of file names or to select BS2000 files in screen masks (see section "Selection of BS2000 files, job variables and node files").
Migrated BS2000 files can be archived as well. The backup includes the catalog entries from the catalog and the data from the migration level. BS2000 files which have already been migrated for a certain period (user-definable) can be archived selectively using the SELECT-FILES operand in the ARCHIVE-FILES statement. The migrated files are copied directly from the migration archive to the long-term archive.
You can also use the HSMS statement ARCHIVE-FILES to archive files of which you are the co-owner (see the “SECOS” manual [16]).
Job variables can also be entered, using the HSMS statement ARCHIVE-FILES with the operand JV-NAMES. The job variables are saved in exactly the same way as with the BACKUP-FILES.
The archive owner can use the SAVE-FILE operand for archiving to define whether
the BS2000 files to be archived are to be written to the archive’s standard save file (=*STD)
a new save file is to be created for this archival operation (=*NEW)
an existing save file is to be continued (=*CONTINUE).
Continuation is only supported for save files on storage level S2.
If they are not the archive owner, nonprivileged users can only perform archiving by using the SAVE-FILE=*STD operand.
HSMS also enables large files (>= 32 GB) to be archived. No particular provisions are required to do this. However, when restoring large files, bear in mind their special characteristics (see section "Restoring large files (> 32 GB)".
Encrypted files are saved in encrypted format and restored again in the original encrypted format. The associated crypto password need not be specified for saving or restoring. Other accesses to the restored file require the crypto password to be specified again.