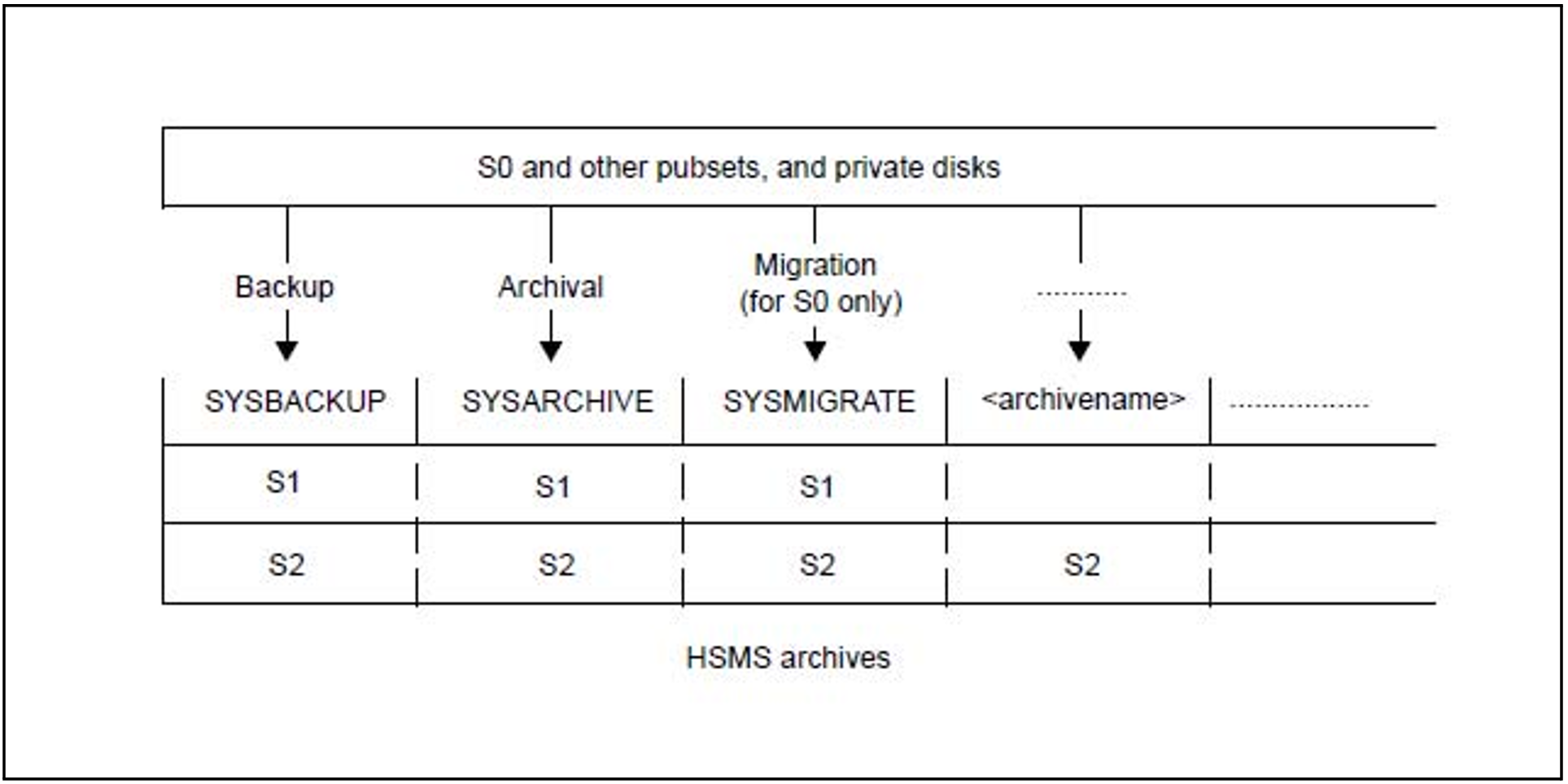
Archives are the basic management units for the data managed by HSMS. HSMS stores all data saved by either backup, archival or migration in archives, keeping separate archives for each of the basic functions:
backup archives for backup
- version backup archives
long-term archives for archival
migration archives for migration.
shadow archives for the copies of save files. The copies are created automatically for backups and archivals.
HSMS makes a distinction between public archives, which are available to all users, and private archives, which may be accessed by the archive owner only.
The HSMS administrator can assign public archives as default system archives:
system-wide
for specific SF pubsets
for SM pubsets.
All users can use these system archives for any of the HSMS basic functions. They are addressable under the following symbolic names:
SYSBACKUP for the default system backup archive
- SYSVERSION for the default system version archive (only pubset specific)
SYSARCHIVE for the default long-term system archive
SYSMIGRATE for the default system migration archive.
Data managed in the archive is stored in save files which can be located on S1 pubsets, private disks, or magnetic tape cartridges. In order to save memory space, the data can be compressed before it is written to the save file.
To increase data security, HSMS offers a function which can be used to copy save files – or excerpts of save files – within the same archive or to another archive.
Summary
To sum up, the data managed by HSMS and the storage media can be classified according to two criteria.
Using volume availability as a criterion, the storage media are assigned to the different levels of the storage hierarchy made up of S0, S1 and S2.
Using utilization as a criterion, the data inventory is subdivided into management units formed by the default system archives and private archives.
Figure 2: HSMS storage management structure
HSMS offers a set of inquiry functions for the management of data, storage units, archives etc. For instance, HSMS can be used to ascertain the occupancy of pubsets in order to forestall possible saturation.