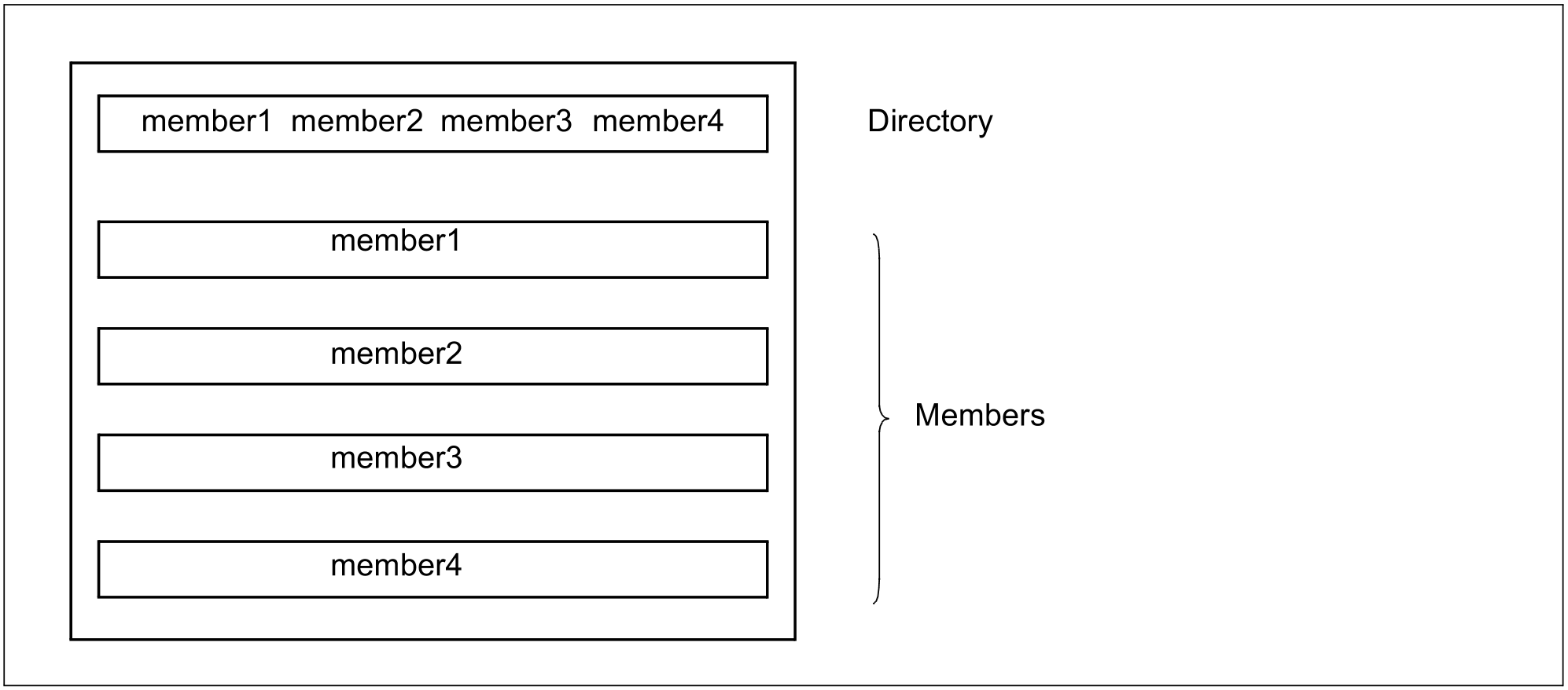
A library is a file with a substructure. It contains members and a directory (table of contents, TOC).
A member (also referred to as “element” in examples and messages) is a logically related set of data, e.g. a procedure, an object module or a source program. Each member of a library can be referenced individually.
Storing a number of files as members in a library decreases the burden on the file name catalog since each library has only one catalog entry. Storage space is saved because the members are always stored in compressed form in the library and, furthermore, may also be stored as delta members.
Each library has a single entry in the system catalog. The user can define the name and other file attributes such as the retention period or shareability. Catalog entries and changes to them are made by the user with the aid of system commands.