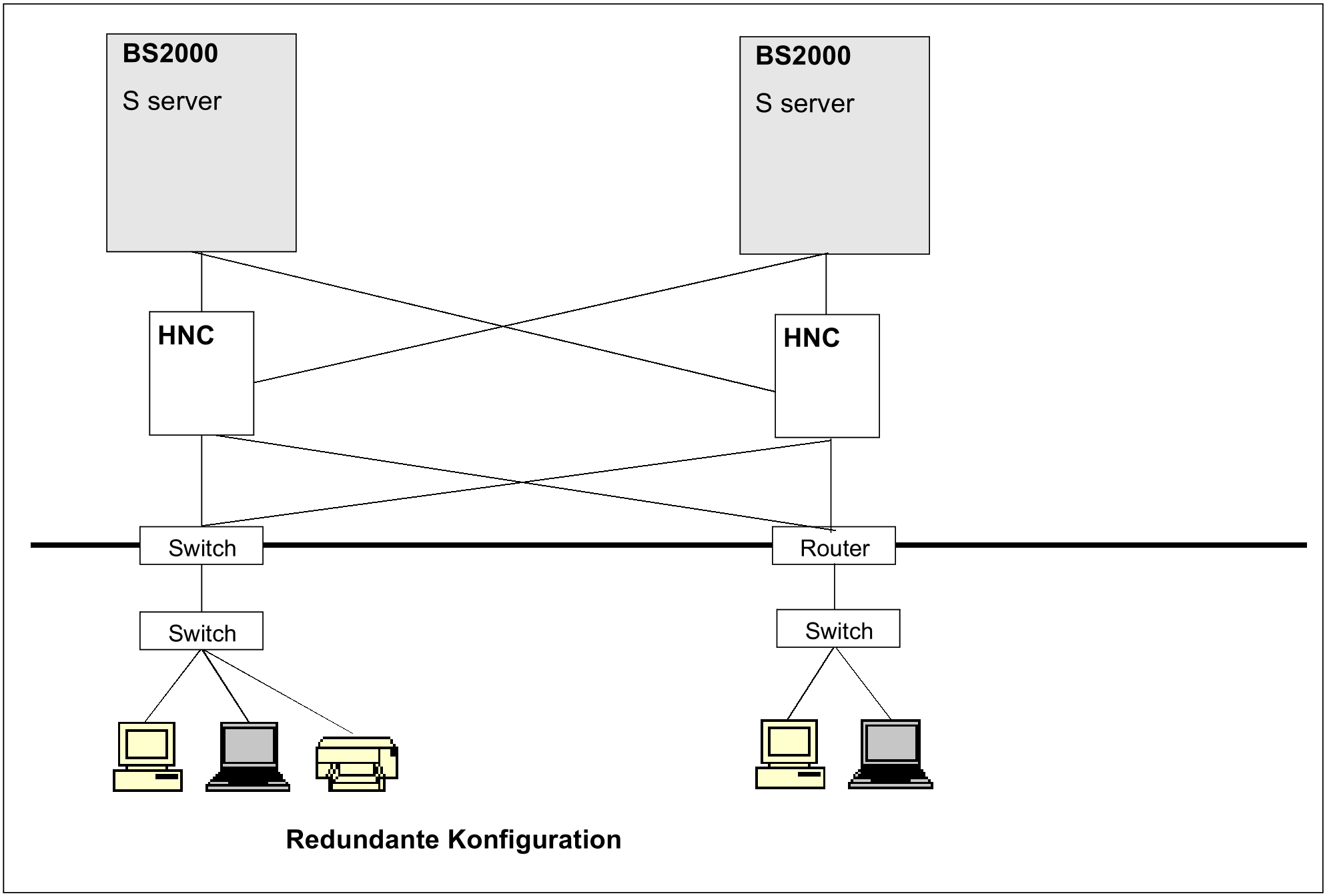
Redundant network topology
Redundant topology
Exacting requirements are also placed on the ability of corporate networks to offer a failureproof level of security. This can be enhanced by means of a redundant network topology, where certain central hardware components are installed on the network more than once. If one network component fails, the intact components take over the functions of the one that has failed.
The redundancy concept can be implemented for Ethernet/Fast and Gigabit Ethernet by using High-Speed Net Connect (HNC) as the network access product. This approach is illustrated in the above diagram. Routers, concentrators, channel adapters and cables are all duplicated, thus allowing operation to be maintained even if one component should break down.
BCAM supports the redundant network topology both with the TCP/IP or IPv6 and ISO protocols (for example ISO9542).
TCP/IP or IPv6 and ISO protocols support automatic rerouting in the event of an error, provided the corresponding network topology and settings for the BCAM operands are available. To increase fault tolerance, BCAM uses ARP and ICMP protocols as well as OSPF protocol information (if present). The partners involved are expected to use ARP dynamically. The IP routers, in particular, must respond to ICMP echo requests with ICMP redirect messages if the partner system addressed is reached via a different route. In the ISO sector, ISO9542 is always used.