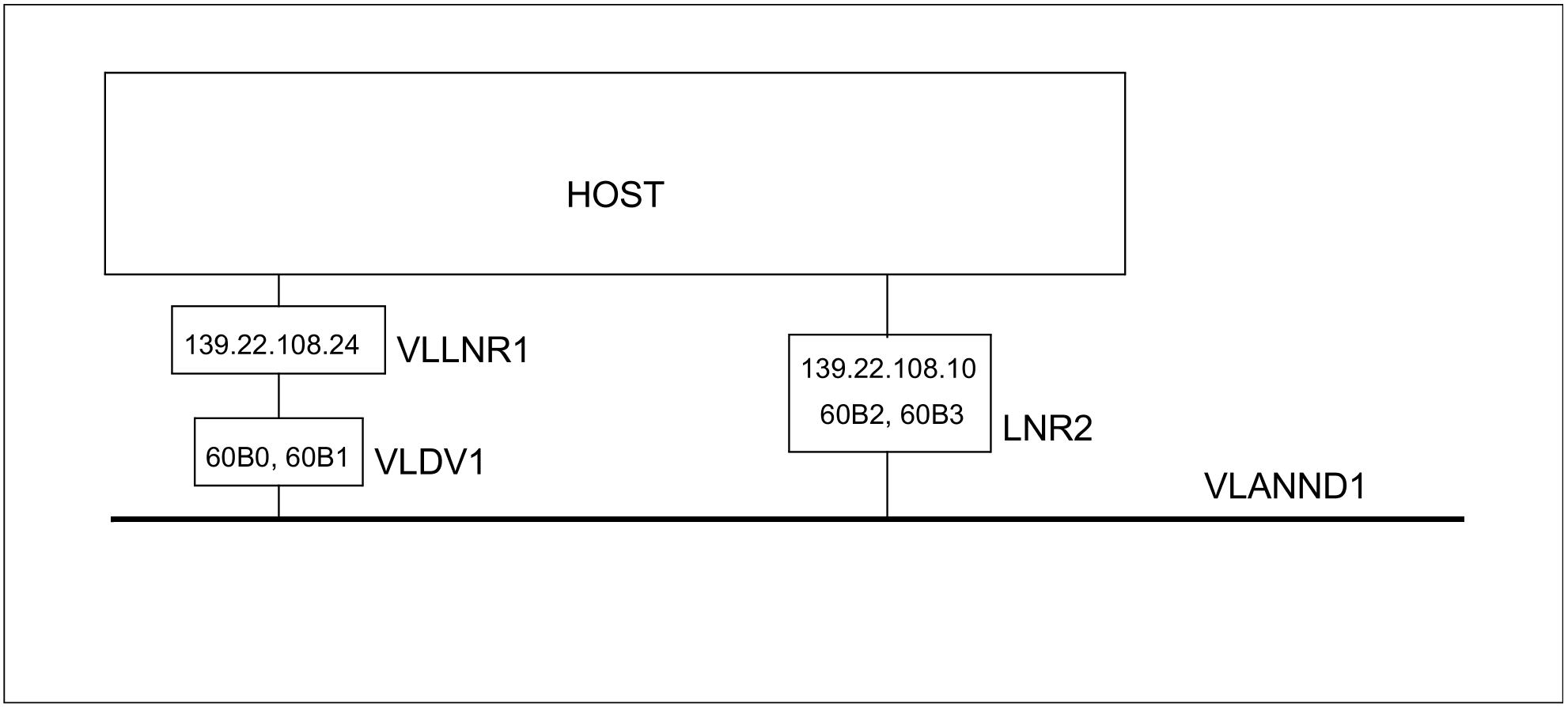
In the following a redundant VLAN configuration is presented in which a VLAN line and a normal line have been defined at the same node. The device with the device mnemonic (60B2, 60B3) does not support VLAN tags but can be used for defining a redundant configuration if the VLAN is defined as untagged.
Dynamic generation
/REMARK Definition of the VLAN device VLDV1
/CREATE-VLAN-DEVICE DEVICE-NAME=VLDV1-
/ ,WRITE-DEVICE=60B0-
/ ,READ-DEVICE=60B1-
/ ,LAN-ADDRESS=*DYNAMIC-
/ ,MAX-LPDU-SIZE=*BY-DEVICE
/REMARK Definition of the VLAN node VLANND1 (untagged)
/CREATE-NODE NODE-NAME=VLANND1-
/ ,IP-SUBNET-MASK=255.255.255.128-
/ ,LAN-TYPE=*VIRTUAL(-
/ VLAN-ID=*UNTAGGED-
/ ,PRIORITY=*STD)
/REMARK Definition of the VLAN line VLLNR1
/CREATE-VLAN-LINE LINE-NAME=VLLNR1-
/ ,HOST-NAME=*STD-
/ ,NODE-NAME=VLANND1-
/ ,DEVICE-NAME=VLDV1-
/ ,IP-ADDRESS=139.22.108.24-
/ ,AUTO-ROUTE-SWITCHING=*OFF-
/ ,ROUTE-RESWITCHING=*OFF
/REMARK Definition of line LNR2
/CREATE-LINE LINE-NAME=LNR2,-
/ IP-ADDRESS=139.22.108.10,-
/ L2-PROTOCOL=*CSMACD(NODE-NAME=VLANND1,-
/ WRITE-DEVICE=60B2,READ-DEVICE=60B3)
Note
The definitions of the VLAN line and a normal line permit switching operations to be controlled by the AUTO-ROUTE-SWITCHING and ROUTE-RESWITCHING operands which become effective when the VLAN line or normal line is activated. In this example the switching of the routes is suppressed, but this can be changed later with appropriate MODIFY-VLAN-LINE commands.
/MODIFY-VLAN-LINE LINE-NAME=VLLNR1,-
/ ,AUTO-ROUTE-SWITCHING=*ON-
/ ,ROUTE-RESWITCHING=*ON
/MODIFY-LINE LINE-NAME=LNR2,-
/ ,AUTO-ROUTE-SWITCHING=*ON-
/ ,ROUTE-RESWITCHING=*ON
Note
As in the preceding examples the local processors, routers and remote processors can be defined.