POSIX is directly in line with the BS2000 policy of open systems as defined in the “Open System Direction”.
This section provides a general overview of
open systems
the advantages of the POSIX standard
the components of POSIX
the hardware requirements for POSIX
terminal support
the BS2000 software products that have been modified for use with POSIX
New requirements facing information technology
For many decades, most companies had a strict hierarchical structure. Flat organizational structures were introduced in recent years. “Lean management” guarantees shorter routes and quicker, more flexible decisions.
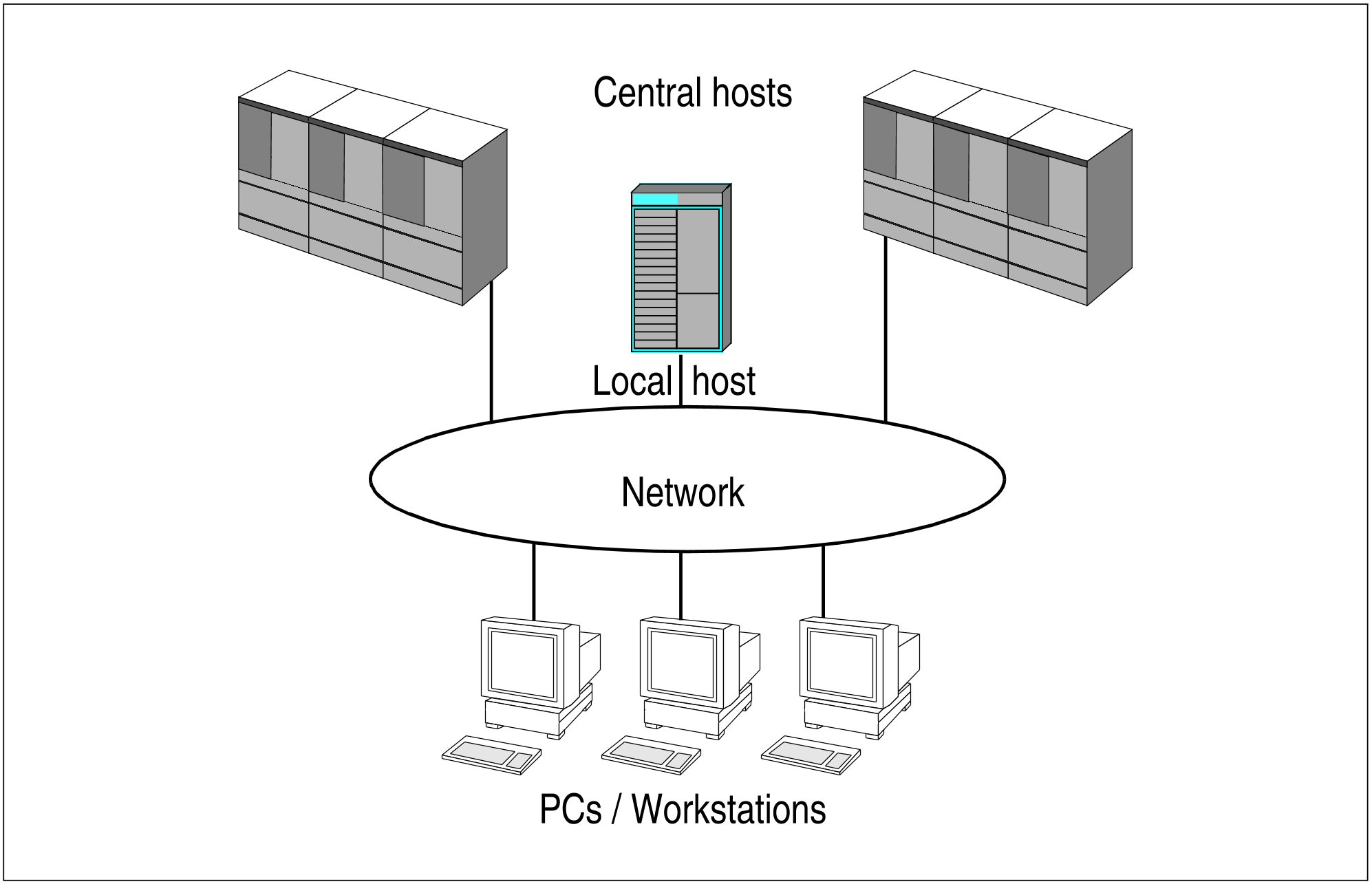
This development also made new demands on information technology. Powerful, low-cost PCs and workstations form part of the basic layout of today’s working environment. The growing desire on the part of users for comprehensive solutions calls for the combination of these PCs and workstations with the present host systems to form an optimal overall system. All systems must be able to communicate with each other in order to use the common resources.
In this regard, networking heterogeneous systems is a basic requirement of information technology. The cost-effectiveness and user-friendliness of PCs and workstations must be linked with the high computer performance, storage capacity, availability, data consistency and security provided by host systems.
Figure 1: Networking heterogeneous systems
Communication between heterogeneous systems and the improved use of such systems are only possible if standards for operating systems interfaces are defined and adhered to.