Element types supported
The bs2fs file system supports the same element types as the bs2cp command (and /COPY-POSIX-FILE), namely the predefined text types (D, J, M, P, S, X) and LLMs (L). Furthermore, types defined by the user (e.g. with openFT) and types derived from the standard types mentioned above are also supported in bs2fs file systems.
Like DMS files of the type SAM, the text, textbin or binary mode in which the text elements (all types other than LLM) are copied to and from the bs2fs container depends on the ftyp option of the mount command for the bs2fs file system.
Representation of PLAM libraries and library elements
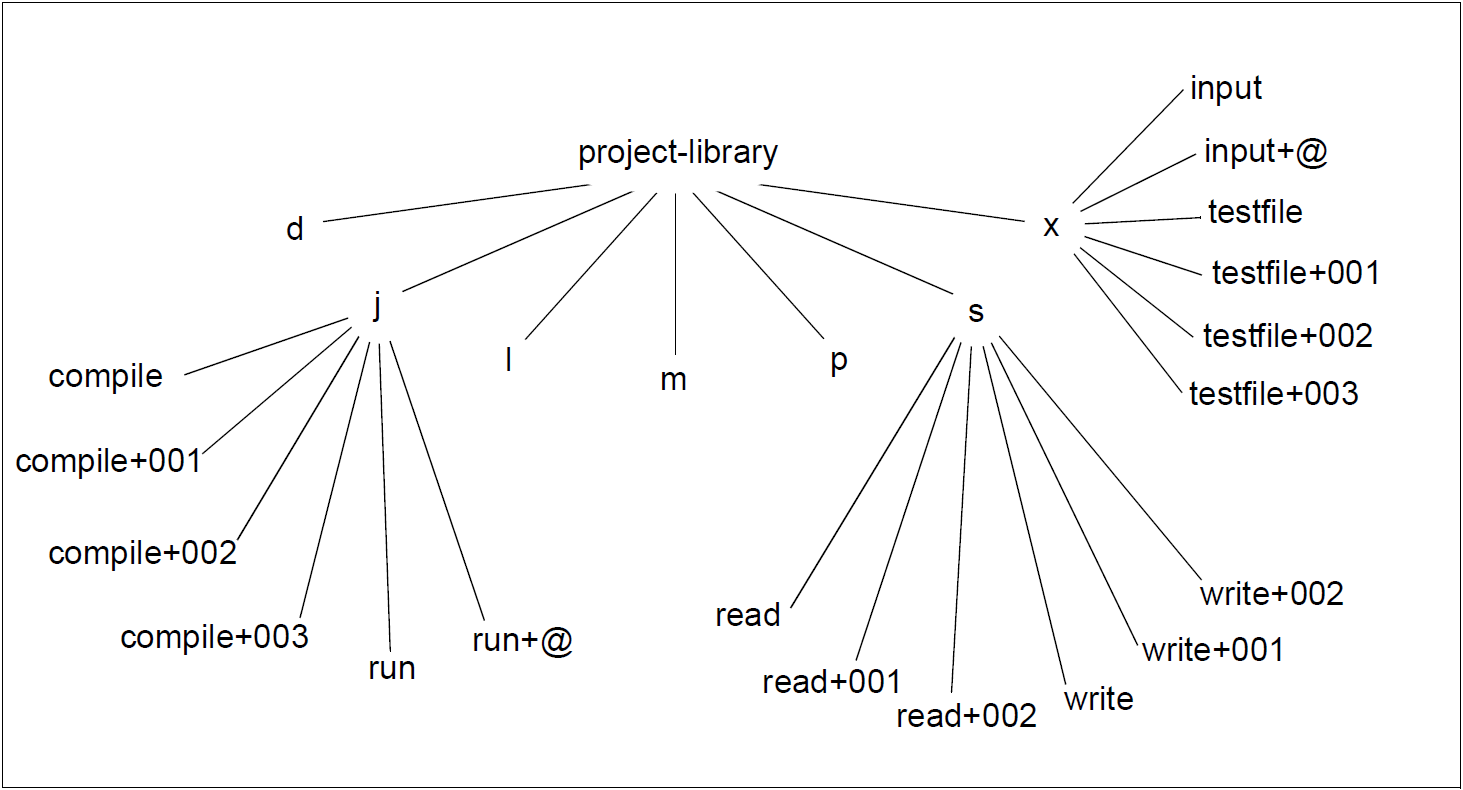
A PLAM library is represented as a directory with the name of the PLAM library. By default this library directory contains the subdirectories of the standard types D, J, L, M, P, S and X in which the corresponding element types are stored.
in addition, the library directory contains further directories with the names of derived element types, but only if at least one element of the relevant type exists and the derived type has one of the standard types D, J, L, M, P, S or X as its basic type.
The standard types C, F, H, R, U and SYSJ and types derived from these are not supported. This also applies for the reserved types whose names begin with '$' or 'SYS'.
If the PLAM library contains user-defined types which do not have a standard type as their basic type, these are represented as corresponding subdirectories. Such types can, for instance, be created with openFT. New PLAM libraries cannot be created with bs2fs means (e.g. with mkdir). New PLAM libraries which were created with other means (e.g. with LMS) after a bs2fs mount can, however, be edited at any time in the bs2fs file system. To permit this, it is only necessary for their name to match the wildcard pattern of the bs2fs mount command.
Library elements are stored as files in the directory whose name corresponds to their type. Their names have the following format: elementname + version. This name permits targeted access to a particular version of an element. The name elementname permits access to the highest version of an element. A hard link to the highest version of an element is involved here.
The following special features apply for this hard link:
If a new element version with a higher version identifier is generated in the bs2fs file system, elementname automatically refers to the new highest version.
Deleting elementname (e.g. with
rmelementname) has the following effect:First the file containing the highest version of the element is deleted. If other versions of the element exist, elementname refers to the new highest version. Otherwise the hard link elementname is also deleted.
If a particular version of an element is deleted (e.g. with
rmelementname+ver), the hard link elementname is also deleted if no other versions of the element exist.All versions of an element can be deleted with
rmelementname+*.
Example of the structure of a PLAM library |