The ADD-VALUE statement is used to define an operand value in the open syntax file. The operand for which this value is defined must already be defined in the syntax file.
The position at which the operand value is inserted depends on whether the operand itself or one of its previously defined values is the “current object” (see "ADD-OPERAND Define operand"):
if the operand itself is the “current object”, the operand value defined will be inserted into the command or statement definition as the first value for this operand;
if another, previously defined value for this operand is the “current object”, the newly defined operand value will be inserted immediately following this existing value.
In both cases, the newly defined operand value then becomes the “current object”.
All names given for the operand value must be unique with regard to its environment. If the names are not explicitly defined but are instead left up to SDF-A, it can happen, in the case of the data type KEYWORD, that the internal name assembled by SDF-A by default is invalid.
An operand value for a command implemented via system modules may be defined only if the command definition is in a group or system syntax file.
ADD-VALUE |
TYPE = *ALPHANUMERIC-NAME(...) / *CAT-ID / *COMMAND-REST(...) / *COMPOSED-NAME(...) / *C-STRING(...) / *DATE(...) / *DEVICE(...) / *FIXED(...) / *FILENAME(...) / *INTEGER(...) / * LONG-INTEGER(…) / *KEYWORD(...) / *KEYWORD-NUMBER(...) / *LABEL(...) / *NAME(...) / *PARTIAL-FILENAME(...) /*POSIX-PATHNAME(...) / *POSIX-FILENAME(...) / *PRODUCT-VERSION(...) /*STRUCTURED-NAME(...) / *TEXT(...) / *TIME(...) / *VSN(...) / *X-STRING(...) / *X-TEXT(...) *ALPHANUMERIC-NAME(...) , SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..255> , LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255> , WILDCARD = *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) TYPE = *SELECTOR / *CONSTRUCTOR , LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH / <integer 1..255> *COMMAND-REST (...) LOWER-CASE = *NO / *YES *COMPOSED-NAME(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..1800> , LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800> , UNDERSCORE= *NO / *YES , WILDCARD = *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) TYPE = *SELECTOR / *CONSTRUCTOR , LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH / <integer 1..1800> *C-STRING(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800> , LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800> , LOWER-CASE = *NO / *YES *DATE(...) COMPLETION = *NO / *YES *DEVICE(...) CLASS-TYPE = *DISK (...) / list-poss(2000): *DISK(...) / *TAPE(...) *DISK(...) EXCEPT= *NO / list-poss(50): <text 1..8 without-sep> , SCOPE = *ALL / *STD-DISK *TAPE(...) EXCEPT = *NO / list-poss(50): <text 1..8 without-sep> , ALIAS-ALLOWED= *YES / *NO , VOLUME-TYPE-ONLY = *NO / *YES , RESULT-VALUE = *BY-NAME / *BY-CODE *FIXED(...) LOWEST = * ANY / <fixed -2147483648..2147483647> , HIGHEST = * ANY / <fixed -2147483648..2147483647> *FILENAME(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..80> , LONGEST-LENGTH= * ANY / <integer 1..80> , CATALOG-ID = *YES / *NO , USER-ID = *YES / *NO , GENERATION= *YES / *NO , VERSION= *YES / *NO , WILDCARD= *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) TYPE = *SELECTOR / *CONSTRUCTOR , LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH / <integer 1..80> , PATH-COMPLETION = *NO / *YES , TEMPORARY-FILE = *YES / *NO *INTEGER(...) LOWEST= *ANY / <integer -2147483648..2147483647> , HIGHEST= *ANY / <integer -2147483648..2147483647> , OUT-FORM = * STD / *BINARY / *PACKED / *UNPACKED / *CHAR *LONG-INTEGER(...) LOWEST = <long-integer -9223372036854775808..9223372036854775807> ,HIGHEST = <long-integer -9223372036854775808..9223372036854775807> ,OUT-FORM = *STD / *BINARY / *PACKED / *UNPACKED / *CHAR *KEYWORD(...) STAR = *OPTIONAL / *MANDATORY *KEYWORD-NUMBER(...) STAR = *OPTIONAL / *MANDATORY *LABEL (...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..8> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..8> *NAME(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..255> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255> , UNDERSCORE= *NO / *YES , LOWER-CASE= *NO / *YES , WILDCARD= *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) TYPE = *SELECTOR / *CONSTRUCTOR , LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH / <integer 1..255> *PARTIAL-FILENAME(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 2..79> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 2..79> , CATALOG-ID = *YES / *NO , USER-ID = *YES / *NO , WILDCARD= *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) TYPE = *SELECTOR / *CONSTRUCTOR , LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH / <integer 2..79> *POSIX-PATHNAME(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1023> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1023> , WILDCARD = *YES / *NO , QUOTES = *OPTIONAL / *MANDATORY *POSIX-FILENAME(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..255> , LONGEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..255> , WILDCARD = *YES / *NO , QUOTES = *OPTIONAL / *MANDATORY *PRODUCT-VERSION(...) USER-INTERFACE= *YES (...) / *NO / *ANY(...) *YES(...) CORRECTION-STATE= *YES / *NO / *ANY *ANY(...) CORRECTION-STATE= *ANY / *NO / *YES *STRUCTURED-NAME (...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255> ,WILDCARD= *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) TYPE = *SELECTOR / *CONSTRUCTOR , LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH / <integer 1..255> *TEXT (...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800> ,LOWER-CASE = *NO / *YES ,SEPARATORS = *YES / *NO *TIME (...) OUT-FORM = * STD / *BINARY / *CHAR *VSN (...) SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..6> ,LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..6> *X-STRING(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..1800> , LONGEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..1800> *X-TEXT(...) SHORTEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..3600> , LONGEST-LENGTH= *ANY / <integer 1..3600> , ODD-POSSIBLE= *YES / *NO , INTERNAL-NAME = *STD / <alphanum-name 1..8> , REMOVE-POSSIBLE = *YES / *NO , SECRET-PROMPT = *SAME / *NO , DIALOG-ALLOWED= *YES / *NO , DIALOG-PROC-ALLOWED= *YES / *NO , GUIDED-ALLOWED= *YES / *NO , BATCH-ALLOWED= *YES / *NO , BATCH-PROC-ALLOWED= *YES / *NO , STRUCTURE= *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) SIZE= *SMALL / *LARGE , FORM = *FLAT / *NORMAL , MAX-STRUC-OPERAND = *STD / <integer 1..3000> , LIST-ALLOWED = *NO / *YES , VALUE= *NO / list-poss(2000): <c-string 1..1800 with-low>(...) <c-string 1..1800 with-low>(...) STANDARD-NAME = *NAME / *NO / list-poss(2000): *NAME / <structured-name 1..30> / <c-string 1..30> , ALIAS-NAME = *NO / list-poss(2000): <structured-name 1..30> , GUIDED-ABBREVIATION = *NAME / <structured-name 1..30> / <c-string 1..30> , MINIMAL-ABBREVIATION = *NO / <structured-name 1..30> / <c-string 1..30> , NULL-ABBREVIATION= *NO / *YES , OUTPUT= *SAME / *EMPTY-STRING / *DROP-OPERAND / <c-string 1..1800> / <x-string 1..3600> , OUT-TYPE = *SAME / *ALPHANUMERIC-NAME / *CAT-ID / *COMMAND-REST / *COMPOSED-NAME / *C-STRING / *DATE / *DEVICE / *FIXED / *FILENAME / *INTEGER / *LONG-INTEGER / *KEYWORD / *KEYWORD-NUMBER / *LABEL / *NAME / *PARTIAL-FILENAME / *PRODUCT-VERSION / *POSIX-PATHNAME / *POSIX-FILENAME / *STRUCTURED-NAME / *TEXT / *TIME / *VSN / *X-STRING / *X-TEXT , OVERWRITE-POSSIBLE = *NO / *YES , OUTPUT= *NORMAL(...) / *SECRET-PROMPT *NORMAL(...) AREA-LENGTH= *VARIABLE / <integer 1..3000> , LEFT-JUSTIFIED = *STD / *YES / *NO , FILLER = *STD / <c-string 1..1> / <x-string 1..2> , STRING-LITERALS = *NO / *HEX / *CHAR , HASH = *NO / *YES(...) *YES(...) OUTPUT-LENGTH = <integer 2..32> , PRIVILEGE= *SAME / *EXCEPT(...) / list-poss(64): <structured-name 1..30> *EXCEPT(...) EXCEPT-PRIVILEGE= list-poss(64): <structured-name 1..30> |
TYPE =
Specifies the data type of the operand value. The various values defined for an operand must not be mutually exclusive with respect to data type (see "Mutually exclusive data types"). (If this is not possible in exceptional cases, the value YES must be specified for VALUE-OVERLAPPING in the ADD-OPERAND or MODIFY-OPERAND statement. Otherwise it is not possible, for example, to define a value of the type NAME and an alternative value of the type STRUC-TURED-NAME for an operand. Only the data type KEYWORD may be specified in more than one alternative operand value definition. When a command or statement is entered, SDF checks whether an operand value entered is of the type defined for it. In the following descriptions of the data types, the term “alphanumeric character” is repeatedly used. This may be a letter (A, B, C, ..., Z), a digit (0, 1, 2, ..., 9) or a special character (@, #, $).
TYPE = *ALPHANUMERIC-NAME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type ALPHANUMERIC-NAME. This is defined as a sequence of alphanumeric characters.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
WILDCARD =
Specifies whether wildcards (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5) may be used in place of characters/strings within the name when the command or statement is entered.
WILDCARD = *NO
No wildcards are allowed when entering the operand value.
WILDCARD = *YES(...)
Wildcards may be used.
TYPE =
Specifies whether the string can be a wildcard selector ()search pattern) or wildcard constructor. Wildcard constructors are used to build names from strings generated with the aid of a wildcard selector.
TYPE = *SELECTOR
The string can be a wildcard selector; the data type receives the suffix with-wild (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
TYPE = *CONSTRUCTOR
The string can be a wildcard constructor; the data type receives the suffixwith-wild-constr (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN =
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard (selector or construction).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH
The maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard is the same as the length specified by the LONGEST-LENGTH operand (for reasons of compatibility).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = <integer 1..255>
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard.
TYPE = *CAT-ID
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type CAT-ID, defined as a sequence of up to 4 characters (without “:” delimiters) from the ranges A-Z and 0-9; the special characters $, @ and # are not permitted. A four-character catalog ID must not begin with the string ’PUB’.
TYPE = *COMMAND-REST(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type COMMAND-REST. This data type is provided only for special purposes for Fujitsu Siemens Computers Software Development and is therefore not described here.
TYPE = *COMPOSED-NAME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type COMPOSED-NAME.
Allowed are letters, numbers and the special characters: '@' , '$' , '#' , '.'and '-'.
Whether the special character '_' is also allowed depends on the operand UNDERSCORE.
- The length is not limited to 54 characters;
The name does not need to include a letter.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).UNDERSCORE = *NO / *YES
Specifies whether the underscore character ’_’ is accepted.
WILDCARD =
Specifies whether wildcards (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5) may be used in place of characters/strings within the name when the command or statement is entered.
WILDCARD = *NO
No wildcards are allowed when entering the operand value.
WILDCARD = *YES(...)
Wildcards may be used.
TYPE =
Specifies whether the string can be a wildcard selector (search pattern) or wildcard constructor. Wildcard constructors are used to build names from strings generated with the aid of a wildcard selector.
TYPE = *SELECTOR
The string can be a wildcard selector; the data type receives the suffix with-wild (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
TYPE = *CONSTRUCTOR
The string can be a wildcard constructor; the data type receives the suffix with-wild-constr (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN =
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard (selector or constructor).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH
The maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard is the same as the length specified by the LONGEST-LENGTH operand (for reasons of compatibility).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = <integer 1..1800>
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard.
TYPE = *C-STRING(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type C-STRING. This is defined as a sequence of EBCDIC characters, enclosed in single quotes. It may be prefixed with the letter C. A single quote as a value within the limiting apostrophes must be specified twice.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
LOWER-CASE = *NO / *YES
Specifies whether lowercase letters within the apostrophes are retained.
TYPE = *DATE(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type DATE. This is defined as a sequence of one four-digit number and two two-digit numbers, joined together by hyphens (<year>-<month>-<day>). The year may also be specified with two digits instead of four.
COMPLETION = *NO / *YES
Specifies whether a two-digit year specification is to be extended. If YES is specified, SDF extends two-digit year specifications (in the form yy-mm-dd) as follows:
20yy-mm-dd if yy < 60
19yy-mm-dd if yy
>=60.
TYPE = *DEVICE(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type DEVICE. The user is offered a list of the disk or tape device types available in the system for operands whose value is defined with the data type DEVICE (see the manual “System Installation” [9 (Related publications)]).
C LASS-TYPE = *DISK / list-poss(2000): *DISK(...) / *TAPE(...)
Specifies the device family.
CLASS-TYPE = *DISK(...)
The device family is disk.
EXCEPT = *NO / list-poss(50): <text 1..8 without-sep>
Specifies the types that will not appear in the list of available types.
SCOPE =
Specifies whether all currently supported disk types appear in the list, or also older types still accepted by DMS for compatibility reasons..
SCOPE = *ALL
All currently supported disk types appear in the list.
SCOPE = *STD-DISK
In addition to the currently supported disk types also older types appear in the list which are still accepted by DMS for compatibility reasons.
CLASS-TYPE = *TAPE(...)
The device family is tape.
EXCEPT = *NO / list-poss(50): <text 1..8 without-sep>
Specifies the types that will not appear in the list of available types.
ALIAS-ALLOWED = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether an alias is allowed for the device type.
VOLUME-TYPE-ONLY = *NO / *YES
Specifies whether the volume type is accepted.
RESULT-VALUE =
Specifies the form in which SDF transfers information to the implementation.
RESULT-VALUE = *BY-NAME
SDF outputs the external device type name. The external device type name is 8 characters in length.
RESULT-VALUE = *BY-CODE
SDF outputs the internal device type code. The internal device type code is 2 bytes long.
TYPE = *FIXED(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type FIXED. This is defined as follows:
[sign][digits].[digits]
[sign] is + or –
[digits] are 0..9
FIXED must consist of at least one digit; it must not exceed 10 characters (digits and a ’.’). The value is stored in the standardized transfer area in the following format:
| n : 1 byte for the number of digits after the period | |
| 4 bytes for the fixed- point number* 10n |
LOWEST = *ANY / <fixed -2 147 483648..2 147 483647>
Specifies whether there is a lower limit for the fixed value and, if so, what this limit is.
HIGHEST = *ANY / <fixed -2 147 483648..2 147 483647>
Specifies whether there is an upper limit for the fixed value and, if so, what this limit is.
TYPE = *FILENAME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type FILENAME. The definition of the character string to be entered is the one given in the BS2000 manual “Introductory Guide to DMS” [7 (Related publications)] for fully qualified file names.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..80>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..80>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
CATALOG-ID = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the catalog ID may be specified as part of the file name.
USER-ID = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the user ID may be specified as part of the file name.
GENERATION = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether a generation number may be specified as part of the file name. If a structure is appended to the file name, NO must be specified.
VERSION = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether a version identifier may be specified as part of the file name. If a structure is appended to the file name, NO must be specified.
WILDCARD =
Specifies whether wildcards (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5) may be used in place of characters/strings within the name when the command or statement is entered.
WILDCARD = *NO
No wildcards are allowed when entering the operand value.
WILDCARD = *YES(...)
Wildcards may be used.
The data type <filename x..y with-wild> also contains partially qualified file names, i.e. it is not necessary to additionally define a value for the operand of the data type <partialfilename>.
TYPE =
Specifies whether the string can be a wildcard selector (search pattern) or wildcard constructor. Wildcard constructors are used to build names from strings generated with the aid of a wildcard selector.
TYPE = *SELECTOR
The string can be a wildcard selector; the data type receives the suffix with-wild (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
TYPE = *CONSTRUCTOR
The string can be a wildcard constructor; the data type receives the suffix with-wild-constr (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN =
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard (selector or constructor).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH
The maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard is the same as the length specified by the LONGEST-LENGTH operand (for reasons of compatibility).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = <integer 1..80>
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard.
PATH-COMPLETION = *NO / *YES
specifies whether the file name is extended to a full path name at the transfer to the implementation. This includes the substitution of aliases by the ACS function.PATH-COMPLETION = *YES can only be specified when CATALOG-ID and USER-ID are permitted and when wildcards in file names are not permitted.
TEMPORARY-FILE = *YES / *NO
specifies whether temporary file names are permitted.
TYPE = *INTEGER(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type INTEGER. This is defined as a sequence of digits, which may be preceded by a sign.
LOWEST = <integer -2 147 483648..2 147 483647>
Specifies whether there is a lower limit for the integer, and if so, what that lower limit is. If no parameter is given, the lowest possible number is taken, -2 147 483 648.
HIGHEST = <integer -2 147 483648..2 147 483647>
Specifies whether there is an upper limit for the integer, and if so, what that upper limit is. If no parameter is given, the highest possible number is taken, 2 147 483 647
OUT-FORM = *STD / *BINARY / *PACKED / *UNPACKED / *CHAR
Specifies the form in which the integer is to be passed by SDF to the implementation. If passed in a transfer area (see section 6.3, “Format of the standardized transfer area”), SDF-A converts *SDT to *BINARY. If a string is passed (commands defined with IMPLEMENTOR=*PROCEDURE(...) or IMPLEMENTOR=*TPR (...,CMD-INTERFACE*STRING,...); see ADD-CMD), SDF-A converts OUT-FORM=*STD to *CHAR. If the integer is passed in BINARY format, SDF creates 4 bytes (see the OUTPUT operand). If the integer is passed in *PACKED format, SDF creates 8 bytes. For *CHAR and *UNPACKED, at least 1 byte is created.
TYPE = *LONG-INTEGER(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type INTEGER. This is defined as a sequence of digits, which may be preceded by a sign.
LOWEST = <long-integer -9223372036854775808..9223372036854775807>
Specifies whether there is a lower limit for the integer, and if so, what that lower limit is. If unspecified -9223372036854775808 is assumed.
HIGHEST = <long-integer -9223372036854775808..9223372036854775807>
Specifies whether there is an upper limit for the integer, and if so, what that upper limit is. If unspecified 9223372036854775807 is assumed.
OUT-FORM = *STD / *BINARY / *PACKED / *UNPACKED / *CHAR
Specifies the form in which the integer is to be passed by SDF to the implementation. If passed in a transfer area (see section 6.3, “Format of the standardized transfer area”), SDF-A converts *STD to *BINARY. If a string is passed (commands defined with IMPLEMENTOR=*PROCEDURE(...) or IMPLEMENTOR=*TPR (...,CMD-INTERFACE-*STRING,...); see ADD-CMD), SDF-A converts OUT-FORM=*STD to *CHAR. If the integer is passed in BINARY format, SDF creates 8 bytes (see the OUTPUT operand). If the integer is passed in *PACKED format, SDF creates 16 bytes. For *CHAR and *UNPACKED, at least 1 byte is created.
TYPE = *KEYWORD(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type KEYWORD. This is defined as a sequence of alphanumeric characters. This character string may be subdivided into several substrings, joined together by hyphens. Substring sequences may contain periods. The periods must not be at the beginning or end of the substring sequence. The entire string, or, as the case may be, the first substring, must begin with a letter or special character. The value range for an operand value of the type KEYWORD is limited to one or a finite number of precisely defined individual values (see the VALUE operand of this statement).
From SDF-A/SDF Version 2.0 onwards, the value ’*...’ is also accepted. This value can be used where a list of keywords has to be defined for an operand (e.g. the definition for all external devices). This permits new keywords (e.g. new device names) to be inserted without having to modify the syntax file, since ’*...’ causes SDF to accept additional values and to analyze them as keywords. The data type KEYWORD may be up to 30 characters long.
STAR =
Specifies whether the string must be preceded by an asterisk when entered.
STAR = *OPTIONAL
An asterisk may be prefixed, but need not be. If an asterisk is prefixed, it is suppressed when the operand value is passed to the implementation.
STAR = *MANDATORY
An asterisk must be prefixed (necessary in order to distinguish between alternative data types).
TYPE = *KEYWORD-NUMBER(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type KEYWORD-NUMBER. This data type is provided only for special purposes for Fujitsu System Software Development and is therefore not described here.
TYPE = *LABEL(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type LABEL. This data type is provided only for special purposes for Fujitsu System Software Development and is therefore not described here.
TYPE = *NAME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type NAME. This is defined as a sequence of alphanumeric characters, beginning with a letter or special character.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
UNDERSCORE = *NO / *YES
Specifies whether an underscore character (_) is accepted.
LOWER-CASE = *NO / * YES
Specifies whether lowercase characters are to be retained.
WILDCARD =
Specifies whether wildcards (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5) may be used in place of characters/strings within the name when the command or statement is entered.
WILDCARD = *NO
No wildcards are allowed when entering the operand value.
WILDCARD = *YES(...)
Wildcards may be used.
TYPE =
Specifies whether the string can be a wildcard selector (search pattern) or wildcard constructor. Wildcard constructors are used to build names from strings generated with the aid of a wildcard selector.
TYPE = *SELECTOR
The string can be a wildcard selector; the data type receives the suffix with-wild (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
TYPE = *CONSTRUCTOR
The string can be a wildcard constructor; the data type receives the suffix with-wild-constr (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN =
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard (selector or constructor).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH
The maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard is the same as the length specified by the LONGEST-LENGTH operand (for reasons of compatibility).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = <integer 1..255>
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard.
TYPE = *PARTIAL-FILENAME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type PARTIAL-FILENAME. The definition of the string to be entered is the one given in the BS2000 manual “Introductory Guide to DMS” [7 (Related publications)] for partially qualified file names.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 2..79>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 2..79>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
CATALOG-ID = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the catalog ID may be specified as part of the file name.
USER-ID = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the user ID may be specified as part of the file name.
WILDCARD =
Specifies whether wildcards (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5) may be used in place of characters/strings within the name when the command or statement is entered.
WILDCARD = *NO
No wildcards are allowed when entering the operand value.
WILDCARD = *YES(...)
Wildcards may be used.
TYPE =
Specifies whether the string can be a wildcard selector (search pattern) or wildcard constructor. Wildcard constructors are used to build names from strings generated with the aid of a wildcard selector.
TYPE = *SELECTOR
The string can be a wildcard selector; the data type receives the suffix with-wild (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
TYPE = *CONSTRUCTOR
The string can be a wildcard constructor; the data type receives the suffix with-wild-constr (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN =
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard (selector or constructor).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH
The maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard is the same as the length specified by the LONGEST-LENGTH operand (for reasons of compatibility).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = <integer 2..79>
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard.
TYPE = *POSIX-PATHNAME(...)
Defines the data type of the operand value as POSIX-PATHNAME. The character string entered here must comply with the conventions below:
The following characters are allowed: letters, digits, and the characters ‘_’, ‘-’, ‘.’,and ‘/’ (the ‘/’ always serves as a delimiter between directories and file names). Control characters are not allowed.
A POSIX-PATHNAME consists of POSIX-FILENAMEs, separated by ’/’. The total lengh of a POSIX-PATHNAME must not exceed 1023 characters.
A ‘\’ (backslash) is used to escape metacharacters in all POSIX-specific names; the backslash character itself is not included when counting the length. The metacharacter * is likewise excluded from the count.
Metacharacters are characters used in wildcard patterns. The following metacharacters may be used:
* ? [S] [!S] where S is | matches zero, one, or any number of characters matches any single character matches any single character from the defined character set S matches any single character that is not an element of the defined a set of fixed characters (e.g. abcd) or |
POSIX-PATHNAMEs which contain characters other than those listed above or which begin with a ’?’ or ’!’ must be enclosed within single quotes on input (as in the case of C-STRINGs). Since the single quotes are not a part of the file name, they are removed by SDF in the standardized transfer area or the transferred string. Single quotes that are part of a file name must be duplicated.
To avoid compatibility problems, the C-string syntax should always be used in procedures.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1023>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1023>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
WILDCARD = *YES / *NO
Defines whether metacharacters (see above) may be specified in the name (instead of characters/strings) when entering a command or statement.
QUOTES = *OPTIONAL / *MANDATORY
Specifies whether the path name can (*OPTIONAL) or must (*MANDATORY) be enclosed within single quotes on input.
TYPE = *POSIX-FILENAME(...)
Defines the data type of the operand value as POSIX-FILENAME. The string to be entered here must comply with the conventions listed for POSIX-PATHNAMEs (see "ADD-VALUE Define operand value"), but with the following restrictions:
the slash (/) is not allowed
the maximum length is limited to 255 characters.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).WILDCARD = *YES / *NO
Defines whether metacharacters (see POSIX-PATHNAME) may be specified in the name (instead of characters/strings) when entering a command or statement.QUOTES = *OPTIONAL / *MANDATORY
Specifies whether the file name can (*OPTIONAL) or must (*MANDATORY) be enclosed in single quotes.
TYPE = *PRODUCT-VERSION(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type PRODUCT-VERSION. The product version has the following format:
C, V and the apostrophe are optional characters and are suppressed in the SDF transfer area.
USER-INTERFACE =
Indicates whether the release status of the user interface can or must be specified.
USER-INTERFACE = *YES(...)
The release status of the user interface must be specified.
CORRECTION-STATE =
Indicates whether the correction state can or must be specified.
CORRECTION-STATE = *YES
The correction state must be specified. Specifications for the data type
PRODUCT-VERSION then have the following format:
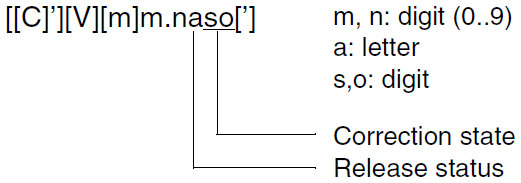
[[C]’][V][m]m.naso[’].
CORRECTION-STATE = *NO
The correction state must not be specified. Specifications for the data type PRODUCT-VERSION then have the following format:
[[C]’][V][m]m.na[’].
CORRECTION-STATE = *ANY
The correction state can be specified.
USER-INTERFACE = *NO
The release status of the user interface and the correction state must not be specified. Specifications for the data type PRODUCT-VERSION then have the following format:[[C]’][V][m]m.n[’].
USER-INTERFACE = *ANY(...)
The release status of the user interface can be specified.
CORRECTION-STATE =
Indicates whether the correction state can or must be specified.
CORRECTION-STATE = *ANY
The correction state can be specified.
CORRECTION-STATE = *NO
The correction state must not be specified. Specifications for the data type PRODUCT-VERSION then have the following format:
[[C]’][V][m]m.na[’].
CORRECTION-STATE = *YES
The correction state must be specified if the release status is specified. Specifications for the data type PRODUCT-VERSION then have the following format:
[[C]’][V][m]m.naso[’].
TYPE = *STRUCTURED-NAME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type STRUCTURED-NAME. This is defined as a sequence of alphanumeric characters. This string may be subdivided into several substrings, joined together by hyphens. The entire string, or, as the case may be, the first substring, must begin with a letter or special character.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..255>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
WILDCARD =
Specifies whether wildcards (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5) may be used in place of characters/strings within the name when the command or statement is entered.
WILDCARD = *NO
No wildcards are allowed when entering the operand value.
WILDCARD = *YES(...)
Wildcards may be used.
TYPE =
Specifies whether the string can be a wildcard selector (search pattern) or wildcard constructor. Wildcard constructors are used to build names from strings generated with the aid of a wildcard selector.
TYPE = *SELECTOR
The string can be a wildcard selector; the data type receives the suffix with-wild (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
TYPE = *CONSTRUCTOR
The string can be a wildcard constructor; the data type receives the suffixwith-wild-constr (see the description of the SDF metasyntax in section 1.5).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN =
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard (selector or constructor).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = *LONGEST-LENGTH
The maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard is the same as the length specified by the LONGEST-LENGTH operand (for reasons of compatibility).
LONGEST-LOGICAL-LEN = <integer 1..255>
Specifies the maximum length of the name matched by the wildcard.
TYPE = *TEXT(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type TEXT. This data type is provided only for special purposes for Fujitsu Software Development and is therefore not described here.
TYPE = *TIME(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type TIME. This is defined as a sequence of one, two or three unsigned numbers, joined together by colons
(<hours>[:<minutes>[:<seconds>]]). The specifications for hours, minutes and seconds must not contain more than two digits. Numbers with less digits may be preceded by leading zeros. The value for minutes and seconds ranges from 0 up to 59.
OUT-FORM = *STD / *BINARY / *CHAR
Specifies the format that SDF uses to represent numbers in the time specification passed to the implementation.
OUT-FORM = *STD
If the transfer is made in a transfer area (see “Format of the standardized transfer area”), then the time specification is passed in the binary format. When passing in a string (for commands that are defined with IMPLEMENTOR= *PROCEDURE(...) or IMPLEMENTOR= *TPR(...,CMD-INTERFACE=*STRING,...), see ADD-CMD), the time specification is passed in the character format.
OUT-FORM = *BINARY
The time specification is passed in the binary format.
OUT-FORM = *CHAR
The time specification is passed in the character format.
TYPE = *VSN(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of data type VSN. SDF is able to distinguish between two types:
VSN with a period:
This VSN must consist of 6 characters. Apart from a single period, only the letters A-Z
and digits 0-9 are accepted. Such a VSN has the format
pvsid.sequence-number,where:
pvsidconsists of 2 to 4 characters andsequence-numberof 1 to 3 characters.This subordinate type of VSN must not be preceded by PUB: PUBA.0 or PUB.02 would be invalid. The period may be the third, fourth or fifth character of the VSN.VSN without a period:
This VSN consists of a string of up to 6 characters. Only letters A-Z, digits 0-9 and special characters $, @ and # are allowed. Such a VSN may start with “PUB”. In this case, the subsequent characters must not be special characters (e.g. PUB@1 or PUB$## will be rejected). Furthermore, VSNs beginning with the string ’PUB’ must be 6 characters long.
SDF makes no further distinctions between public or private VSNs or PUBRES.SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..6>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..6>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
TYPE = *X-STRING(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type X-STRING. This is defined as a sequence of hexadecimal characters (digits 0 through 9, capital letters A through F), enclosed in apostrophes. It is prefixed by the letter X.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..1800>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
TYPE = *X-TEXT(...)
Specifies that the operand value is of the data type X-TEXT. This data type is very similar to the data type X-STRING, but it is not enclosed in single quotes and is not preceded by the letter ’X’.
SHORTEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..3600>
Specifies whether the string must have a minimum length, and if so, what that minimum length is (specified in bytes).
LONGEST-LENGTH = *ANY / <integer 1..3600>
Specifies whether the string is not to exceed a maximum length, and if so, what that maximum length is (specified in bytes).
ODD-POSSIBLE = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether an odd number of characters is accepted.
INTERNAL-NAME = *STD / <alphanum-name 1..8>
Internal operand value name. SDF identifies an operand value by means of this name. Unless otherwise specified, SDF-A takes the first eight characters (omitting hyphens) of the data type specified for the TYPE operand. For operand values of the data type KEYWORD, the default value for SDF-A is the first eight characters (omitting hyphens) of the first individual value specified for the VALUE operand.
SECRET-PROMPT = *SAME / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value is to be treated as secret. SECRET-PROMPT= *SAME assumes the setting of the operand to which the defined operand value belongs (see ADD-OPERAND ...,SECRET-PROMPT= , "ADD-OPERAND Define operand"). The input fields for values of secret operands are kept blank, and logging is suppressed.
If SECRET-PROMPT=*NO is specified, the operand value is not treated as secret. If a secret operand is not preset with a secret value, the input field is not kept blank. The input field can be kept blank by entering the ^ character or a value defined using OUTPUT=*SECRET-PROMPT.
REMOVE-POSSIBLE = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value may be deleted (see REMOVE).
DIALOG-ALLOWED = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value is allowed in interactive mode. Specifying YES presupposes that the operand to which the value pertains is allowed in interactive mode.
DIALOG-PROC-ALLOWED = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value is allowed in interactive mode within a procedure. Specifying YES presupposes that the operand to which the value pertains is allowed in interactive mode within a procedure.
GUIDED-ALLOWED = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value is allowed in guided dialog. Specifying YES presupposes that the operand to which the value pertains is allowed in guided dialog.
BATCH-ALLOWED = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value is allowed in batch mode. Specifying YES presupposes that the operand to which the value pertains is allowed in batch mode.
BATCH-PROC-ALLOWED = *YES / *NO
Specifies whether the operand value is offered in batch mode within a procedure. Specifying YES presupposes that the operand to which the value pertains is allowed in batch mode within a procedure.
STRUCTURE =
Specifies whether the operand value introduces a structure.
STRUCTURE = *NO
The operand value does not introduce a structure.
STRUCTURE = *YES(...)
The operand value introduces a structure.
SIZE = *SMALL / *LARGE
Specifies whether, at the MINIMUM or MEDIUM level of guided dialog, the structure is to be integrated into the higher-level form (SMALL), or if a separate form is to be created for it (LARGE).
FORM = *FLAT / *NORMAL
Relevant only for statements and for commands defined with IMPLEMENTOR=
*TPR(...,CMD-INTERFACE=*NEW/*TRANSFER-AREA,...) (see ADD-CMD). If LIST-ALLOWED=*YES is specified, FORM=NORMAL must also be specified. In the default case (*FLAT), the structure is linearized for the implementation in the transfer area, and the operands for the structure are integrated into a higher-ranking operand array. In the NORMAL case, the structure receives its own operand array. In it, the operands are passed for which a higher structure level is defined for RESULT-OPERAND-LEVEL than for the operand to which the defined operand value that introduces a structure pertains (see ADD-OPERAND ...,RESULT-OPERAND-LEVEL=,... and section “Format of the standardized transfer area").
MAX-STRUC-OPERAND = *STD / <integer 1..3000>
Number of operand positions to be reserved in the structured transfer. Unless otherwise specified, the operand array will be made as large as necessary for the structure. However, it may also be made larger to accommodate planned expansions. This operand refers to the structure introduced by the operand value, and is only relevant when NORMAL was specified for the preceding operand.
LIST-ALLOWED = *NO / *YES
Specifies whether a list may be specified for the operand value when the command or statement is entered. This presupposes that the operand to which the value pertains was defined with LIST-POSSIBLE=*YES (see ADD-OPERAND). For statements and commands defined with IMPLEMENTOR=*TPR(...,CMD-
INTERFACE=*NEW/*TRANSFER-AREA,...) and STRUCTURE=*YES with FORM=*FLAT, only LIST-ALLOWED=*NO may be specified.
VALUE =
Specifies which values are permitted as input.
VALUE = *NO
All values corresponding to the operand type are permitted. Limitations exist only insofar as these have been specified in the definition of the operand type (e.g. length restrictions). For operands of the type KEYWORD, NO is not permitted.
VALUE = list-poss(2000): <c-string 1..1800 with-low>(...)
The permissible values are limited to the specified values. In contrast to STANDARD-NAME and ALIAS-NAME, the user may abbreviate the specified values of the type KEYWORD during input. For values of the type KEYWORD, a list of single values is not permissible (a separate ADD-VALUE must be issued for each individual value).
STANDARD-NAME = *NAME / *NO / list-poss(2000):<structured-name 1..30>/<c-string 1..30>
Relevant only for operand values of the type KEYWORD. This specifies the standard name of the operand value, and may be alternatively used when entering the command or statement. It must not be abbreviated when entered. In contrast to an ALIAS-NAME, a STANDARD-NAME must not be deleted and is reserved for Fujitsu Software Development.
ALIAS-NAME = *NO / list-poss(2000): <structured-name 1..30>
Relevant only for operand values of the type KEYWORD. This specifies the alias name for the operand value, which may be alternatively used when the command or statement is entered. It must not be abbreviated when entered. In contrast to STANDARD-NAME, an ALIAS-NAME may be deleted.
GUIDED-ABBREVIATION = *NAME / <structured-name 1..30> / <c-string 1..30>Relevant only for operand values of the type KEYWORD. This specifies the name by which SDF identifies the operand value at the medium help level of guided dialog. Unless otherwise specified, SDF-A takes as GUIDED-ABBREVIATION the individual value entered for the VALUE operand.
MINIMAL-ABBREVATION = *NO / <structured-name 1..30> / <c-string 1..30>
Only for operand values of the type KEYWORD:
Determines the shortest permissible abbreviation for the operand value. Any shorter abbreviation will not be accepted by SDF.
The following should be noted:
Checking against the minimum abbreviation is carried out only after SDF has checked the input for ambiguity. It may thus happen that SDF selects the correct operand value but then rejects it because the abbreviation entered is shorter than the specified minimum abbreviation.
The minimum abbreviation must be derived from the KEYWORD.
The ALIAS-NAMEs and STANDARD-NAMEs of the operand value must not be shorter than the minimum abbreviation if they are an abbreviation of the operand value.
The minimum abbreviation may only be shortened - not lengthened - within a syntax file hierarchy.
NULL-ABBREVIATION = *NO / *YES
Relevant only for operand values of the type KEYWORD defined with STRUCTURE=*YES. It specifies whether the operand value may be omitted in front of the opening structure parenthesis when the command or statement is entered, e.g. an operand value introducing a structure, when there are no alternative values for the operand.
OUTPUT =
Specifies which value is passed to the implementation when OUTPUT=*NORMAL applies (see below).
OUTPUT = *SAME
The value specified for the VALUE operand is passed.
OUTPUT = *EMPTY-STRING
An empty string is passed.
OUTPUT = *DROP-OPERAND
Transfer of the operand is suppressed.
OUTPUT = <c-string 1..1800>
The value specified here is passed.
OUTPUT = <x-string 1..3600>
The value specified here is passed.
OUT-TYPE = *SAME/*ALPHANUMERIC-NAME/*CAT-ID/*COMMAND-REST/*COMPOSED-NAME/*C-STRING/*DATE/*DEVICE/*IXED/*FILENAME/
*INTEGER / *KEYWORD / *KEYWORD-NUMBER / *LABEL / *NAME / *PARTIAL-FILENAME / *PRODUCT-VERSION / *POSIX-PATHNAME / *POSIX-FILENAME / *STRUCTURED-NAME / *TEXT / *TIME / *VSN / *X-STRING / *X-TEXT
Relevant only for statements and for commands defined with IMPLEMENTOR=
*TPR(...,CMD-INTERFACE=*NEW/*TRANSFER-AREA,...) (see ADD-CMD). OUT-TYPE specifies whether SDF changes the data type of the operand value, and if so, in what way, when the value is stored in the transfer area for the implementation (see section “Format of the standardized transfer area”). If not otherwise specified, SDF does not change the data type.
OVERWRITE-POSSIBLE = *NO / *YES
Relevant only for statements and for commands defined with
IMPLEMENTOR=*TPR(...,CMD-INTERFACE=*NEW/*TRANSFER-AREA,...) (see ADD-CMD). OVERWRITE-POSSIBLE specifies whether the operand value entered is overwritten by a value dynamically generated by the implementation (see the DEFAULT operand in the CMDRST and CMDTST macros). The program-generated value must represent a valid operand value. In guided dialog, SDF shows the implementationspecific value in the form.
Example: The value UNCHANGED in MODIFY statements for SDF-A is overwritten by SDF-A with the current value.
OUTPUT =
Specifies whether, and if so, in what way SDF is to pass the operand value entered to the implementation.
OUTPUT = *NORMAL(...)
SDF passes the operand value to the implementation.
AREA-LENGTH = *VARIABLE / <integer 1..3000>
Specifies the length of the field in which SDF stores the operand value for the implementation. The field must be large enough to hold the maximum value which can be entered during execution. If the value specified for AREA-LENGTH is less than the value defined for LONGEST-LENGTH, SDF issues a warning and accepts the value specified for AREA-LENGTH.
There are two possible cases when a value that is greater than AREA-LENGTH and less than LONGEST-LENGTH is analyzed:
Values that are of type C-STRING with LONGEST-LENGTH 32 and which are part of a secret operand are compressed by SDF and stored in a hexadecimal string with the length defined for AREA-LENGTH. This behavior is typically used for passwords. The passwords are compressed with the aid of a hash algorithm and are protected against unauthorized access by their hexadecimal storage format.
Notes:
The same hash algorithm is used as in the HASH-STRING function provided in SDF-P.
The command server or the program that processes the value analyzed by SDF may need to be adapted if the password definition was changed in order to support hash passwords. The hash value returned by SDF may otherwise be rejected by the semantic analysis module of the program or command server.
In all other cases, i.e. those which deviate from case 1, the value is truncated to the length specified for AREA-LENGTH.
LEFT-JUSTIFIED = *STD / *YES / *NO
Relevant only when a fixed length has been defined for the field in which the operand value is stored. LEFT-JUSTIFIED specifies whether SDF stores the operand value in the field left-justified or right-justified. SDF-A changes STD to NO for numeric values and to YES for all other values.
FILLER = *STD / <c-string 1..1> / <x-string 1..2>
Relevant only when a fixed length has been defined for the field in which the operand value is stored. FILLER specifies the character with which SDF pads the field when necessary. SDF-A changes *STD to X’00’ for values of the type X-STRING or INTEGER, and to C’’ (blank) for all other values.
STRING-LITERALS = *NO / *HEX / *CHAR
Specifies whether SDF converts the operand value into the data type X-STRING or C-STRING to be passed on to the implementation. In the default case, SDF does not change the data type. It must then be kept in mind that, for operand values of the type C-STRING, SDF transfers only the content of the string (without the apostrophes and the prefixed C). This operand is valid only if VALUE=*NO is specified.
HASH = *NO / *YES(...)
Specifies whether the input value can be converted to a value with a defined length using a hash algorithm.
HASH = *YES(...)
Is only permitted for operand values of the data type C-STRING which are defined with LONGEST-LENGTH <= 32.
The other operands in the structure OUTPUT=*NORMAL(..) do not format the value until after the hash function has been carried out. The value then has the data type X-STRING and may then contain unprintable characters.
OUTPUT-LENGTH = <integer 2..32>
Length of the value into which the input value can be converted.
OUTPUT = *SECRET-PROMPT
The operand value is not passed to the implementation, but instead causes SDF to request the user to enter one of the alternative values for the operand. The input that follows is then not displayed and is not logged. Prerequisites are:
the operand is defined as secret (see ADD-OPERAND ...,SECRET-PROMPT=*YES)
input is made in unguided dialog or in a foreground procedure
a single value is specified as permissible input for the operand value defined with SECRET-PROMPT (see the operand VALUE=<c-string>; in the normal case it is of the type KEYWORD).
The following case occurs in an application with guided dialog:
The input field for a secret operand set to a value which is not secret, is not kept blank. The input field can be kept blank by entering the defined value with OUTPUT=*SECRET-PROMPT.
PRIVILEGE =
Specifies the privileges assigned to the operand value.
PRIVILEGE = *SAME
The operand value is assigned the same privileges as the operand for which this operand value is defined.
PRIVILEGE = *EXCEPT(...)
With the exception of those defined by *EXCEPT(...), the operand value is assigned all currently defined privileges and all privileges defined subsequently.
EXCEPT-PRIVILEGE = list-poss(64): <structured-name 1..30>
Specifies those privileges that are not assigned to the operand value.
PRIVILEGE = list-poss(64): <structured-name 1..30>
The operand value is assigned only those privileges specified in this list.