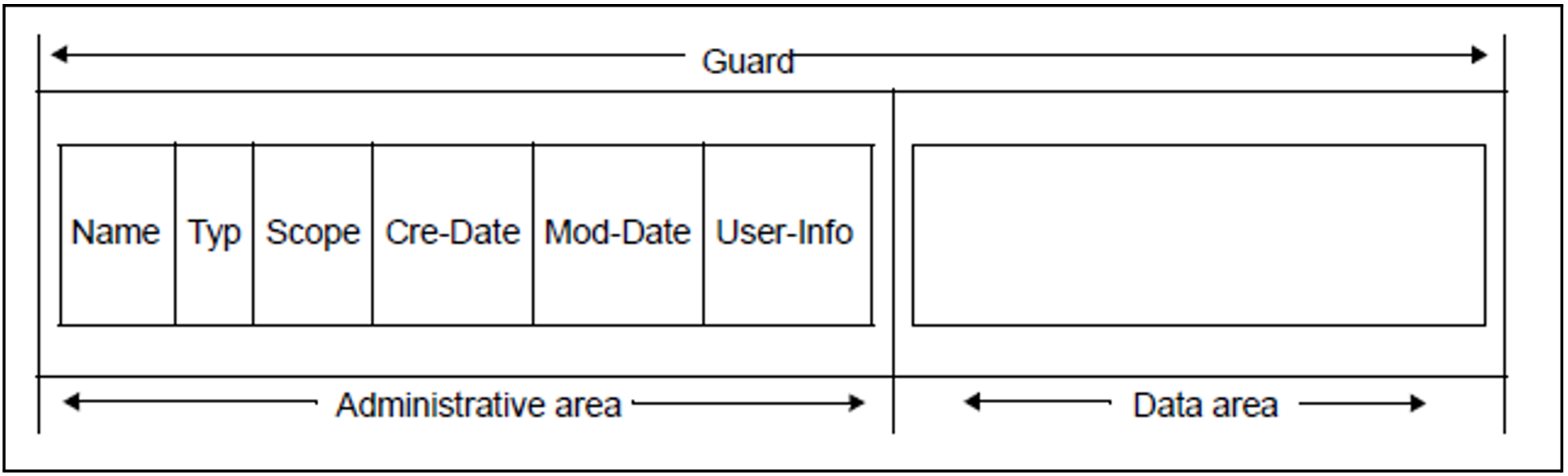
A guard consists of an administrative part and a data part. The administrative part contains administrative information, such as the type of guard in question. The data part contains the specifications of the protective measures to be implemented, such as access conditions or co-owner protection rules.
The guards administration system has no knowledge of the contents or semantic significance of the data part. It does not perform any evaluations relating to the contents of the data part. This is the responsibility of the default condition, default protection and co-owner protection administration systems which also provide the associated commands (described in more detail in the following sections).
The user who sets up a guard is its owner and is able to administer it. However, it is also possible to set up a guard so that it can also be used by other users to protect their objects. User IDs that have the GUARD-ADMINISTRATION privilege are co-owners of all of the guards in the system. They are therefore able to administer them and change their contents in the same way as their owners.
The guard administration system provides the following commands for management of the guards’ container function:
CREATE-GUARD | Creates a guard of type UNDEF. |
COPY-GUARD | Copies a guard of any type without changing the type. |
DELETE-GUARD | Deletes a guard of any type. |
MODIFY-GUARD-ATTRIBUTES | Renames a guard of any type or modifies its administrative attributes. |
The following diagram presents the structure of a guard which can be administered using the commands listed above:
Meaning of the administrative information:
Name:
User-definable guard name
Type:
Type of guard on the basis of its contents.
Scope:
Specification of the users who can use the guard (USER-ID, GROUP-ID, HOST-SYSTEM).
Cre-Date:
Date on which the guard was created.
Mod-Date:
Date on which it was last modified.
User-Info:
User-definable additional information.