There are two aspects involved in checking TSOS co-ownership:
checking the system environment
checking the TSOS co-owner accesses
Checking the system environment
For the purpose of job processing, tasks are created in the system that use the TSOS privilege in order to execute their jobs (system tasks). The dialog and batch tasks that run under the user ID TSOS also have the TSOS privilege. So as not to interfere with the running of the system, TSOS co-ownership can only be monitored in a very specific system environment. This means that TSOS co-owner accesses are only checked when the task under which they are executed has the following attributes:
It is of the type DIALOG or BATCH.
ANDIt runs under the user ID TSOS.
ANDIt has the TSOS privilege.
Unrestricted TSOS co-ownership rights apply to every other task, regardless of whether or not restricted TSOS co-ownership has been specified.
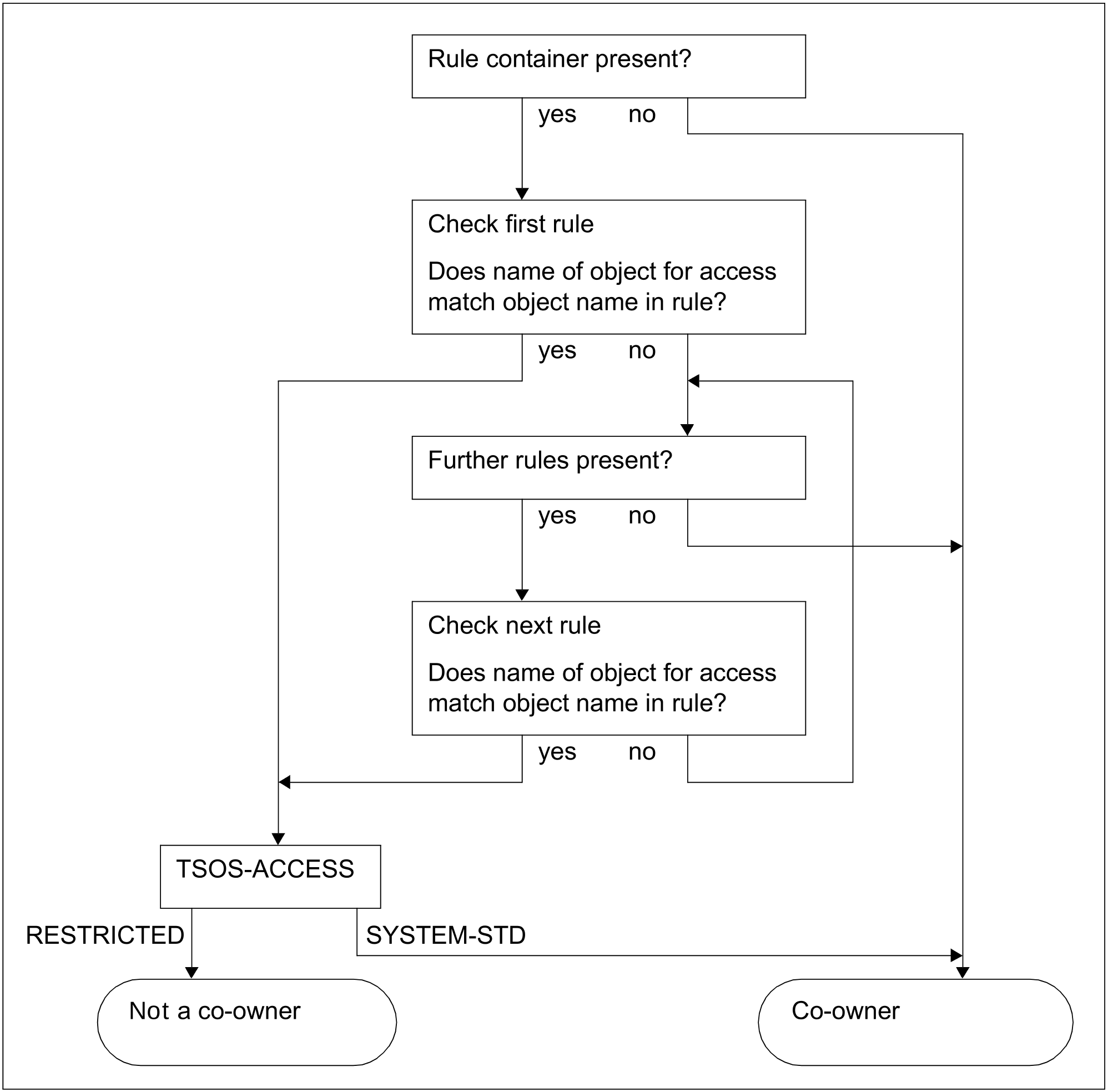
Checking the TSOS co-owner accesses
The following figure illustrates the logic of the co-owner protection checking process for the user ID TSOS:
Figure 22: Logic of the co-owner protection check for the user ID TSOS
CAUTION!
To check TSOS co-ownership, active rule containers for co-owner protection must be read and evaluated within the system. If a system error that prevents the required check from being carried out occurs during such a read operation, the user TSOS retains his or her co-administration rights.
.