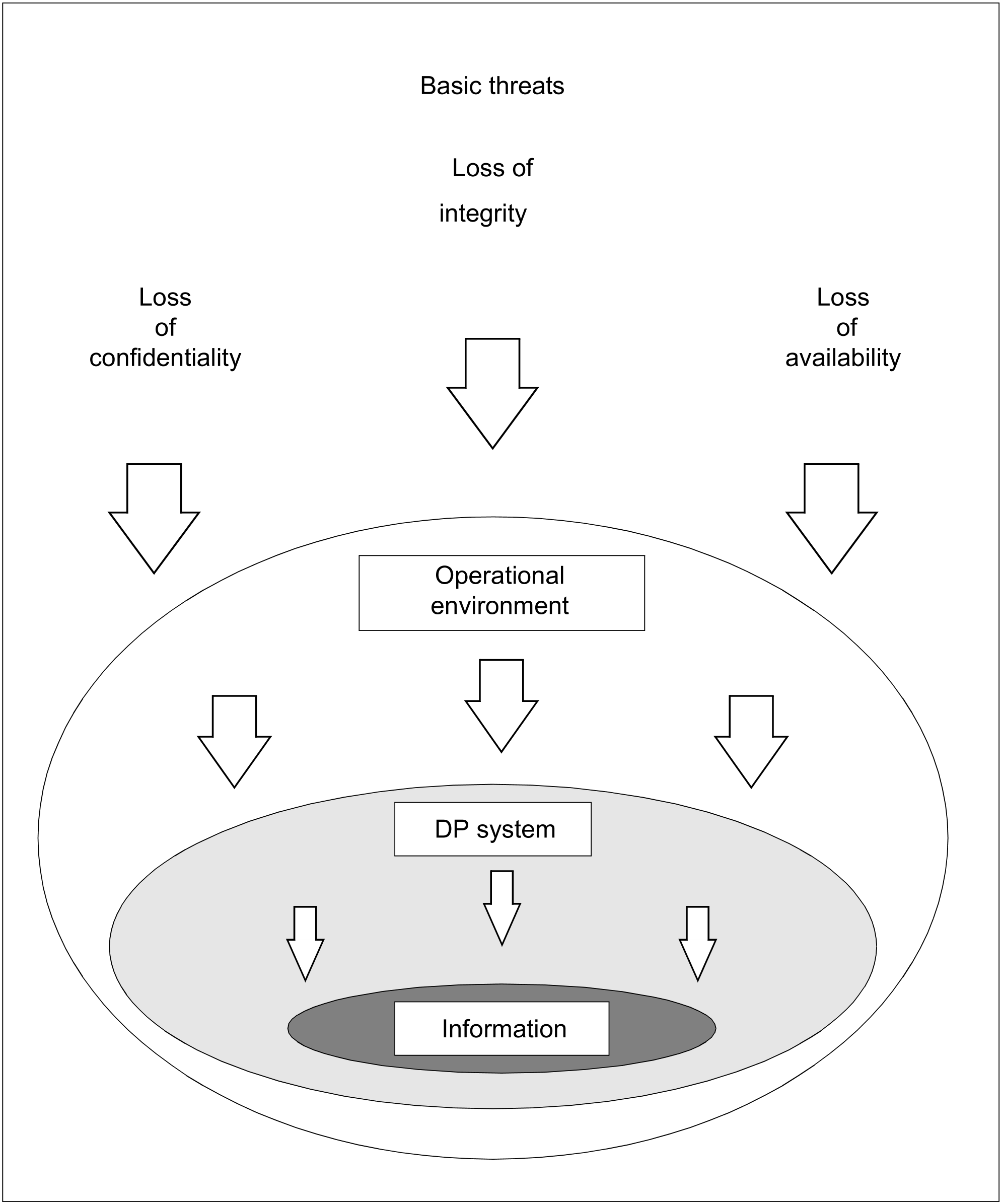
Three basic threats to the security of a DP system can be distinguished; these threats are contingent on the function which the system serves, its operational environment and the sensitivity of the data stored in the system (see figure 1):
loss of confidentiality
loss of integrity
loss of availability
In order to optimize data security it is vital to reduce or, ideally, completely eliminate these basic threats by means of appropriate measures applied within the operational environment of the DP system as well as within the DP system itself.
Figure 1: Basic threats to DP systems
Loss of confidentiality
The confidentiality of the data stored in a DP system is guaranteed if the possibility of unauthorized access to the data can be excluded, i.e. if unauthorized persons can be effectively prevented from obtaining information. Loss of confidentiality means that there is no guarantee that the stored data can be handled with the care required by its confidential character.
As a matter of principle, access to confidential data must be restricted to persons who require this data in order to carry out their work or who have been granted a special access authorization. Effective access control mechanisms and encryption are two examples of how the risk of unauthorized access to information can be significantly reduced in an operating system.
Loss of integrity
The integrity of data stored is guaranteed if the data is
complete
uncorrupted
correct
In this context, data is considered to be complete if all required information is available whenever the data is processed.
The data is considered to be uncorrupted if it has been stored without errors.
The data is considered to be correct if it is an error-free reflection of the reality it describes.
Loss of integrity can be caused by errors or unauthorized modification of data. The rigorous application of access control mechanisms contributes to safeguarding the integrity of stored data.
Loss of availability
The availability of a DP system is guaranteed if full use can be made of all information stored and of all system functions (hardware and software components) whenever required. Loss of availability can be caused by errors or unauthorized intervention in the hardware or software configuration. The application of effective system and data access control mechanisms therefore also serves to increase the availability of a DP system.