The rules described below apply to the administration of user IDs and user groups. It is particularly important to remember that the same administrative activities may be subject to different rules, depending on whether they are performed by a group administrator or a global user administrator.
The accompanying examples are intended to illustrate the rules with respect to the most important administrative activities. In each of the examples, only those attributes are described which are relevant to the administrative activity illustrated by the example.
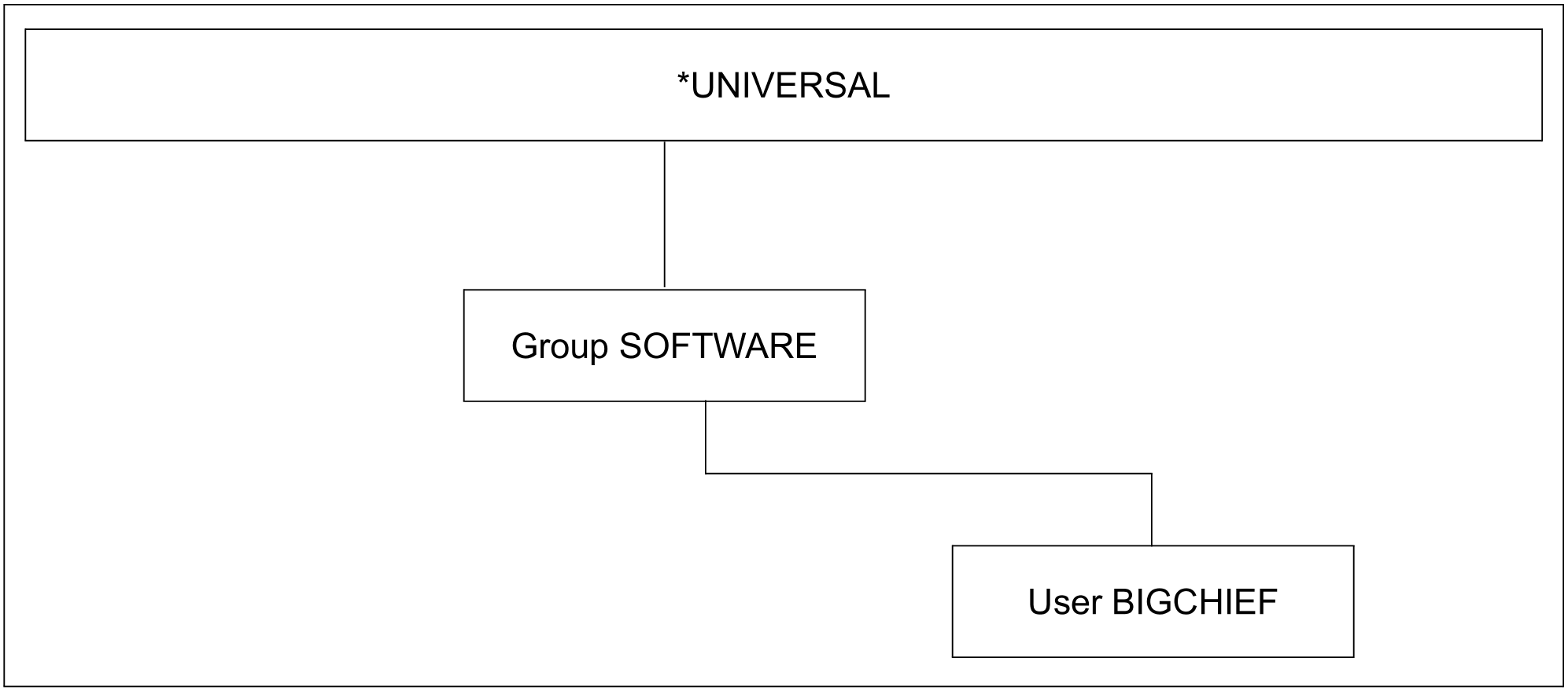
In the following examples, a user group structure for a software house is to be set up and then modified to match changes in the requirements. The initial situation is as follows:
Figure 6: Initial situation for SRPM examples
This initial situation was created as follows:
Generating the group administrator ID BIGCHIEF:
/add-user user-identification=bigchief,public-space-excess=*allowed, -/ profile-id=pro1,pubset=x,default-pubset=x, -/ account-attributes=*parameters(account=acc1)Generating the group SOFTWARE:
/add-user-group group-identification=software,pubset=x, -/ group-administrator=bigchief,add-group-member=bigchief, -/ adm-authority=*manage-groups,max-group-members=100,max-sub-groups=100, -/ public-space-excess=*allowed,add-profile-id=(pro1,pro2), -/ add-account=(acc1,acc2)