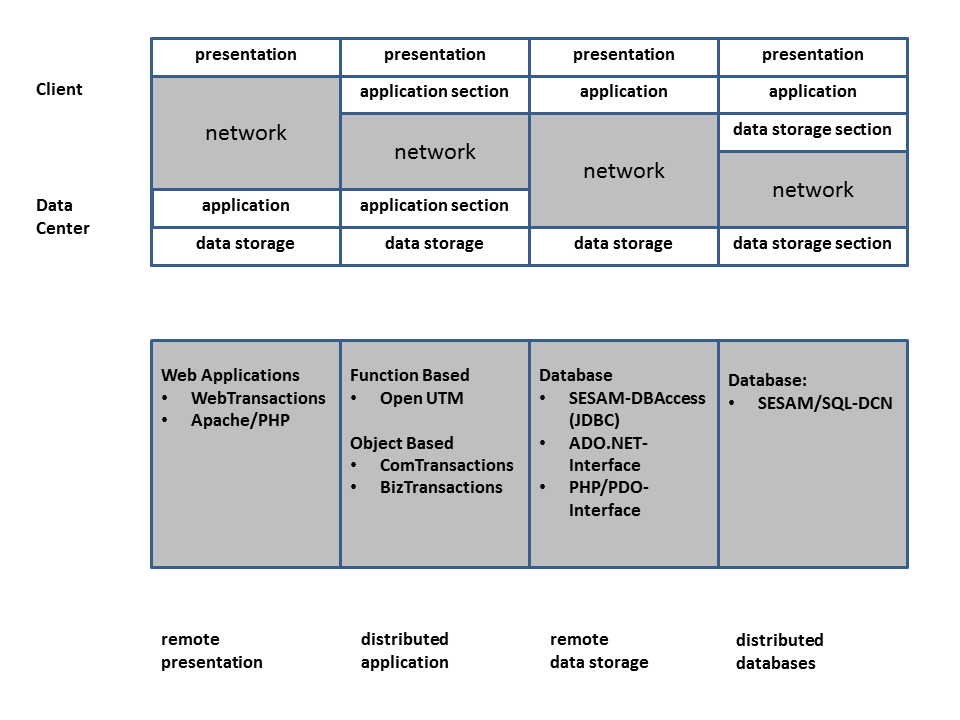
Figure 4: Incorporation in client/server architecture
Remote presentation
Graphical user interfaces use a considerable part of the available computing power for the processing of the display. If this function is transferred to a client system, the data center is relieved of part of its workload and is available for performing other tasks. This combines the qualities of an intelligent graphical workstation and a Data Center. The user can then access local and remote applications which all have the same “look and feel”. Utilization of the client/server option improves productivity and at the same time reduces the load on the Data Center.
Distributed application
With a distributed application, the individual tasks performed by an application are distributed to those systems which are best suited for them. This distribution of tasks means that it is possible to achieve improved overall computer performance.
Remote data storage
In the case of remote data storage, the client application works with a database located on a remote Data Center. This allows data to be stored centrally and thus in a consistent state. At the same time, the Data Center can use all of the available resources for data access, since it has no need to control either the application or the presentation.
Distributed databases are a special form of remote data storage.
Distributed databases
Distributed databases allow the structure of the organization to be reflected by the way in which the data is stored, e.g. in terms of headquarters and branches. The data is stored on the servers on which it is most frequently needed. This has the effect of alleviating the bottleneck caused by the network. This is of particular importance if public networks, which generally only support lower transfer rates, are used. This also means that data transfer costs are kept low.
SESAM/SQL provides additional components in client/server architectures with “remote data storage” and “distributed databases”.