There is an agent for the SNMP management of SESAM/SQL databases in BS2000 named SESAM/SQL agent. This subagent supplies information on SESAM databases and SESAM-DBHs and works on outputting data from the performance monitor SESMON. The SESAM/SQL agent is described in detail in the manual "SNMP Management (NET-SNMP) for BS2000".
This section provides a short introduction to the structure of an SNMP installation for BS2000 and then discusses the use of the SESAM/SQL agent.
Structure of an SNMP installation in BS2000
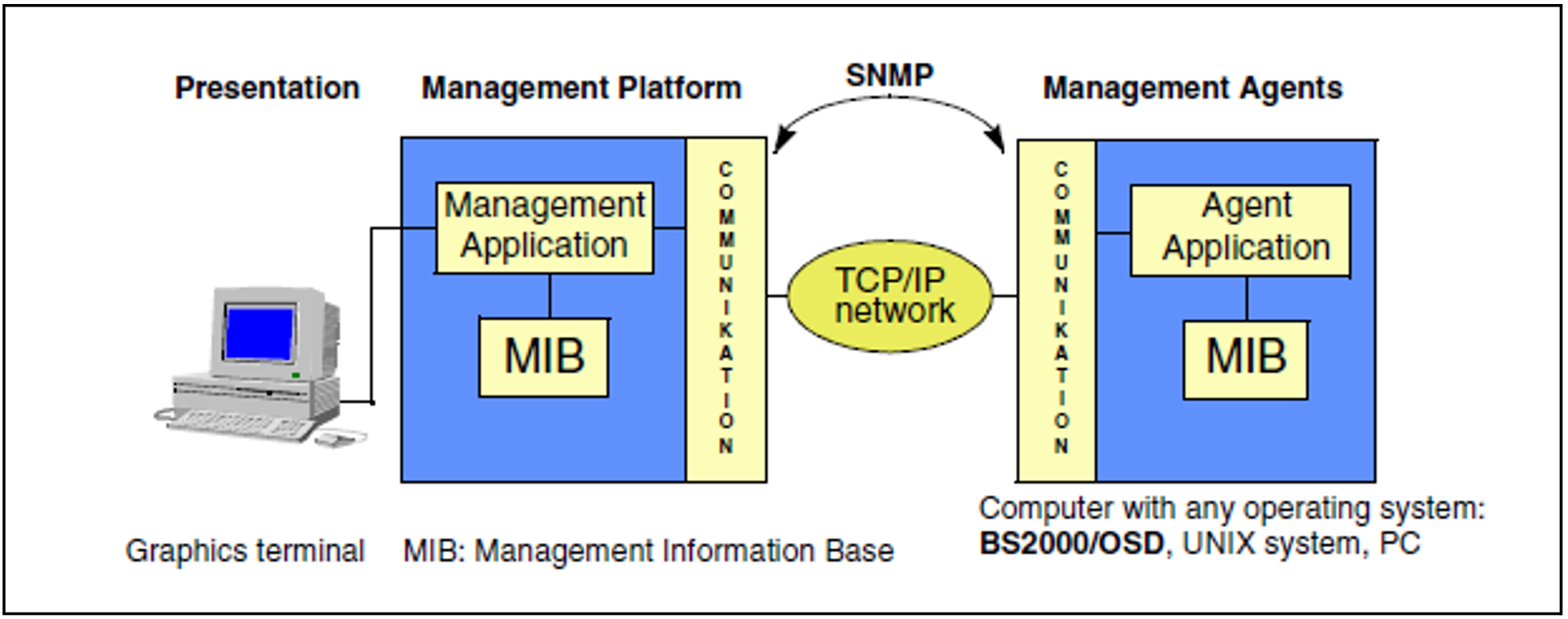
SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol and was developed as a protocol for network management services in the TCP/IP internet. SNMP’s range of application has since been extended to include system management, application management and even management of middleware products such as databases and transaction monitors. Similarly to TCP/IP, the name SNMP does not just stand for the protocol but for the entire management system which is based on SNMP. SNMP employs a client/server architecture, where the management platform is the client and the management agents are the servers.
Figure 9: Communication between management platform and agents via SNMP
The SNMP manager (Management Application) is the software which generates the requests to the individual agents and sends them via SNMP to the corresponding agents. The SNMP manager displays the information received from the agent.
An SNMP agent (Agent Application) is the software which receives, executes and responds to the requests sent by the SNMP manager. For the SNMP management in BS2000 there is an SNMP agent available which is structured according to a master-subagent principle.
The master agent centrally performs basic tasks such as processing of the SNMP protocol, safety functions, work distribution, etc. Each subagent is only responsible for a specific subarea of the monitored components. The subagent communicates with the master agent.
In the Management Information Base (MIB), the management-specific objects of the relevant component are defined and the object attributes are described. The MIB therefore forms the basis of the communication between the management platform and an agent.
You will find further information in the manual “SNMP Management (NET-SNMP) for BS2000”.
Prerequisites for using SESAM/SQL agent
The local computer must be embedded in an SNMP environment. This means that the SNMP agent for BS2000 (i.e. the BS2000 master agent) must be active on the computer.
Communication between management platform and SESAM/SQL agent
The task of the management platform is to request the required data via the BS2000 master agent (GET-Request) and to present it. The management platform can define refresh times or request data directly, i.e. refresh the data in the memory pool regardless of the refresh times (SET-Request, MIB fields sesamCnfRecCacheTime or sesamCnfRecUpdate).
The MIB is shipped as part of SESAM/SQL-Server (File “fscSesam.my” in the library SYSLIB.SESAM-SQL.version.SNMP-SA).
The layout of the MIB is based on the layout of the file output from SESMON (see "Layout of output to a file"). You will find information on the individual fields online at the management station.
The statistical data generated by the performance monitor SESMON are supplied via the SESAM/SQL agent to the management platform.
Starting the SESAM/SQL agent in Net-SNMP environment
The SESAM/SQL agent is installed during the installation of SNMP Agents and starts automatically during the startup of the posix subsystem. So a manual start of the agent usually is not needed.
Starting the performance monitors
You start the SESMON performance monitor or monitors which are to operate together with the SESAM/SQL agent as a batch job. In this case you indicate the operand OUTPUT=*SNMP under the statement SET-MONITOR-OPTIONS (see "Start parameters when running SESMON in batch mode").
A performance monitor sets up resources on starting and waits for requests from the SESAM/SQL agent.
Performance monitors and SESAM/SQL agent can be started independently.
How SESAM/SQL agent works
For a description of the working principles of the management platform and SNMP agents work, see the manual “ SNMP Management (NET-SNMP) for BS2000”.
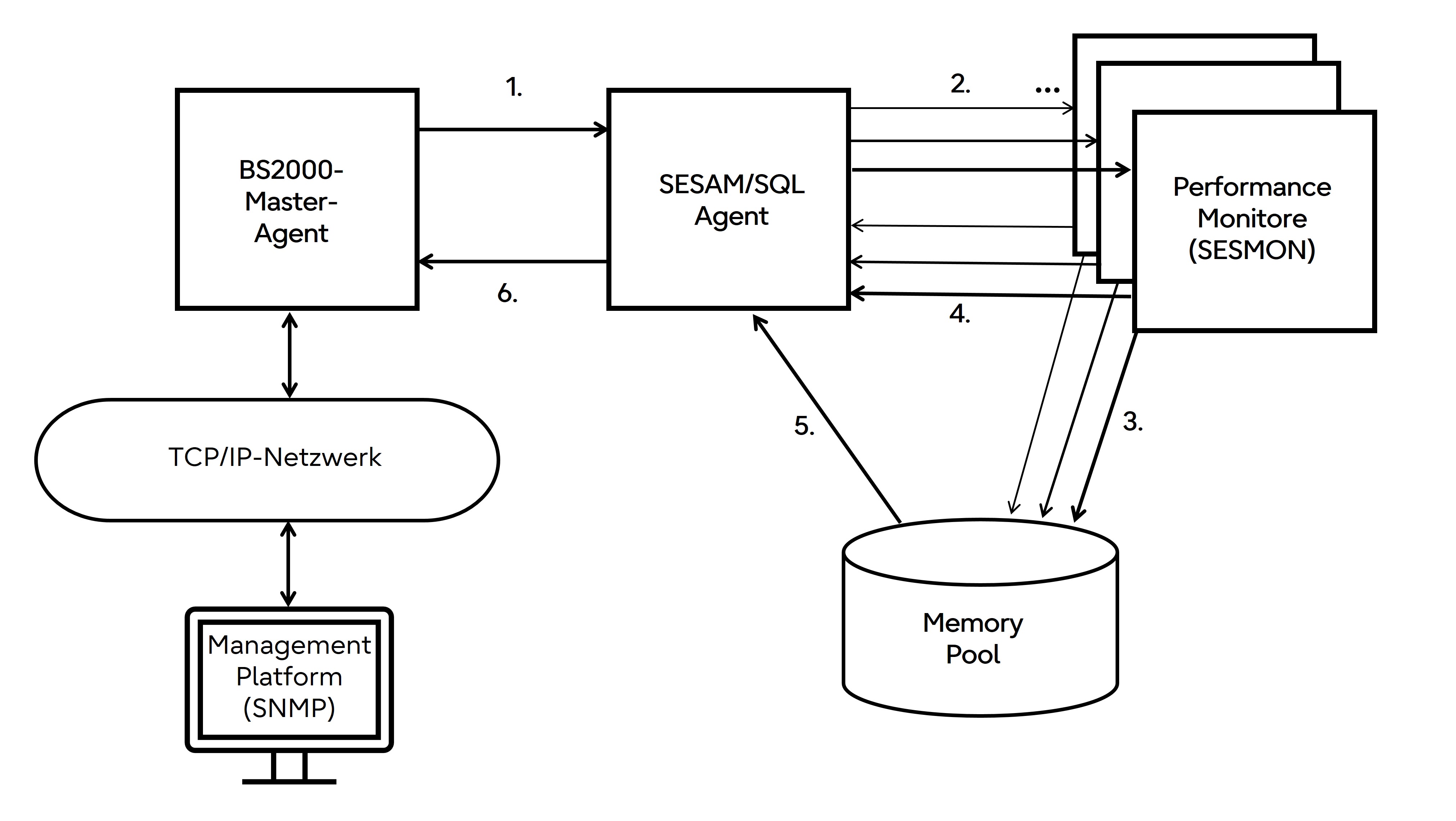
Figure 10: How SESAM/SQL agent works
The SESAM/SQL agent receives via the BS2000 master agent a request to prepare data from a management platform. The request may relate to all SESAM applications on a computer.
The SESAM/SQL agent communicates with one or more SESAM performance monitors via memory pools. Thus data from all SESAM applications on a computer can be requested by the management platform. The SESAM/SQL agent uses the different performance monitors, depending on the configuration and the DBHs.
To start the retrieval of information from the memory pools, the SESAM/SQL agent transmits a signal via P1-Eventing to the appropriate performance monitor.
The performance monitors write the result data independently into the common memory pool.
After the result data have been written, the performance monitors notify the SESAM/SQL agent via SOLSIG of the event identification. The SESAM/SQL agent waits from (2) in P1 eventing.
The SESAM/SQL agent transfers the result data from the common memory pool to the MIB and on to the management platform.
Request end for the SESAM/SQL agent.
Termination of the SESAM/SQL agent in Net-SNMP environment
The SESAM/SQL agent is installed to terminate automatically during the termination of the posix subsystem. So a manual termination of the agent usually is not needed.
Termination of the performance monitors
You terminate the SESMON performance monitor or monitors which operate together with the SESAM/SQL agent as described on "SESMON administration".
A performance monitor is automatically terminated when all the tasks which SESMON is to monitor are completed.