A descriptor area is a storage area that you use to store values or information about the SQL data types for dynamic statements or cursor descriptions.
A descriptor area can be used in the following cases:
The SQL data types of the placeholders in a prepared statement or cursor description can be queried and stored in a descriptor area (DESCRIBE INPUT).
The SQL data types of the derived columns of a prepared SELECT statement or cursor description can be queried and stored in a descriptor area (DESCRIBE OUTPUT).
The values for the placeholders in a dynamic statement or cursor description can be transferred from a descriptor area upon execution (USING clause of EXECUTE or OPEN).
The values returned by a dynamic statement or cursor description can be stored in a descriptor area (INTO clause of EXECUTE or FETCH).
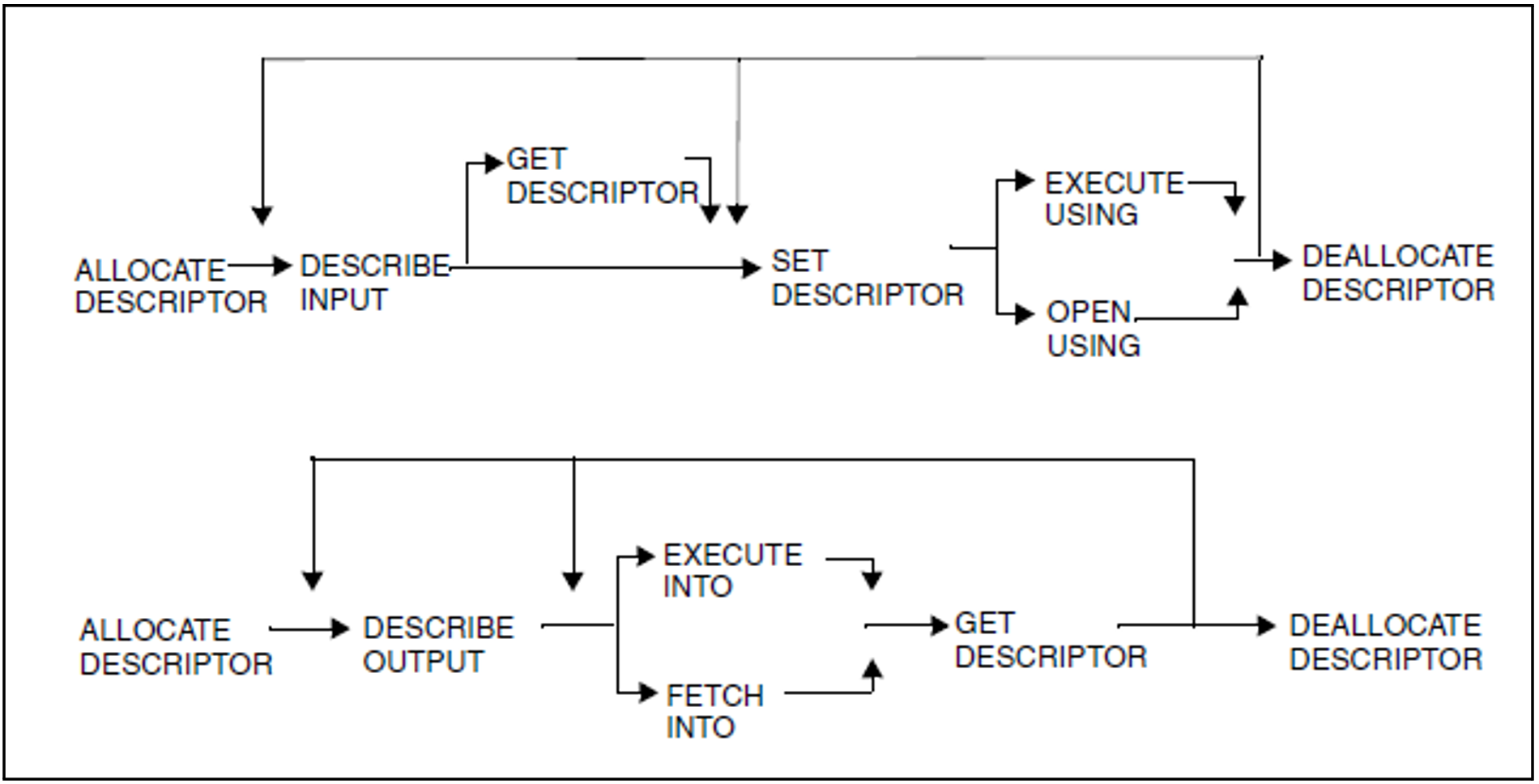
There are a number of SQL statements that use descriptor areas. These statements must be called in a predefined order.
The figure below provides you with an overview of these statements and indicates the order in which the statements can be called (GET/SET DESCRIPTOR can be a series of GET/SET DESCRIPTOR statements).