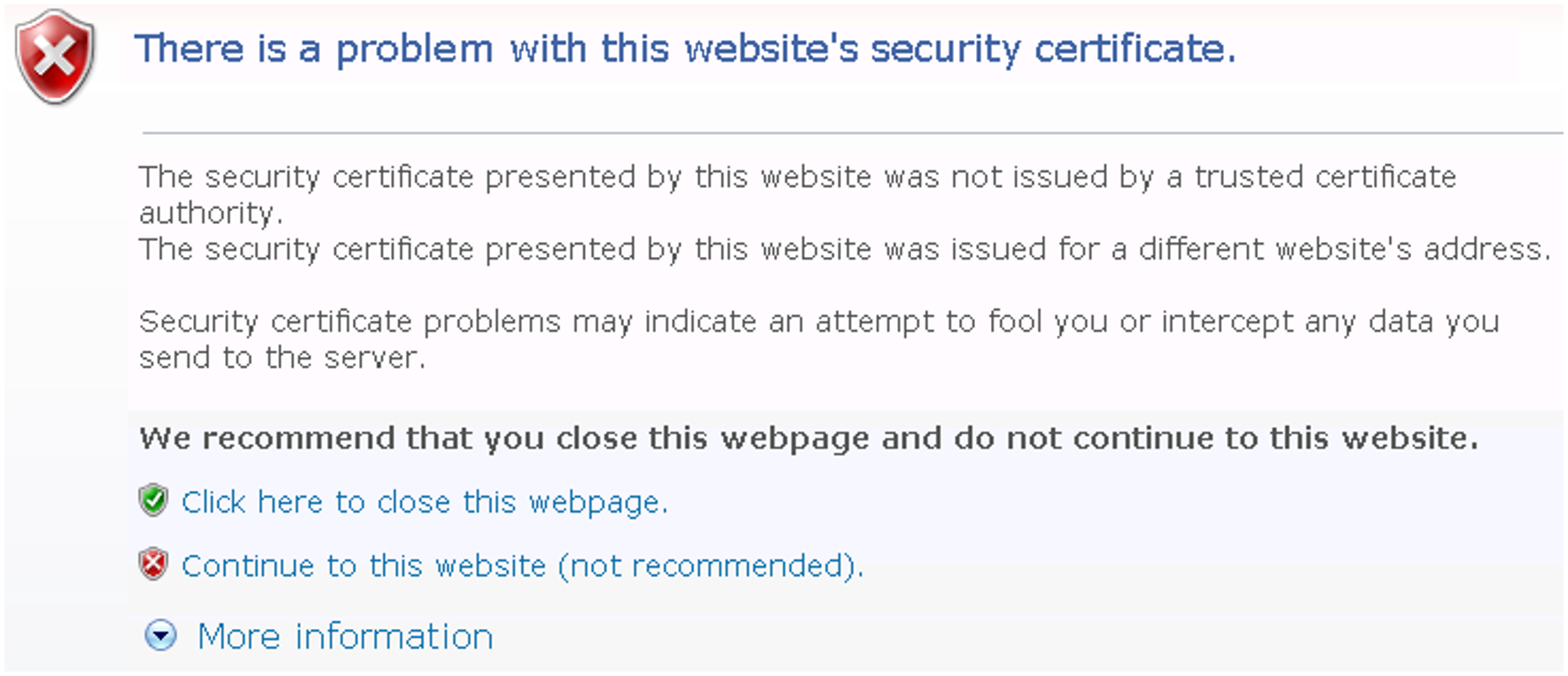
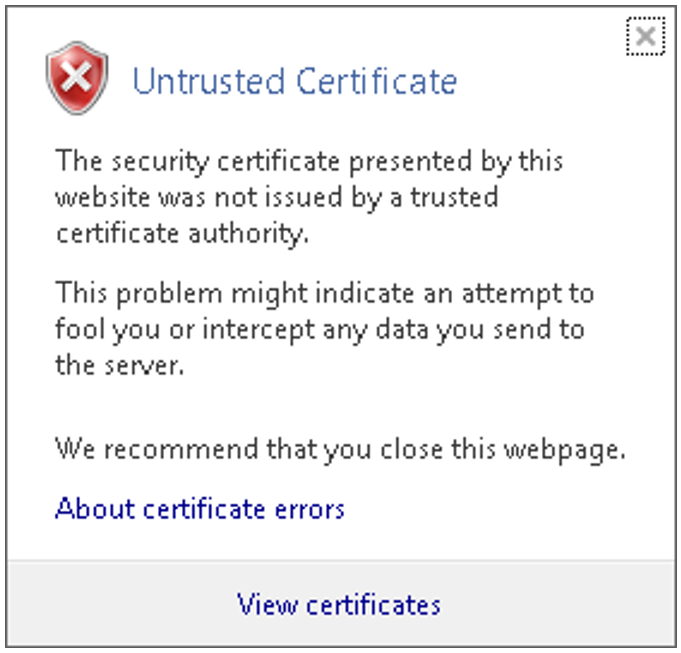
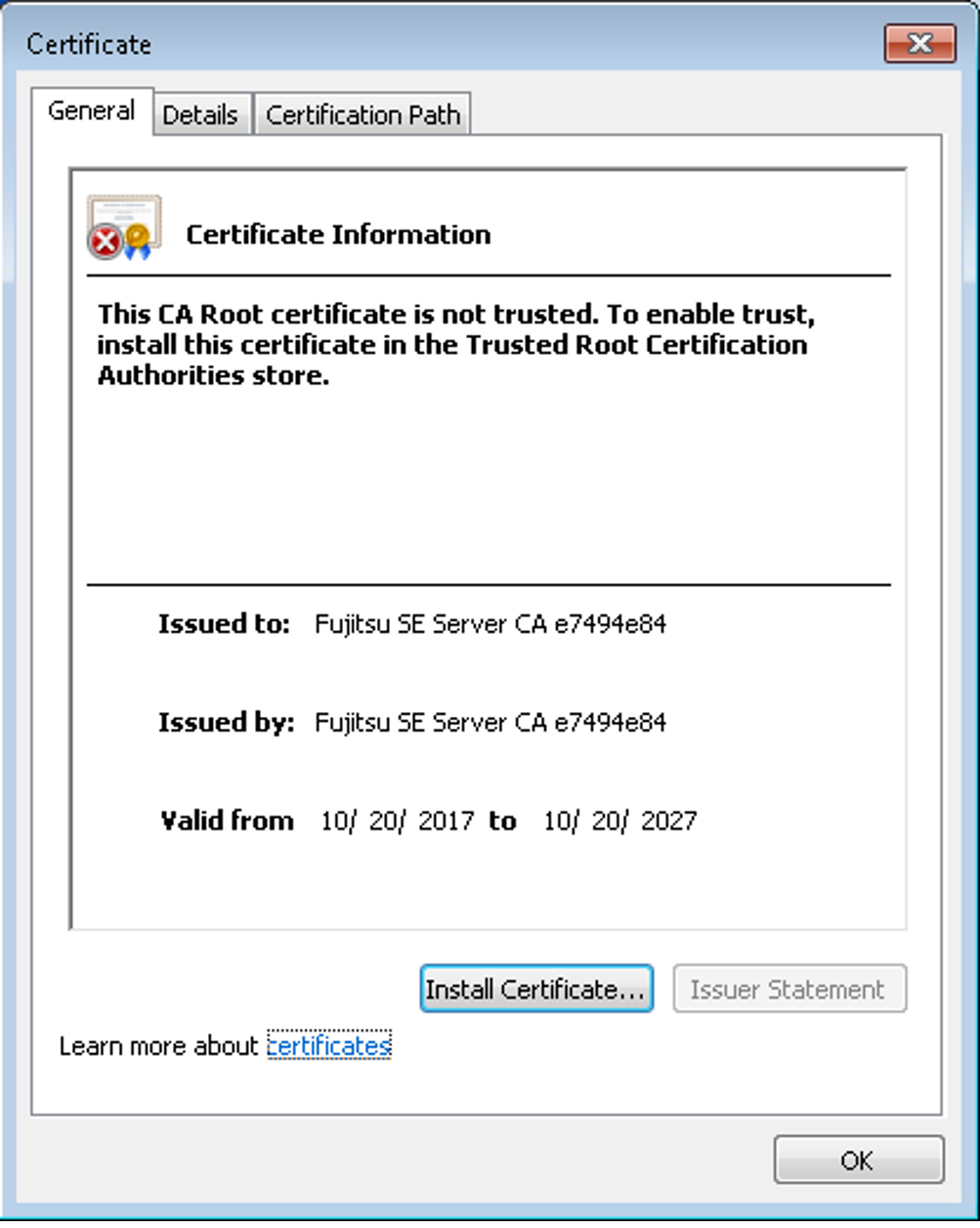
If the web interface called uses a self-signed certificate (i.e., for example, the preinstalled standard certificate), web browsers reject the call for the page because, from their viewpoint, the certificate is not trusted. To permit pages of the SE Manager to be loaded in the browser at all, you must either temporarily accept the certificate error or import the certificate permanently in the browser.
The procedure described in principle below is based on Internet Explorer Version 11 or higher and differs according to the browser used and the version. You will find details of the specific procedure in your browser‘s online help.
> | Open your web browser. |
> | In the browser window call the SE Manager of the required system. The web browser reports a certificate error. |
> | Confirm that the website should be loaded. You are shown the login page. The browser‘s address bar displays Certificate error as a warning. The certificate has now been temporarily accepted for this session, and you can now work with the SE Manager of this system. |
To prevent this browser message from being displayed in future, you can also import the certificate.
> | Click Certificate error in the browser‘s address bar. You are shown information about the potential security risk, and About certificate errors enables you to view more detailed information in the browser’s online help. |
> | Click View certificates. Check the certificate (further details are provided on the Details and Certification Path tabs). |
> | Click Install Certificate. The certificate import wizard starts and guides you through installation of the certificate step by step. You have to explicitly select "Trusted root certification authorities" as certificate memory (for details, see "Security Manual" [7]). |
Alternatively or for other browsers, you can also download and install the CA certificate, see "Uploading and activating a customer-specific certificate".