SNMP integration of the SE Server
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a communication protocol for network, system and application management and enables the SE server to be monitored over a LAN. From a management station (customer's own computer), a system monitoring application can communicate with the SNMP agent present on the MU.
You administer central SNMP integration of the SE server using the SE Manager on the Management Unit. In the case of an SE server configuration with several MUs, redundant SNMP integration is recommended: The MUs must be integrated independently of each other in order to be used for SNMP monitoring, with the same functionality for the same SNMP integration.
The preconfiguration on MU, HNC and SU x86 is created in such a manner that you can also use SNMP to monitor the other units of the SE server on the management stations, provided a configuration for SNMP integration exists on the Management Unit (read access, trap receiver).
On AUs, on the other hand, you have to configure SNMP by yourself. The online help of SEM contains instructions.
The following monitoring functions are possible:
Queries
Queries regarding the Server Unit /390 are possible at the MU (see the MIBs provided for this purpose).
- Queries regarding the individual BS2000 systems and the applications running there are possible (see BS2000's own MIBs and the measures and prerequisites required for SNMP communication in the corresponding BS2000 documentation).
Management stations cannot address the SNMP agent on the SU x86 or HNC directly, but only via the MU. The SNMP agent on MU, HNC and SU x86 supports MIB-II and private MIBs for queries.
The host name of the system or the SENET name of the unit must be used for the query - see the examples below.
- Traps
In defined error situations (e.g. status changes) the SNMP agent on the Server Unit x86 or HNC sends traps via the Management Unit to the external management stations.
- The traps generated by applications in the individual BS2000 systems are also forwarded via the MU to the external management stations.
The sender of the trap is always the Management Unit.
In the case of two MUs (integrated in SNMP) in an SE server, traps are sent twice.
MIB files (MIBs) must be used to read and interpret the output.
The traps usually contain neither the trap weight nor the message text. This information can only be read from the MIB.
Therefore at least the following MIBs should be imported at the management station:
/usr/share/snmp/mibs/FUJITSU-SESERVER-MIB.txt/usr/share/snmp/mibs/FUJITSU-SU390-MIB.txt/usr/share/snmp/mibs/FSC-RAID-MIB.txt
At the Management Units and Server Units x86, ServerView RAID periodically checks hardware components. These events are reported by trap, even in good case with the weightNOTIFICATION. Text example of such a successful test: "Patrol Read started" and "Patrol Read finished".
In order for ServerView RAID's traps to be correctly represented by the management station, this MIB must be imported to the management station.- Access to the above MIBs is possible on the Management Unit, e.g. with scp (secure copy) under any administrator ID.
- The corresponding MIBs from BS2000 should be used to interpret the SNMP data from the BS2000 systems. Details can be found in the manual "SNMP Management" for BS2000.
The following examples with standard SNMP commands are intended to illustrate the addressing of the units or systems and the use of the MIBs. In a system monitoring application this is to be done analogously.
- Determining the SE server-specific data:
admin@abgsilver(M): snmpwalk -v 2c -m +FUJITSU-SU390-MIB:FUJITSU-SESERVER-MIB -c seserver abgblack.abg.fsc.net 1.3.6.1.4.1.fujitsu.product.se-server...FUJITSU-SU390-MIB::Model = STRING: "SU710-20"...
- The read community (in this case "seserver") must be configured on the MU to be queried (in this case on abgblack) and allowed for the requesting side (in this case abgsilver).
- The MIBs must be accessible on the requesting side (in this case on abgsilver).
- The OIDs are usually documented in the MIBs.
- Determination of data from an SU x86:
admin@abgsilver(M): snmpget -v 2c -c su1-se1.seserver abgblack.abg.fsc.net sysName.0SNMPv2-MIB::sysName.0 = STRING: abgafrica- As read community <senet-name>.<read-community> has to be specified, “
su1-se1.seserver” in this case.
- Determination of openSM2 data from a BS2000 system:
admin@abgsilver(M): snmpwalk -v 2c -m FJ-OPENSM2-MIB -c D020ZE01.seserver abgblack.abg.fsc.net .1.3.6.1.4.1.231FJ-OPENSM2-MIB::sm2Status.0 = INTEGER: running(1)FJ-OPENSM2-MIB::sm2Version.0 = STRING: "V20.0A04"...- As read community <hostname>.<read-community> has to be specified, “
D020ZE01.seserver” in this case.
SNMP integration of the SE server via SEM
> Select Hardware -> Units -> [<se server> (SE<model>) ->] <unit> (MU) -> Management, SNMP tab:
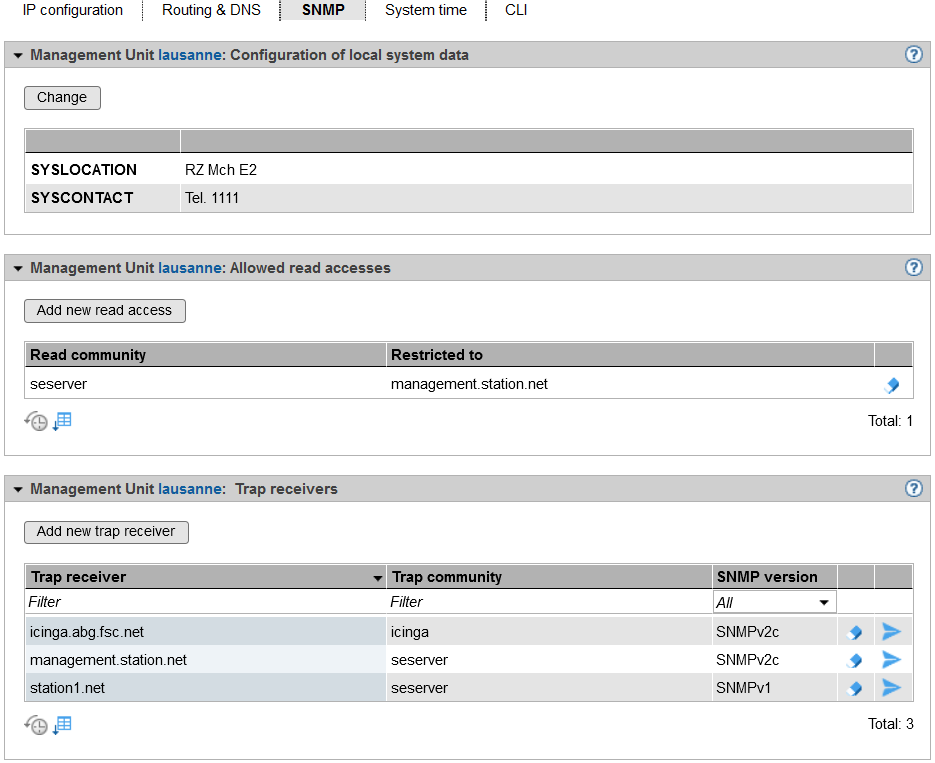
Example of an SNMP configuration
The SNMP tab displays information for the selected MU on the configuration of the local system data, allowed read accesses, and trap receivers.
The following functions are available in the SNMP tab:
- Changing local system data for SNMP
Click on the Change icon in the Configuration of local system data group and make the changes to the system file in the following dialog.
Hints:
The SE Manager displays the SYSLOCATION in the header line.
In a management cluster, SYSLOCATION should match the location of the SE server of the unit.
- Adding or removing allowed read accesses
In the Allowed read accesses group select one of the following procedures:
> To add a new read access, click Add new read access, and confirm the action after entering the necessary information.
You can restrict the read access to a management station by specifying its host name or IP address.
> To remove a read access, click the Remove icon by the required read access and confirm the action.
- Adding or removing trap receivers
In the Trap receiver group select one of the following procedures:
> To add a trap receiver, click Add new trap receiver, and confirm the action after entering the necessary information.
> To remove a trap receiver, click the Remove icon by the required trap receiver and confirm the action.
- Sending a test trap
> To send a test trap, click the Send test trap icon by the required trap receiver and confirm the action.