SnapOPC+ snap sessions can be created on REC source and target units, i.e. snap units can be assigned to both the source and the target unit of a remote copy pair. The snap unit and the source/target unit then form a snap pair in the context of a snap session. The source/target unit is then also the original unit of the snap pair.
A snap unit cannot become an REC original unit./SWAP-REMOTE-COPY can also be used together with SnapOPC+.
When a snap pair consists of a target unit and a snap unit, access to the snap pair via the VSN or pubset ID is not possible because the target unit is generally not readable. If the source unit is attached, the pubset ID of the source unit can also be specified in the snap session commands using the UNIT=*BY-PUBSET(...) operand in conjunction with SELECT=*TARGET-UNIT.
Prerequisites for addressing a snap pair with target unit via the pubset ID or VSN:
The source unit is attached.
In addition, in the case of
/START-SNAP-SESSIONremote copy mode must either be suspended (/SHOW-REMOTE-COPY-STATUSshows the remote copy statusIN-HOLDorERROR) or, if remote copy mode is active, the remote copy pair must be synchronized.
SF pubsets can also be implicitly renamed with /ACTIVATE-SNAP or /START-SNAP-SESSION NEW-PUBSET=<new cat id>. The I/Os to the source unit can be suspended in ongoing operation using the HOLD-IO=*UNTIL-ACTIVATED operand to ensure consistent splitting.
Scenarios for SnapOPC+ in REC configurations
REC can be operated in synchronous and asynchronous copy mode for all mentioned cases, see chapter "Remote replication with REC (ETERNUS DX/AF)".
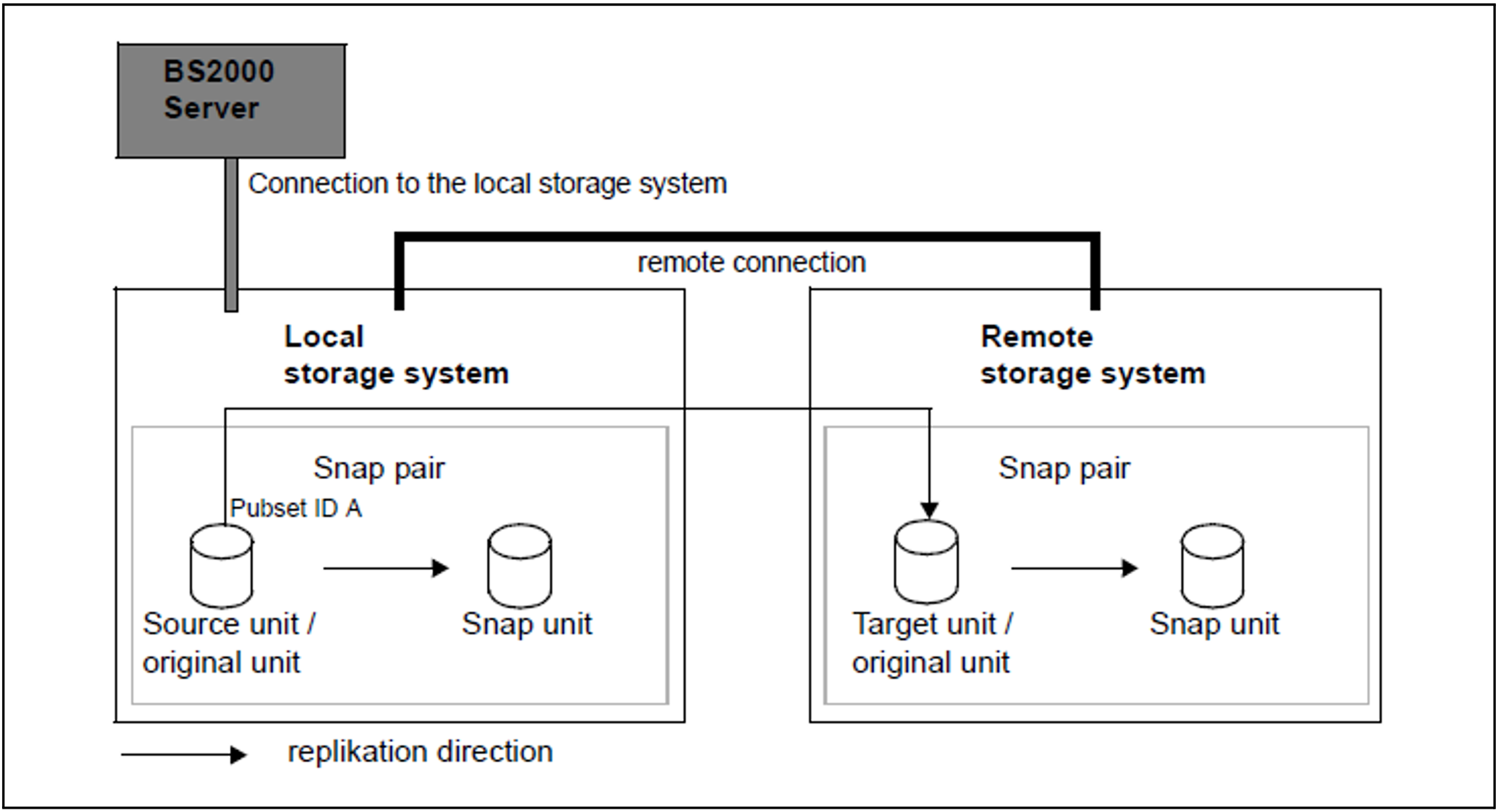
No renaming of the snap units
The source unit and target unit form a remote copy pair (see the figure below).
At the same time each of the two units forms a snap pair:
The source unit with the snap unit of the local storage system
The target unit with the snap unit of the remote storage system
Figure 29: SnapOPC+ with REC, no renaming of the snap units
The server has no connection to the remote storage system and cannot therefore be accessed directly from the server. The target unit cannot be addressed via the VSN or pubset ID. The source unit has pubset ID A.
The snap pair in the remote storage system is activated using /START-SNAP-SESSION UNIT=*BY-PUBSET(PUBSET=A),SELECT=*TARGET-UNIT.
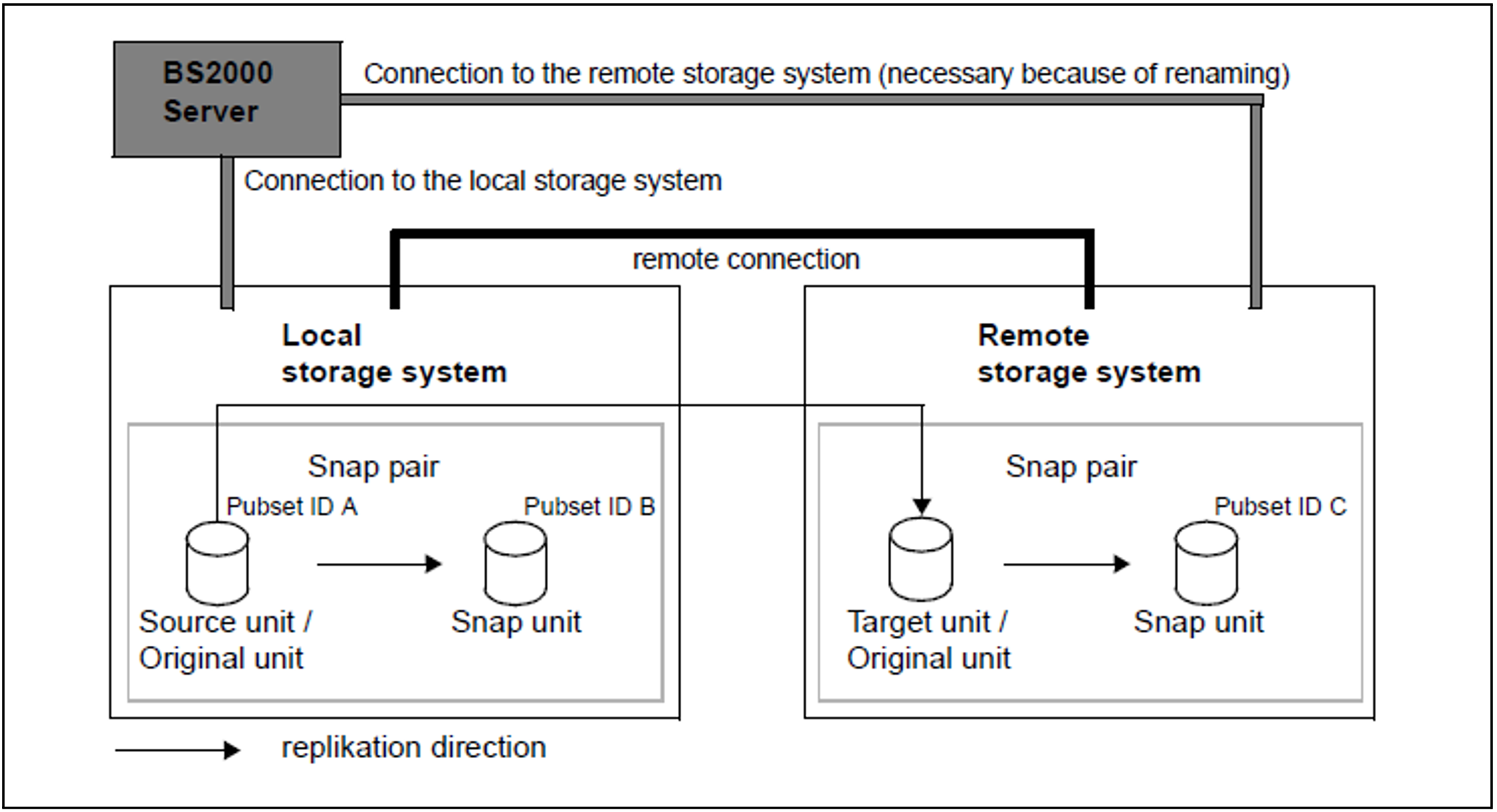
With renaming of the snap units
The source unit and target unit form a remote copy pair (see figure 30).
At the same time each of the two units forms a snap pair:
The source unit with the snap unit of the local storage system
The target unit with the snap unit of the remote storage system
Figure 30: SnapOPC+ with REC with renaming of the snap units in the remote storage system
The server has connections to the remote storage system, which means that it can be accessed directly by the server. The target unit cannot be addressed via the VSN or pubset ID. The source unit has pubset ID A.
/START-SNAP-SESSION UNIT=*BY-PUBSET(PUBSET=A,NEW-PUBSET=B) is used to configure the snap pair in the local storage system. The pubset ID of the snap unit is changed to C.
/START-SNAP-SESSION UNIT=*BY-PUBSET(PUBSET=A,NEW-PUBSET=C),SELECT=*TARGET-UNIT
is used to split the snap pair in the remote storage system, and the pubset ID of the snap unit is changed to C.
This permits the units to be used as follows, for example:
the source unit (with pubset ID A) for the main application
the snap unit of the local storage system (with pubset ID B) for the backup
the target unit as a copy in case a disaster occurs
the snap unit of the remote storage system (with pubset ID C) for evaluations
/RESTORE-FROM-SNAP for an REC target unit can be used only if the target unit is in the READY status, i.e. the remote copy status is IN-HOLD or ERROR and TARGET-ACCESS has the value DIRECT. As a result of this, the last consistent status can, for example, be copied from the snap unit to the target unit in the event of a disaster.