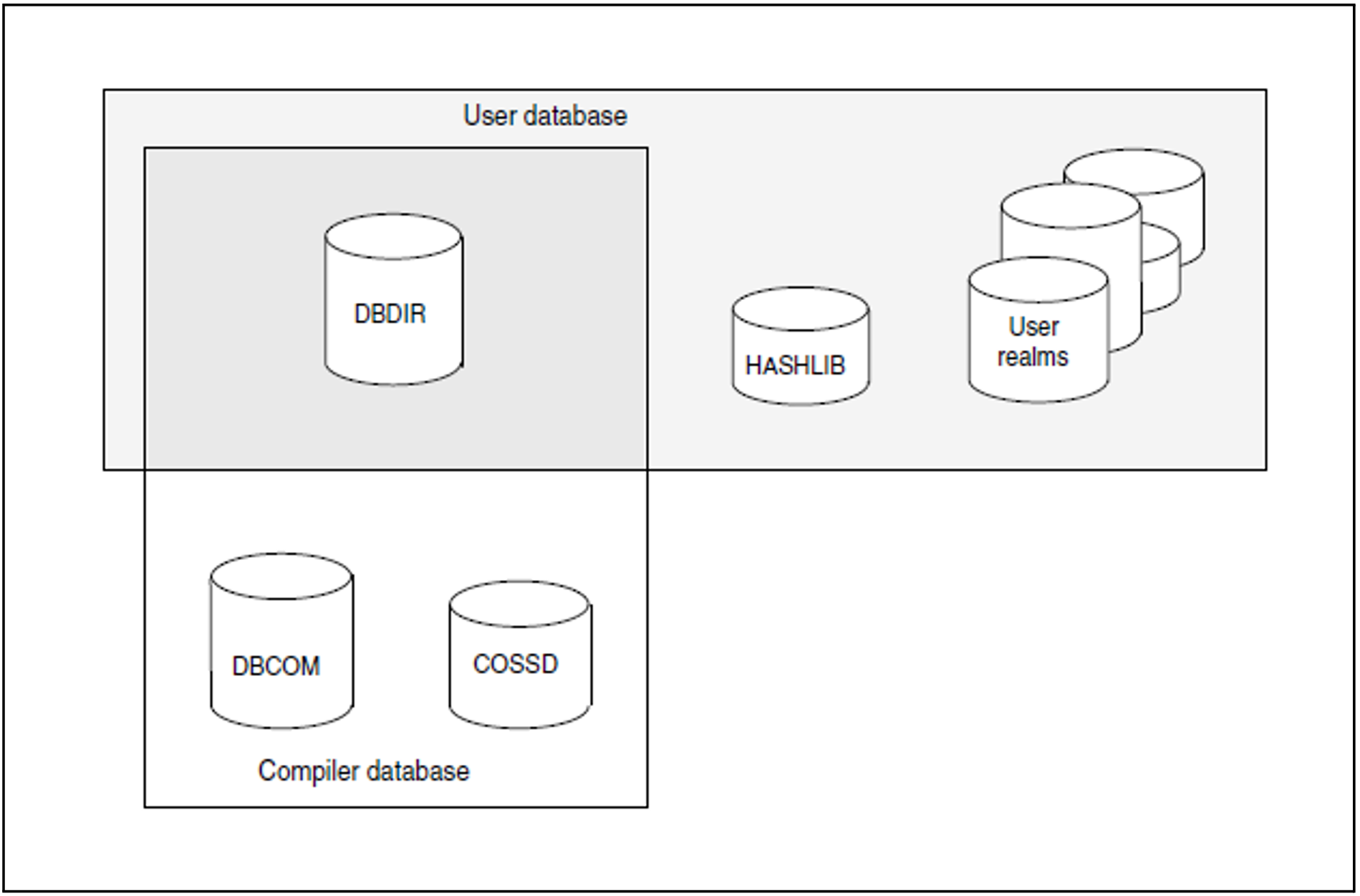
A UDS/SQL database consists of the user database and the compiler database and comprises a number of areas (known as realms).
The user database contains all the realms and files that are needed by the user to store data in the database and retrieve data from it. This includes:
the user realms
the database directory (DBDIR)
the module library for hash routines (HASHLIB)
The compiler database, which is required by the DDL compiler and the COBOL compiler, contains the compiled schema and subschema descriptions. It includes:
the database directory (DBDIR)
the database compiler realm (DBCOM)
the COBOL subschema directory (COSSD)
Figure 5: The UDS/SQL database
In addition to the files belonging to the user and compiler databases, certain other files are necessary for data security and for setting up the connection to the database.
The following is a comprehensive list of the files of a UDS/SQL database:
Database realms
dbname.realmname dbname.DBDIR dbname.DBCOM | original user realm(s) database directory database compiler realm |
Files for database operation
dbname | link file to database for mono-DB operation |
dbname.COSSD | COBOL subschema directory |
dbname.HASHLIB | hash routine storage library |
configuration-name | link file for database configuration |
confname.DBSTAT | DB status file |
confname.DBSTAT.SAVE | duplicate of the DB status file |
confname.SLF | session log file (SLF) |
confname.TEMPO.nnn | temporary user file |
UDS.ENTER.tsn.ST0nn | ENTER files for starting server tasks |
Files for ensuring the security of the database
Shadow database
dbname.DBDIR.copyname
dbname.DBCOM.copyname
dbname.COSSD.copyname
dbname.HASHLIB.copyname
dbname.realmname.copyname
ALOG file
dbname.A.seqno
RLOG files
confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.1
confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.2
confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.1.SAVE
confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.2.SAVE
Files of the database converted with BPGSIZE
dbname.DBDIR.NEW
dbname.DBCOM.NEW
dbname.COSSD.NEW (if BPGSIZE is used to convert to a larger page format)
dbname.realmname.NEW
Syntax rules
dbname
Database name; max. 17 characters in length. Used as a partial qualifier in almost all file names for database realms and files. It has to conform to the following rules:
dbname must be the same for all the files in the database.
dbname must not contain special characters or blanks, and its first character must be a letter.
:catid:$userid.dbname.realmname.copyname may be at most 54 characters in length.
With UDS-D:
dbname must be unique network-wide.
configuration-name
Freely selectable name of the database configuration; in mono-DB operation this name can be identical to dbname. It has to conform to the following rules:
configuration-name may be at most 41 characters in length.
The first seven characters of all the configuration-names in a BS2000 session must be unique network-wide.
The first eight characters of configuration-name must not contain special characters.
confname
the first eight characters of the database configuration defined by the database administrator at the start of the session
With UDS-D:
confname must be unique in the first seven characters.
nnn number of the transaction to which the file has been allocated
nn number of the server task
pool name of the common memory pool
tsn task sequence number of the master task
realm-name
name of a realm of the database;
for user realms: realm name as defined in the AREA clause of the Schema DDL
for database directory: DBDIR
for database compiler realm: DBCOM
copyname
suffix for the shadow database; copyname consists of up to seven characters.
seqno
nine-digit sequence number allocated to each ALOG file
rlogtimestamp
time at which the corresponding RLOG file was opened
The following is a short description of all the files and realms in a UDS/SQL database:
Database realms
User realms (dbname.realmname)
Before loading the realms with data, they have to be defined in the AREA clause of the Schema DDL.
Database directory (dbname.DBDIR)
The database directory (DBDIR) includes the full schema description, all subschema descriptions, and information on access rights.
It also contains information as to whether AFIM logging is switched on or off and whether realms are added or dropped or have been deleted during restructuring. The database handler needs this information in order to handle the user’s database access requests within the area of the used subschema.Database compiler realm (dbname.DBCOM)
The database compiler realm (DBCOM) stores information on the realms, records and sets that the user has defined in the Schema DDL and the Subschema DDL. The DBCOM is required only for compiling the Schema DDL and the Subschema DDL and for creating the DBDIR and the COSSD.
Files required for database operation
Link file (dbname)
Empty link file for the database in mono-DB operation.
COBOL subschema directory (dbname.COSSD)
On compiling the subschema, the DDL compiler writes information on it into the COBOL subschema directory (COSSD). This information is required by the COBOL compiler to compile DB application programs. The COSSD provides the COBOL compiler with the data structure of the subschema and with a table for checking the validity of the DML commands.
Module library for hash routines (dbname.HASHLIB)
The module library dbname.HASHLIB stores the hash routines for the database.
Link file (configuration-name)
Empty link file for the DB configuration in multi-DB operation.
DB status file
(confname.DBSTAT)
(confname.DBSTAT.SAVE)The DB status file is required by openUTM for a restart; it contains information on the transaction that was most recently rolled back in each UDS/SQL/openUTM application. The DB status file is duplicated for data security reasons.
With UDS-D please note:
In distributed processing with UDS-D, this file may also hold information stored when the transaction is committed.
Session log file (confname.SLF)
The session log file (SLF) is required by the DBH for restarts, as it contains information on the databases attached to the configuration and the current values of the DBH load parameters.
Temporary user file (confname.TEMPO.nnn)
If a temporary realm has been declared for (at least) one of the databases in the configuration, the DBH creates a temporary file for each main reference (parallel open transaction). This file stores temporary information.
nnn number of main reference
ENTER files (UDS.ENTER.tsn.ST0nn)
The master task generates one or more ENTER files for server tasks
(UDS.ENTER.tsn.ST0nn).These ENTER tasks are started by the master task using the ENTER commands. If the session is terminated normally, the master task deletes all ENTER files.
Files for ensuring data security
Shadow database
(dbname.DBDIR.copyname)
(dbname.DBCOM.copyname)
(dbname.COSSD.copyname)
(dbname.HASHLIB.copyname)
(dbname.realmname.copyname)You can use the COPY-FILE command to copy the realms and files of the database.
The MODIFY-FILE-ATTRIBUTES commands allow you to rename the database. You can also save the database using the BS2000 utility ARCHIVE.ALOG files (dbname.A.seqno)
The DBH or any updating utility routine logs every update to a page, i.e. the status of the page after the update (after-image) in ALOG files. These ALOG files can thus be used to apply updates to the database.
The shadow database has no ALOG files; however, all changes can be incorporated into the shadow database by using the ALOG files of the original database.RLOG files
(confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.1)
(confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.2)
(confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.1.SAVE)
(confname.RLOG.rlogtimestamp.2.SAVE)The RLOG files are used by the DBH to log information (data) being changed both before the change (before-image, or BFIM) and after the change (after-image, or AFIM) as needed for use in any rollbacks or warm starts that may be required.
Maximum size of UDS/SQL files
UDS/SQL can administer a maximum of 16777214 database pages in a realm. This results in the following limit values for the maximum file sizes:
Database page size | Maximum file size in PAM pages |
2 Kbyte | 16777214 |
4 Kbyte | 33554428 |
8 Kbyte | 67108856 |
Table 7: Limit values for file sizes
UDS/SQL supports of utility routines realm files, temporary files, logging files and work files as LARGE FILEs. Files which, because of their nature, can only be of a limited size are not processed with the LARGE FILE property by UDS/SQL (DBSTAT, COSSD, HASHLIB, parameter files).
The monitor’s output files also do not have the LARGE FILE property.
Files set up as auxiliary files by the UDS/SQL utility routines are not created with BLKCNTRL=PAMKEY so that it is not made implicitly impossible to use them as LARGE FILEs.
The following prerequisites must be fulfilled in the system if the LARGE FILE property is to be used:
Large files may only be used in pubsets that have the property
LARGE-FILES-ALLOWED.Large files cannot be used in the HOME pubset.
Large files cannot be used with BLKCTRL=PAMKEY.
Passwords for UDS/SQL files
UDS/SQL protects the automatically generated files with the default password: C’UDS'BLANK'’.The RLOG file is an exception. The password for the RLOG file, which is made up of parts of the RLOG time stamp, is assigned automatically. The password can only be deleted without password protection in the system ID ($TSOS).