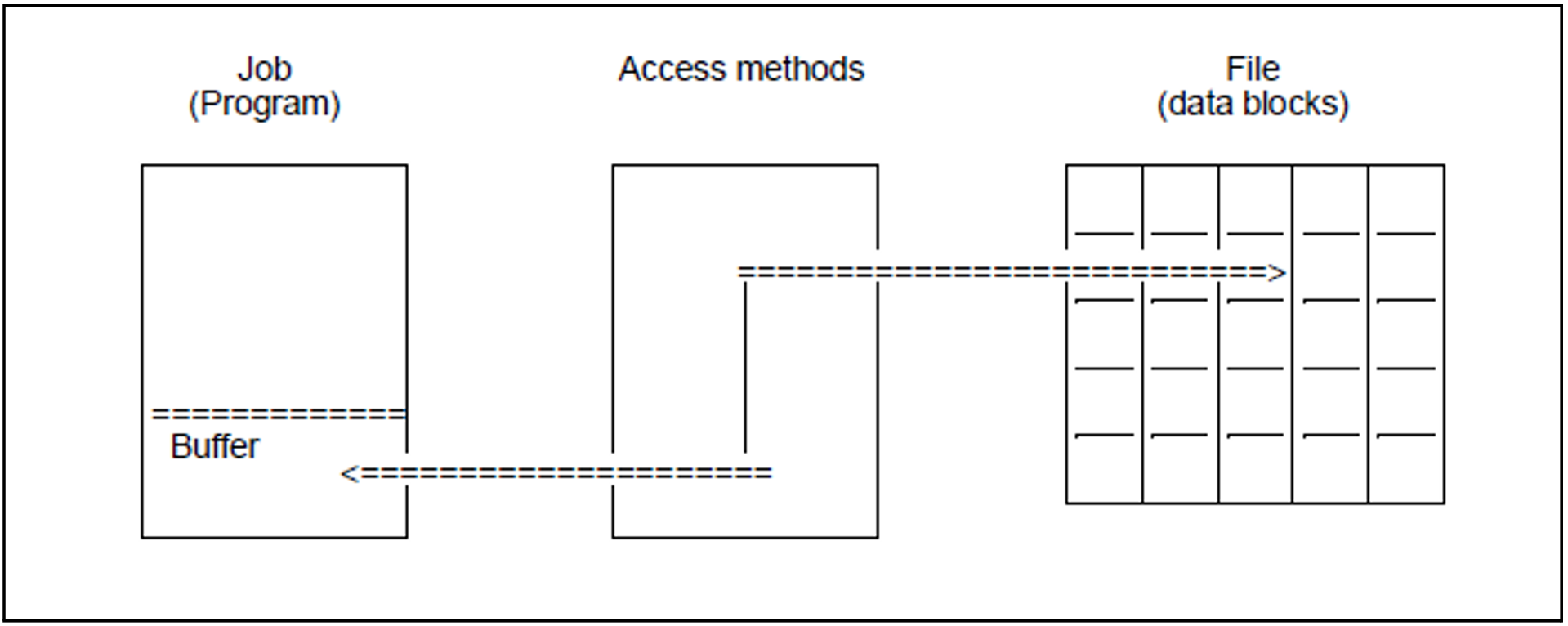
The access methods of DMS transfer data between a file and the address space of a job. Technically, this is a data transfer between the peripheral devices and the main memory of the CPU. DMS handles the devices and the volumes and provides the user with an interface for access to records and/or data blocks.
For access by a user program to the contents of a file, a distinction can be made between record-oriented and block-oriented access and between the operating modes “move” and “locate”.
For all access methods, DMS transfers data blocks between the peripheral device and main memory. The area of main memory in which one or more blocks are stored, or from which blocks are transferred to the peripheral device, is called a buffer. The buffer is part of the address space of the job which initiates the I/O operation. In the case of NK-ISAM processing, the buffers are located in ISAM pools (see "ISAM pools"). For the record-oriented processing of a file in move mode, DMS transfers the records from the buffer to the work area of the program.