Particularly the non-sequential processing of ISAM files tends to produce a high I/O rate. NK-ISAM reduces this I/O rate and enhances the performance significantly by processing the files in appropriately sized ISAM pools which are used to buffer file blocks.
ISAM pools can be created and managed both explicitly by the user using special macros and implicitly by DMS.
Pools opened implicitly by DMS are called standard ISAM pools (see section "Standard ISAM pools").
Pools created by the user are called user ISAM pools (see section "User ISAM pools").
In addition, two areas of application are distinguished for pools:
A task-local ISAM pool (SCOPE=*TASK) is stored in the class 5 storage of the owner task. No other tasks may access this storage - or the ISAM pool. A task-local ISAM pool is consequently only suitable for ISAM files which are opened in SHARUPD=NO mode.
A cross-task ISAM pool (SCOPE=*HOST-SYSTEM) is stored in a privileged data space which all tasks in the system can access. Details on this enhanced concept are provided in section "ISAM pools in data spaces".A cross-task pool is essential for processing ISAM files in SHARUPD=YES mode. It would be possible to edit ISAM files opened in SHARUPD=NO mode in cross-task pools, too. However, for performance reasons (e.g. superfluous serialization) this is not recommended.
SCOPE=*USER-GROUP and SCOPE=*USER-ID are only accepted for reasons of compatibility. Internally, however, they are mapped to SCOPE=*HOST-SYSTEM (cross-task pool).
The commands and macros for managing task-local ISAM pools are also available to RFA (see the "RFA" manual [6 (Related publications)]).
An overview of the ISAM pool macros can be found in section "User ISAM pools".
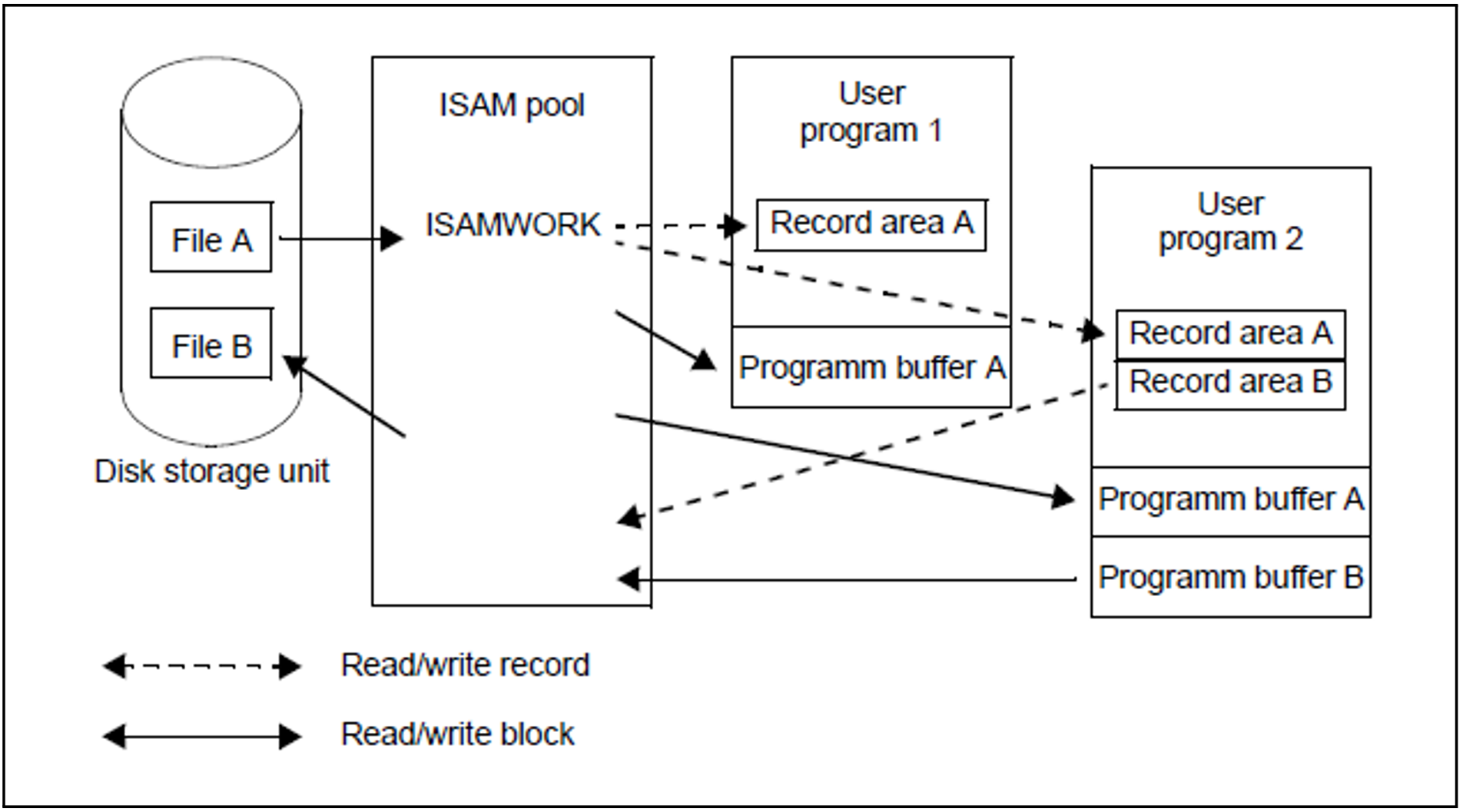
File A is being read by user programs PROG A and PROG B, and file B is being created by PROG B. The ISAMWORK ISAM pool is a cross-task pool.