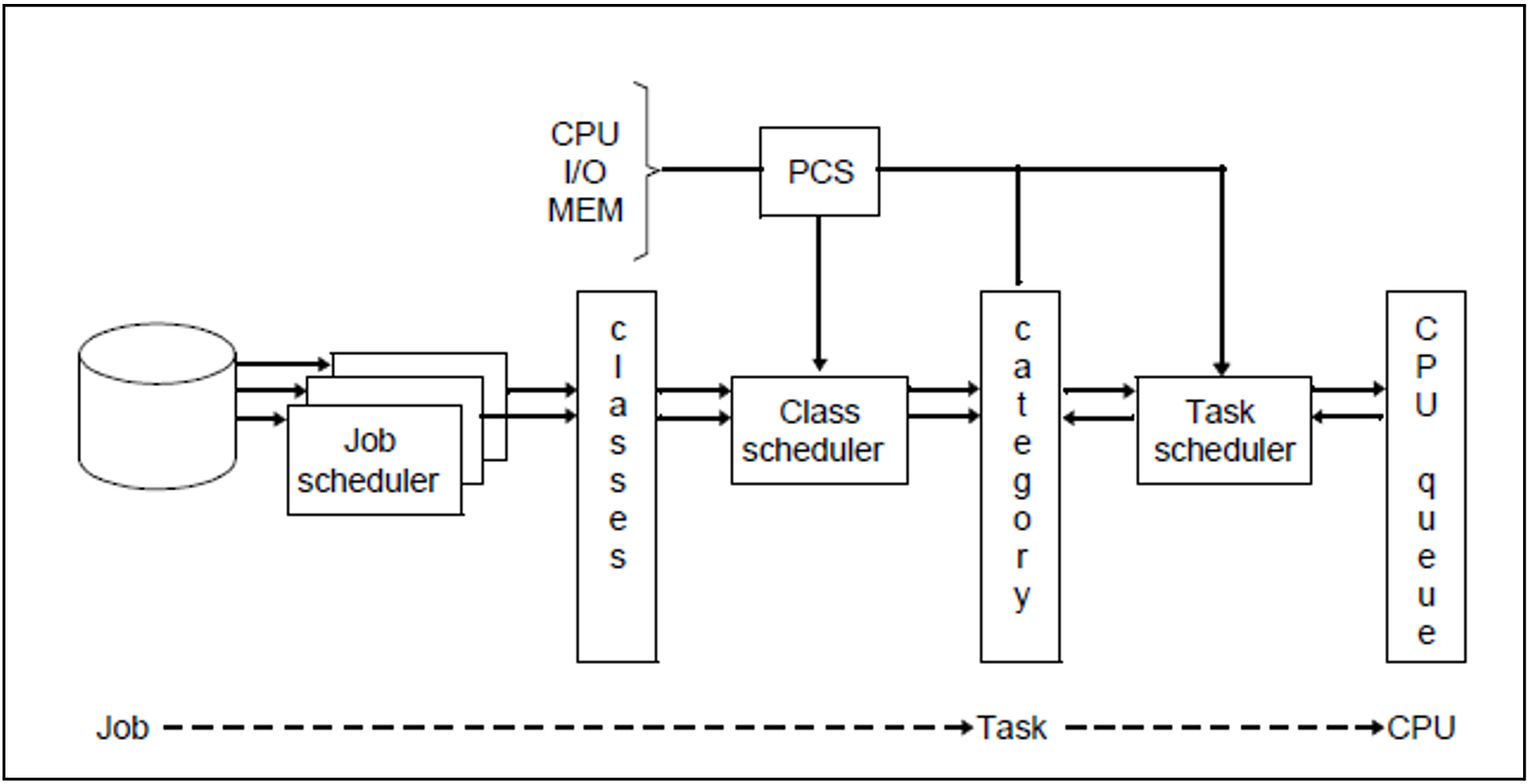
The optional PCS subsystem (Performance Control System) supports systems support in achieving the optimum configuration of the computer system. It enables the performance of a computer system to be distributed among the various task categories and tasks according to user requirements.
Figure 18: Job management – PCS – Task management
In the case of complex mixed mode PCS regulates the various shares of the load in accordance with the customer-specific requirements. At short intervals PCS adjusts the control variables in such a way that predefined optimization strategies (response time/throughput time optimization) and the optimum operating point for these are complied with at all times.
During operation, PCS monitors: the performance requirements of the tasks and categories and the utilization of the CPU, the main memory and the I/O system.
If these variables do not match the setpoint values defined by systems support (PCS option), PCS corrects the performance levels by changing manipulated variables within BS2000 (such as task priority, MIN-MPL and MAX-MPL values of the categories).
When PCS intervenes for control purposes, in the following cases messages are issued on the console. The messages are also logged in the CONSLOG file.
When the job scheduler is made to start no more jobs globally or in a category.
When task activation upon reaching the MAX-MPL value is set.
PCS measures its control variables over periods of around 10 seconds and adjusts the manipulated variables to the current load situation in this period.
PCS works with PRIOR, the task priority control function of which is disabled when PCS is started, and with job management.
For further information on PCS, see the “PCS” manual [36].