Users can only start jobs if they have access to the system. In BS2000, access permissions can be finely regulated, with a careful distinction being made in particular between dialog and batch access. Information about persons with access permissions (such as your user ID and user-specific user rights) must be entered by the user manager in the user catalogs of all the processors in the network. In the access request (e.g. SET-LOGON-PARAMETERS, i.e. request for dialog access for a specific processor), the user identifies himself to the system by means of his user ID. The system then checks whether the user is also really the owner of the specified user ID (authentication) by looking at the LOGON password supplied when the connection was set up and the accounting number supplied.
Access is only ever granted based on the user ID. If a user wants to work with several user IDs, access must be obtained for each of them.
In the MSCF network, a user who wants to use a random number of processors, must usually possess the necessary access permissions for all the processors. The access permissions are checked differently depending on the type of network (see below). When batch jobs are transmitted, it becomes clear that dialog and batch accesses are handled quite separately. The batch access permission is a requirement on the destination processor, whereas the dialog access permission is not.
As a rule, the MSCF network requires access permissions that can be set flexibly and that are guaranteed by the use of the product SECOS (see the user guide “SECOS - Access Control” [16 (Related publications)]).
The following applies to batch access permission in the MSCF network:
The access rules must be entered separately on all the processors in the network. We recommend selecting identical settings on all of the processors and only deviating from this recommendation for a specific purpose.
The access permission is always checked on the destination processor. When a batch job is initiated on another processor, this means that the permission of the batch access is checked on the destination processor based on the entries there.
Where an LCS connection exists, the processors to be linked are given general protection by means of passwords. Before the access check, the right of the user to use services on all processors under his user ID is checked via the LOGON password that is also transmitted (in this example, the right to start batch jobs on any processor). If the password of the job submitter’s user ID does not match the password of a user ID with the same name on the destination processor, the destination processor rejects the job. This password check is not made in the case of a CCS connection. The access permission is checked on the destination processor irrespective of the type of connection.
If the job submitter ID and the destination ID are different, specifications as to the destination ID must be made in the PROCESSING-ADMISSION operand (it contains the user ID, the accounting number and the password, see ENTER-JOB/ENTER-PROCEDURE) commands. Access is approved for the destination ID on the basis of these specifications.
If the batch job is to run under the same ID, the PROCESSING-ADMISSION operand can also be omitted in the case of jobs applicable to more than one processor; the values of the job submitter task apply.
Example
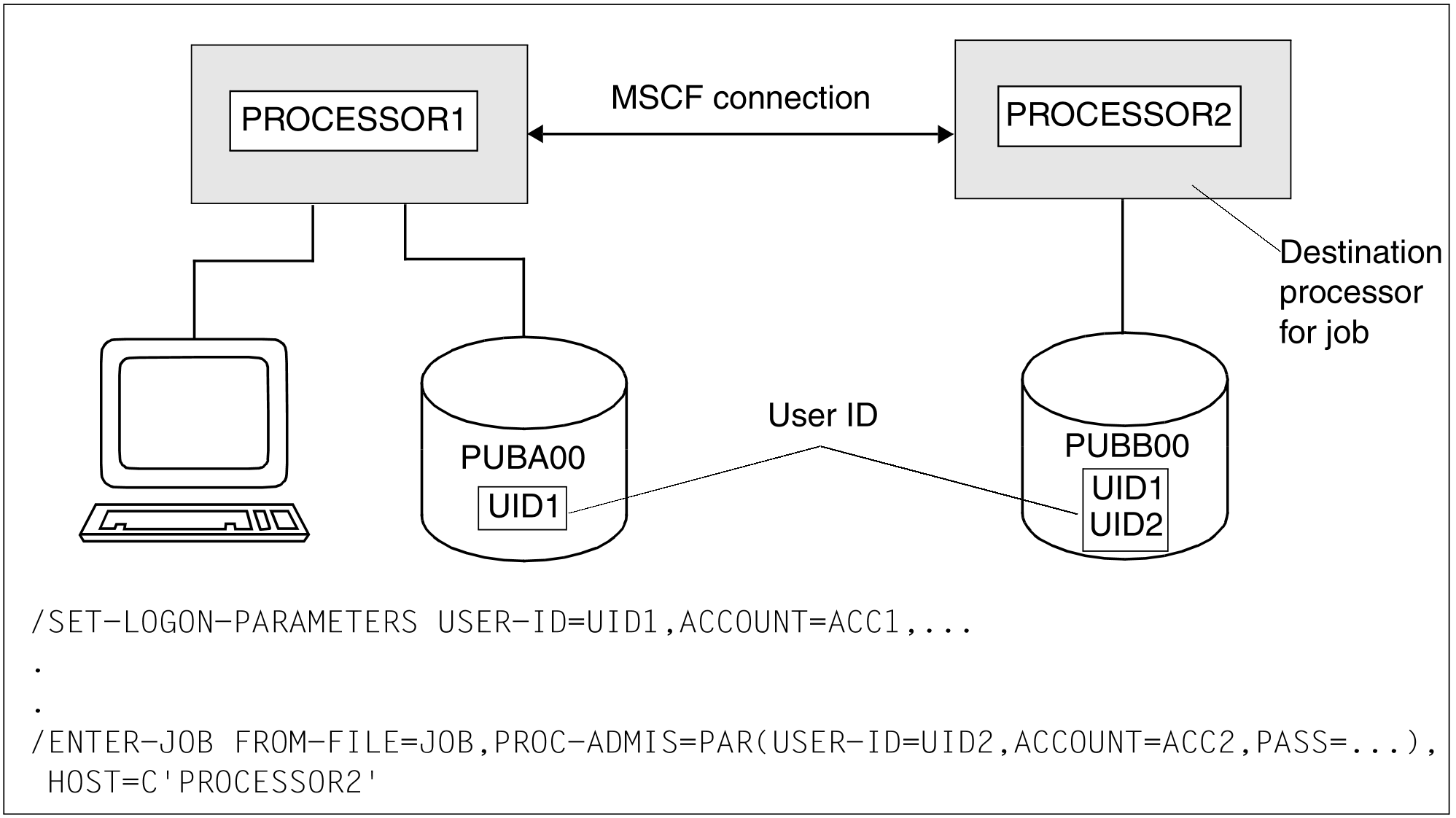
A user wants to pass a job on to another processor in the MSCF network. In addition, the job is to be started under a different user ID (see figure 10).
Figure 10: Access permission on a destination processor
The different user ID must be entered on PROCESSOR2 together with the accounting number and password before the job can be started. The user ID under which the command is entered, must be known on the destination processor. In the case of an LCS, the password must also agree.