This chapter
explains LCS, CCS, shared pubset and XCS networks
discusses the connections, partner types, applications, special features and restrictions of the different network types
describes entry, reentry to and exit from the XCS network
explains the XCS reconfiguration.
Terms "connection", "network" and "partner"
The terms "connection" and "network" are defined in HIPLEX MSCF as follows:
Connection denotes the communication path implemented by BCAM which links two processors to each other (even different BS2000 versions).
Network, on the other hand, denotes a group of processors which work together in a functional sense. HIPLEX MSCF makes the connections and the coordination mechanisms available with which the distributed system functions form the function network.
HIPLEX MSCF makes a distinction between the following connection types:
LCS connection
CCS connection.
These connection types form the basis of the network types listed below.
LCS network (“Loosely Coupled System” formed via an LCS connection)
as well as via CCS connections:
CCS network (“Closely Coupled System”)
SPVS network (“Shared Pubset Network”)
XCS network ("Cross Coupled System").
All the new features and latest developments are exclusively supported via CCS connections. The functional scope supported via LCS connections will not be extended.
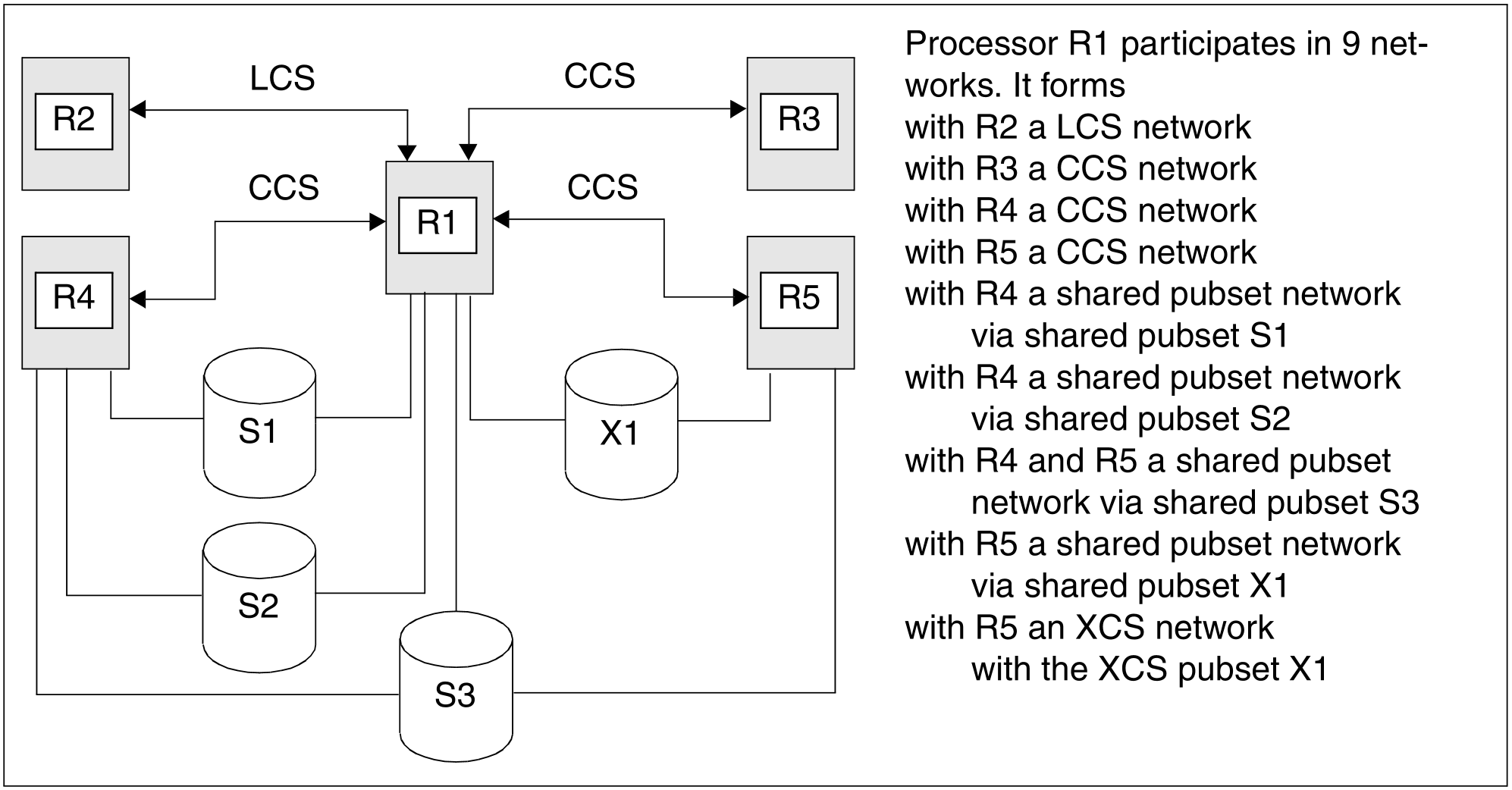
Example
Processor R1 is coupled via an LCS connection with processor R2 and via CCS connections with processors R3, R4 and R5. Pubsets S1 and S2 are used by processors R1 and R4, pubset S3 by processors R1, R4 and R5 as a shared pubset while pubset X1 is used by processors R1 and R5 as an XCS pubset.
Figure 6: Network types
From the point of view of a processor, the network relationship with a partner processor is defined by the partner type. A distinction is made between the partner types LCS, CCS and XCS.
A partner processor is called an LCS partner when it has an LCS-type MSCF connection.
A partner processor is called a CCS partner when it has a CCS-type MSCF connection, but the two processors do not participate in the same XCS network.
A partner processor is called an XCS partner when both processors participate in the same XCS network.