The HIPLEX MSCF function network makes available the operating system functions, that were originally only available on one processor, throughout the network. A pubset can then be accessed not only by the one processor but by all of the processors in the network. The network itself may not necessarily be visible to an application, e.g. files made available on a shared pubset via the registered system function "shared pubset manager" are also available on all processors that access that pubset, as if they were local files. Only the use of processor-independent functions (e.g. shared update from several processors) can require that the network configuration is taken into account in the applications.
The registered functions themselves use the services of the HIPLEX MSCF communication system to exchange requests with their partner systems on other processors.
HIPLEX MSCF recognizes different types of function network which differ in the way they cooperate. The starting of a request on a partner processor, for example, is a two-network cooperation between the two processors. Accessing shared pubset is a network cooperation between all processors that have imported the shared pubset. Global locks are a network cooperation between all of the processors that are currently participating in the same XCS network.
The following network types exist with different functionalities:
LCS network with the "remote catalog access (RCA)", "remote enter" and "remote job control" functions.
CCS and the shared pubset network with a "closer" coupling between two processors and management operations applicable to all the processors that simultaneously access a shared pubset.
XCS network with a "closer" coupling between two processors and a management entity for the XCS participants. The "shared file system" and "global locks" functions, among other things, are supported in this kind of network.
Each network type includes the functionality of all the preceding network types.
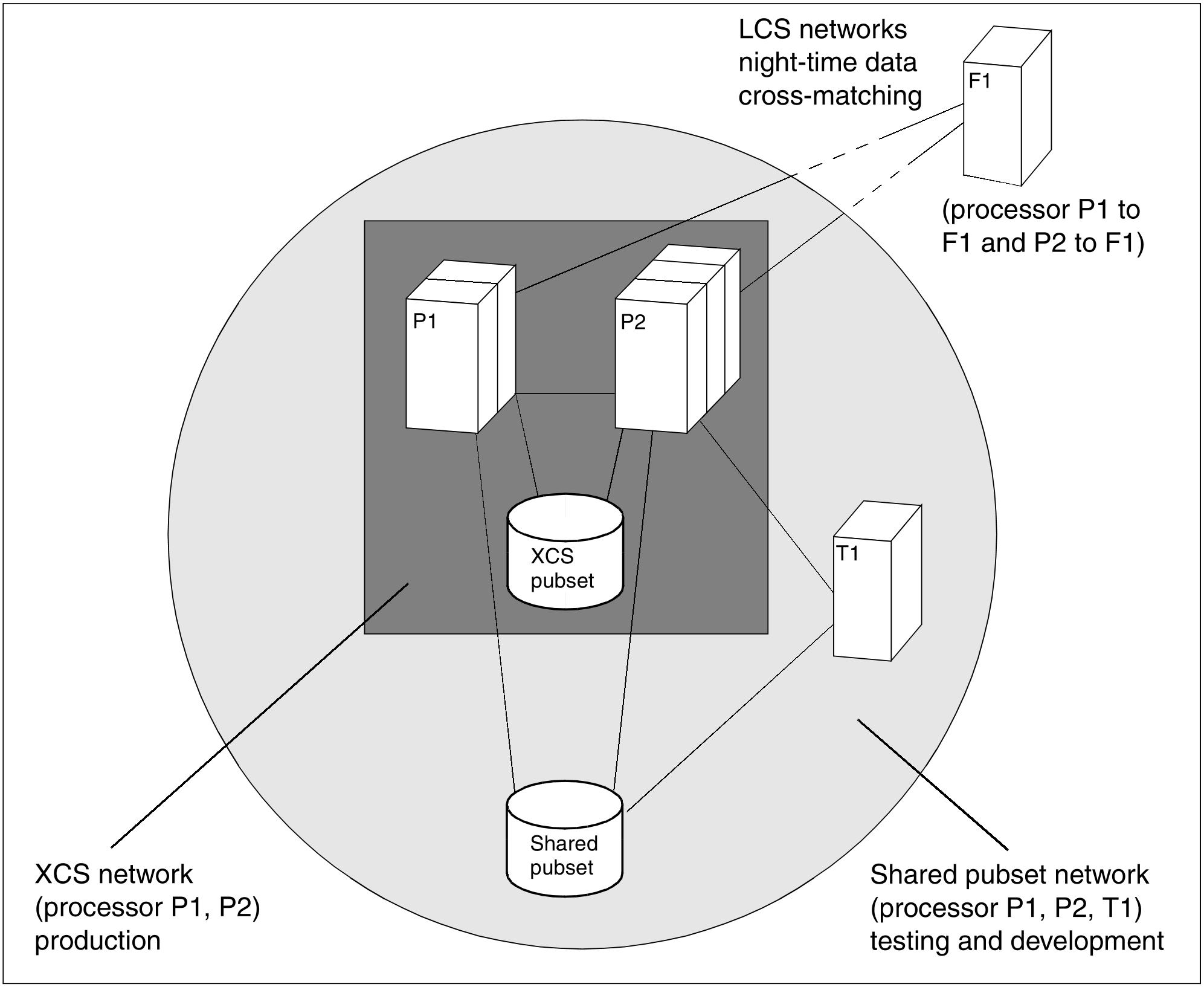
The figure below illustrates the characteristics of the different network types. It shows a HIPLEX with four processors.
Processors P1 and P2 are linked in an XCS and form an XCS network. They are responsible for production. The production data is stored on shared pubsets which can be accessed by both processors. The processors form a shared pubset network in relation to the shared pubsets which both processor have jointly imported.
Processor T1 is used for testing and development. Shared tools and programs are stored on a shared pubset which processors P1, P2 and T1 can access. Together they form a shared pubset network. The connection to processor F1 is only set up when cross-matching of the data is carried out (e.g. during the night using RFA, controlled via CJC).
Figure 5: Network types