DNS (Domain Name Service) is a global network of DNS servers that map names to IP addresses. Neither the internet nor the operation of intranets would be possible without DNS.
DNS names have a hierarchical tree structure spanning various domain levels. The root domain is the starting point for all searches within the entire DNS name space. Besides the names, the DNS also includes addresses and other information.
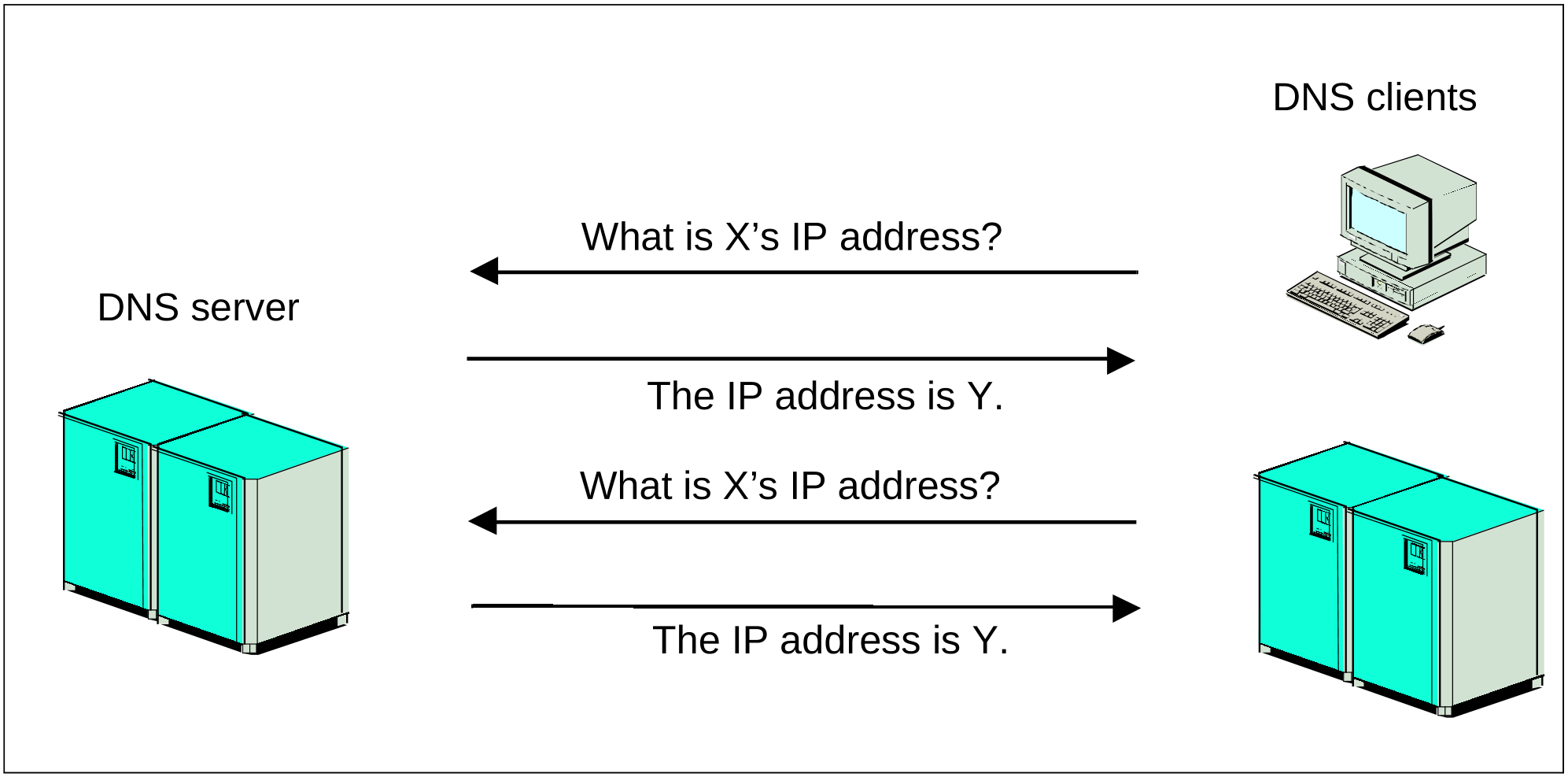
The Domain Name Service is a distributed and replicated database system with DNS servers and DNS clients (resolvers). The data is maintained on several DNS servers, each of which may be responsible for one or more DNS domains. If desired, redundant DNS servers may be used for failover security. The resolvers (or clients), by contrast, do not have a local database. For each DNS query, a client may contact one or more DNS servers to obtain the information it needs. These DNS queries can optionally be signed.
When queries are made, cryptographic signatures only secure communication between servers. Cryptographic signatures are not supported for communication between client and server.
BS2000 provides its users with both the server and the resolver functionality of DNS.
Both the server and the resolver functionality were ported from the BIND coding, which is considered the standard implementation for DNS. This provides BS2000 users with access to all DNS functions and services. In addition, the high availability of BS2000 also guarantees reliable access to the DNS servers on the network.