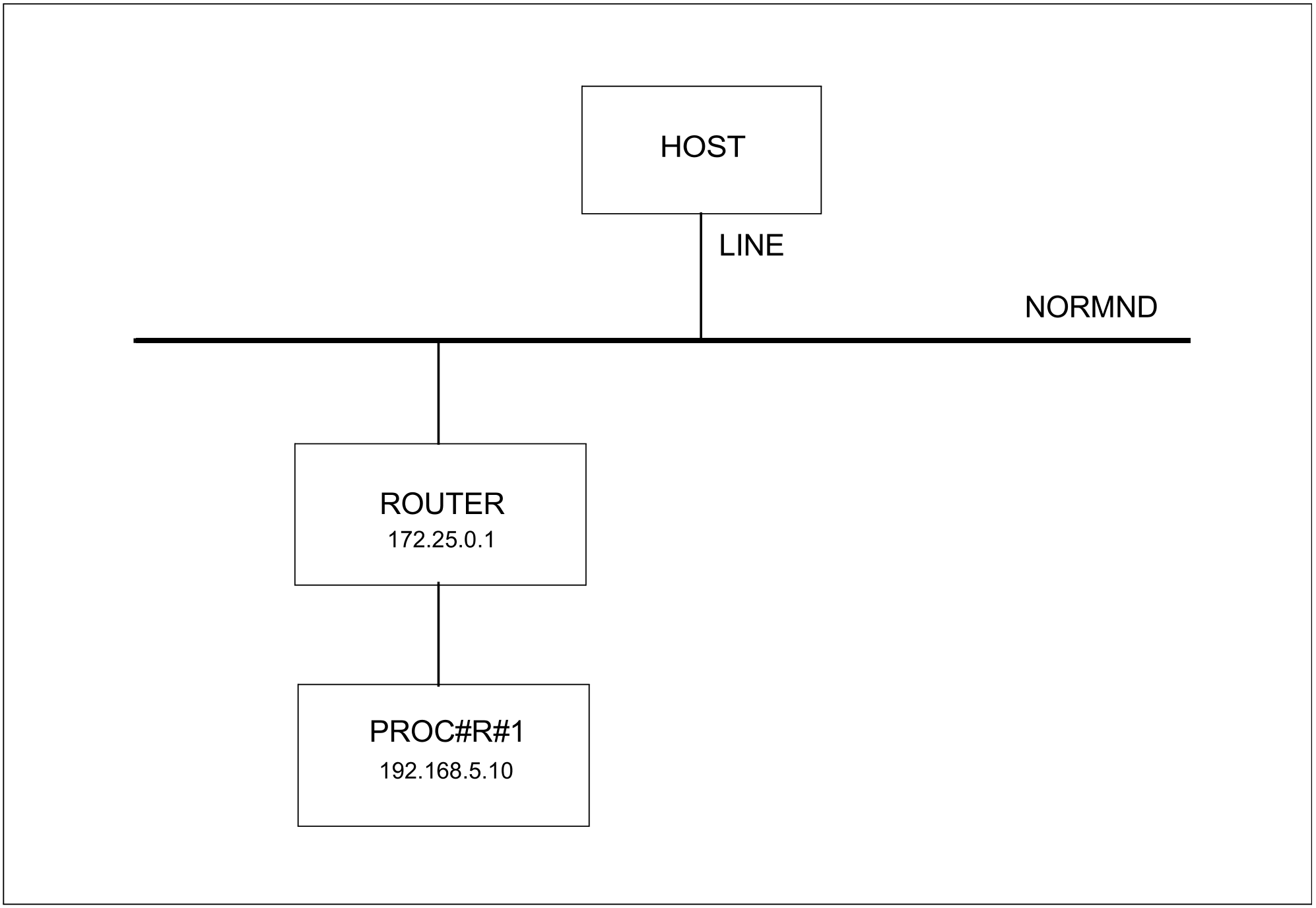
In this example the remote processor PROC#R#1 behind the router ROUTER is examined.
Dynamic generation
/REMARK Definition of the LAN node NORMND
/REMARK Definition of the router ROUTER
/CREATE-PROCESSOR PROCESSOR-NAME=PROC#R#1,ADMINISTRATION-TYPE=*BCAM
/CREATE-ROUTE ROUTE-NAME=PROC#R#1,PATH=*VIA-ROUTER(-
/ROUTER-ROUTE-NAME=ROUTER,L3-PROTOCOL=*IP(IP-ADDRESS= 192.168.5.10))
Definition through AEC (automatic end system creation)
The remote processor PROC#R#1 shown in the figure can alternately be specified in the processor file and generated by automatic end system creation. To do this the “automatic end system creation” option must be specified. In addition, the system must be included in the processor file.
Setting options
/BCOPTION A-E-C=ON
Entry in the processor file
PROC#R#1 IP 192.168.5.10
Definition through DNS
Another way of defining the remote processor PROC#R#1 is to use DNS. To do this you must start the LWRESD utility routine (by default this is already possible in the DCOPT/ DCSTART command) and specify the option for DNS. DNS accesses can be restricted using the MODIFY-DNS-ACCESS command.
Entries in the SOF file
/MODIFY-BCAM-OPTIONS DNS-OPTIONS=*PARAMETERS(DNS-USAGE=*ON)
/MODIFY-DNS-ACCESS IP-ADDRESS-RANGE= -
/ *ADD(FROM= 192.168.5.10,TO= 192.168.5.10)
/MODIFY-DNS-ACCESS IPV6-ADDRESS-RANGE=*NONE
/MODIFY-DNS-ACCESS NAMES=PROC#R#1