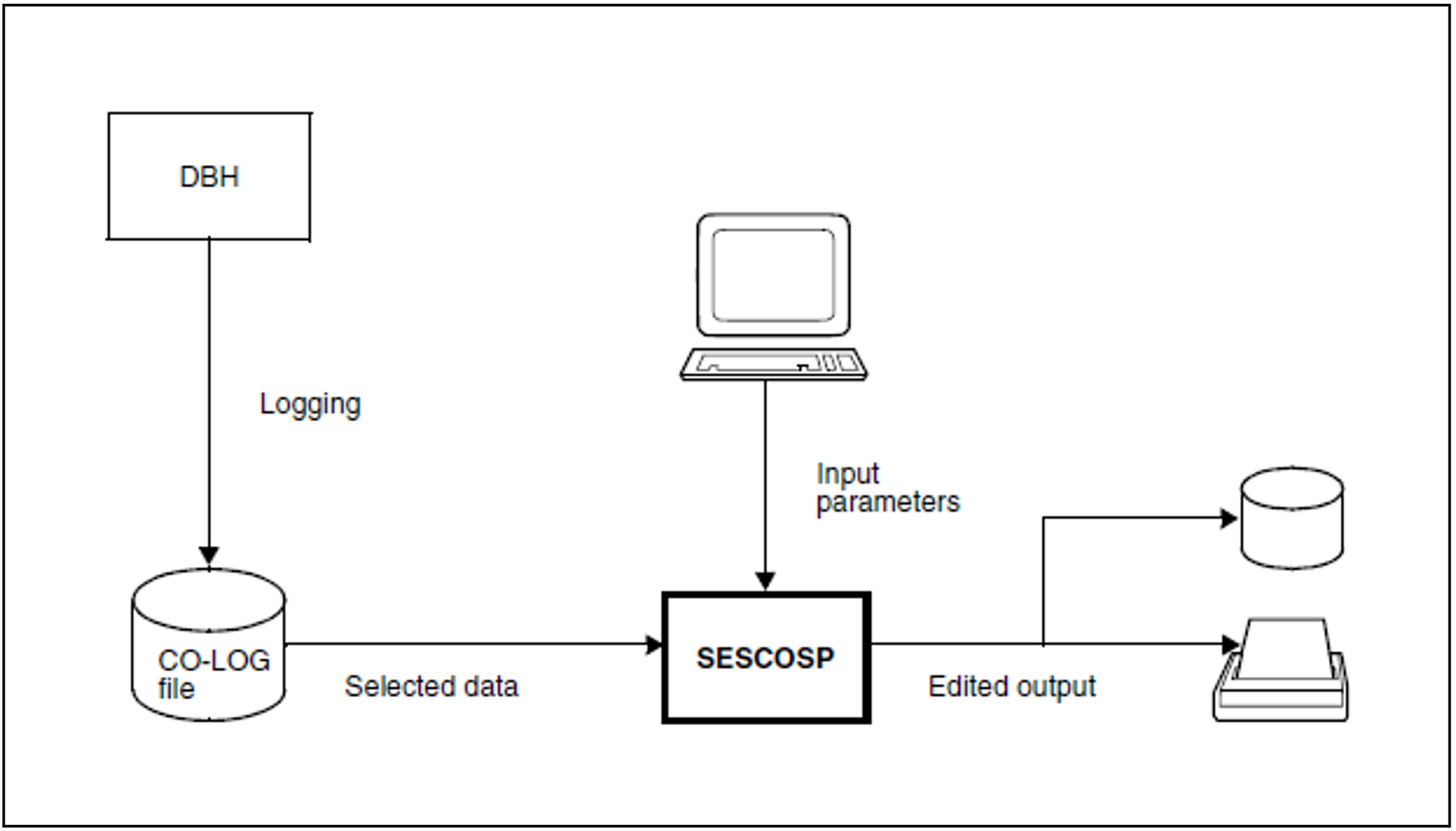
SESAM/SQL logs request-specific data; From the user's viewpoint, a SESCOSP request corresponds to a statement.
The system administrator uses the SET-TUNING-TRACE administration statement or the COS administration command (see "SET-TUNING-TRACE") to turn request logging on and off. The system administrator controls the logged data amount by means of the operand PROTOCOL=*STD/*LONG. When request logging is on, the DBH logs data in a request log file (the CO-LOG file). The request log file contains a large amount of data, which the SESCOSP utility then evaluates.
The logged data indicates which statements have been executed for which program, and which spaces, tables and databases have been addressed. The system administrator can use the logged data to follow what happened during the relevant period and carry out a precise analysis. In this way, SESCOSP reports can be used as a basis for finding out performance-critical statements. The “ Performance” manual provides assistance in analyzing performance problems and indicates any measures required to improve throughput.
The user can set parameters to cause SESCOSP to evaluate only a subset of the data logged in the request log file. You can limit the evaluation to selected databases, parts of databases, users, statements and time periods.
SESCOSP reports essentially provide the following information:
for each statement: I/Os and time behavior
for each statement step: I/Os, time behavior and accesses to resources
for each transaction: I/Os and time behavior
for each statement group: termination statistics in the form of total and average values.
SESCOSP outputs the data in selectable report formats.
Figure 6: Request logging and evaluation with SESCOSP