Central data of the SE Server configuration is stored (irrespective of the existence of a cluster) on a so-called configuration disk (or CRD disk) of a unit (MU, SU x86, HNC):
- General data of the SE Server:
- Model, name and location
- Unit-overarching data
- Unit-specific data the content of which must be available also after an outage or after the unit (MU/SU /390, SU x86) has been turned off:
- Model, SW version and hostname
- IP configuration
- FC configuration
- VM data for BS2000
- Storage of the last CSR backup
- Current configuration of the Net Unit switches
By default the above mentioned data are written locally on an internally mirrored disk of the MU/SU/HNC – the internal configuration disk (CRD disk).
CRD with external configuration disks
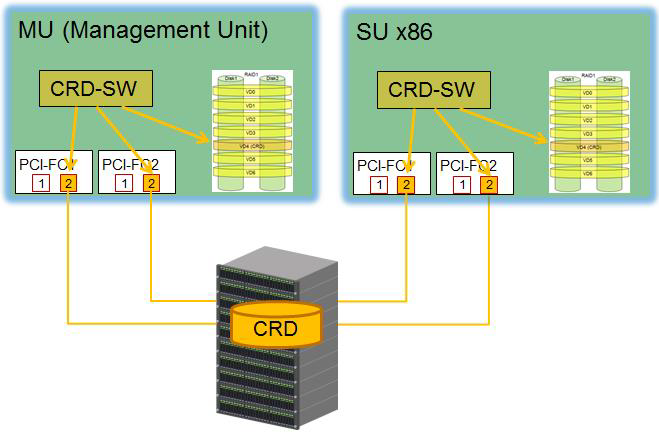
Additionally to the internal CRD disk, up to two external CRD disks can be configured situated on external FC RAID systems to which all MU and SU x86 have access through a redundant connection.
The internal and the external CRD disks are combined to a logical unit („logical disk“) via mirroring in SW-technical way and built up to the so-called "CRD" ("Configuration Raw Device") which provides the “CRD functionality” to all MU and SU x86.
The above mentioned central data of the SE Server configuration are „written on the CRD“ and read from there.
With the CRD functionality every MU and SU x86 has the same view on the data of the SE Server and the actions on these units can be done in coordinated way. (unit-overarching consistence)
External configuration disks (also called CRD disks) are required in the following cases:
MU redundancy | -> mandatory
|
MU redundancy | -> recommended
|
Cluster | -> mandatory for every type of cluster
|
Technically, it is external disks with FC connection and a capacity of at least 8 GB that have to be used for external CRD disks.
The MU and the SU x86 access the external CRD disks directly through FC. SU /390 access the external configuration through the BS2000 subsystem REWAS and one MU (in normal operation through a server-local MU).
Recommendations and notes
- To avoid a „single point of failure" a configuration with two external CRD disks in different storage systems with redundant FC connections is recommended.
- Every external CRD disk must be accessible from every MU (X-cabling or SAN-X-configuration of the RAID periphery).
- In case of a SU x86 cluster the external CRD disks must be also accessible from every SU x86.
- A maximal distance of 15 km between the locations is recommended.
- Note:
The cluster software does not check whether the above conditions are met. This has to be ensured by the customer through a suitable configuration of the infrastructure.
The CRD disks are provided by the customer and are set up by the customer’s service.
The unit specific CRD disks and their current status are displayed under
Hardware -> Units -> <server> (SE<model>) -> <unit> (MU) -> Information tab CRD disks in the SE Manager.
Their current status is displayed in the main window of the cluster for which it is relevant.