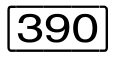/SHOW-VM-DEFINITION is used to display the attributes, resources and devices entered for a VM in the VM definition, as well as information on the automatic startup of the guest system on the VM.
The command provides the following information:
Attributes entered for the VM in its VM definition
Displays whether the VM definition is active, i.e. the VM is initialized
Displays whether the high-availability (HA) attribute is reserved for the VM
Settings for the CPU management of the VM
Settings for the main memory of the VM
Settings for the privileges of the VM
Settings for automatic startup of the guest system on the VM when the VM definition is activated next time
Devices that are assigned to the activated VM or that are to be assigned to the VM when it is activated.
This command is reserved for the VM2000 administrator. It can also be entered for initialized VMs.
SHOW-VM-DEFINITION |
VM-NAME = *ALL / <name 1..8 with-wild(20)> ,INFORMATION = *STD / *CPU / *MEMORY / *PRIVILEGES / *IPL / *UNITS / *ALL |
VM-NAME =
Determines the VM definitions whose contents are to be output.
VM-NAME = *ALL
The contents of all VM definitions are output.
VM-NAME = <name 1..8 with-wild(20)>
The contents of all VM definitions whose VM name matches the specified pattern are output.
INFORMATION =
Specifies the output information.
INFORMATION = *STD
Only the entered attributes of the VM.
INFORMATION = *CPU
Only the settings for the CPU management of the VM.
INFORMATION = *MEMORY
Only the settings for the main memory of the VM.
INFORMATION = *PRIVILEGES
Only the settings for the privileges of the VM.
INFORMATION = *IPL
Only the settings for automatic startup of the guest system on the VM when the VM definition is next activated.
INFORMATION = *UNITS
Only the devices which are assigned to the VM which has already been initialized or are to be assigned to the VM when it is activated.
INFORMATION = *ALL
All the information of all outputs.
Command return codes
(SC2) | Main code | Meaning |
0 | CMD0001 | Command successfully executed |
Output in S variables (in user task)
The INFORMATION operand of the command is used to specify which S variables are to be supplied with values. The following can be specified for INFORMATION:
Notation of command | Abbreviated form used in table |
INFORMATION = *STD | 1 |
Output information | Name of S variable | T | Contents | Cond. |
Name of VM | var(*LIST).VM-NAME | S | <name 1..8> | 1 - 7 |
Index of VM (0 = *ANY) | var(*LIST).VM-INDEX | I | <integer 0..99> | 1 - 7 |
Is the VM definition active | var(*LIST).ACTIVE | B | TRUE / FALSE | 1 - 7 |
Does the VM have the | var(*LIST).PERSISTENT | B | TRUE / FALSE | 1, 7 |
Is it a highly available VM? | var(*LIST).HA | B | TRUE / FALSE | 1, 7 |
Maximum I/O utilization | var(*LIST).MAX-IO-UTILIZATION | I | <integer 1..100> | 1, 7 |
Multiprocessor level | var(*LIST).NUM-OF-CPUS-SPEC | S | *BY-NUMBER | 1, 2, 7 |
Multiprocessor level | var(*LIST).NUM-OF-CPUS | I | <integer 1..32> | 1, 2, 7 |
Name of the CPU pool | var(*LIST).CPU-POOL | S | *BY-VM-GROUP | 1, 2, 7 |
Name of the VM group | var(*LIST).VM-GROUP | S | *NONE | 1, 2, 7 |
Value of the CPU quota | var(*LIST).FINE-CPU-QUOTA | S | <fixed 0.01..99.99> | 2, 7 |
Maximum CPU utilization | var(*LIST).FINE-MAX-UTIL | S | <fixed 0.01..100.00> | 2, 7 |
Setting for VM-ACTIVE-IDLE | var(*LIST).VM-ACTIVE-IDLE | S | *NO | 2, 7 |
Size of the main memory | var(*LIST).MEM-SIZE | S | <integer 1..1048576> | 1, 3, 7 |
Minimum size of the main | var(*LIST).MIN-MEM-SIZE | S | <integer 1..1048576> | 3, 7 |
Maximum size of the main | var(*LIST).MAX-MEM-SIZE | S | <integer 1..1048576> | 3, 7 |
Functional scope for the VM | var(*LIST).ADM-PRIVIL | S | *STD / *MIN / *MAX | 4, 7 |
Is the IO-RESET privilege | var(*LIST).IO-PRIVIL | B | TRUE / FALSE | 4, 7 |
Is the IO-PRIORITY privilege | var(*LIST).IO-PRIO-PRIVIL | B | TRUE / FALSE | 4, 7 |
Is the AUTO-SNAP- | var(*LIST).AUTO-SNAP-PRIVIL | B | TRUE / FALSE | 4, 7 |
Is the ASSIGN-BY-GUEST | var(*LIST).ASS-BY-GUEST-PRIVIL | B | TRUE / FALSE | 4, 7 |
Specification of the assignment | var(*LIST).ASSIGNMENT-SET-SPEC | S | *NONE / *ALL / | 4, 7 |
List of the assignment sets | var(*LIST).ASSIGNMENT-SET(*LIST) | S | *STDSET / <name 1..8> | 4, 7 |
Is the guest system on the VM | var(*LIST).AUTO-IPL-PAR.EFFECTIVE | B | TRUE / FALSE | 5, 7 |
Mnemonic name of the IPL | var(*LIST).AUTO-IPL-PAR.IPL-UNIT | S | <alphanum-name 2..2> | 5, 7 |
Mnemonic name of the KVP | var(*LIST).AUTO-IPL-PAR.CONS-OUT | S | <alphanum-name 2..2> | 5, 7 |
Mode for the automatic start | var(*LIST).AUTO-IPL-PAR.MODE | S | *AUTOMATIC / | 5, 7 |
System name for the | var(*LIST).AUTO-IPL-PAR.SYS-NAME | S | <name 1..8> | 5, 7 |
Do the parameters of the | var(*LIST).LAST-IPL | B | TRUE / FALSE | 5, 7 |
Are the parameters of the | var(*LIST).LAST-IPL-PAR.EFFECTIVE | B | TRUE / FALSE | 5, 7 |
Mnemonic name of the | var(*LIST).LAST-IPL-PAR.IPL-UNIT | S | <alphanum-name 2..2> | 5, 7 |
Mnemonic name of the | var(*LIST).LAST-IPL-PAR.CONS-OUT | S | <alphanum-name 2..2> | 5, 7 |
IPL mode at the last IPL | var(*LIST).LAST-IPL-PAR.MODE | S | *AUTOMATIC / | 5, 7 |
System name at the last IPL | var(*LIST).LAST-IPL-PAR.SYS-NAME | S | <name 1..8> | 5, 7 |
Number of device assignments | var(*LIST).NUM-OF-UNITS | I | <integer 0..32767> | 6, 7 |
Devices of the VM | var(*LIST).UNIT(*LIST).MN | S | <alphanum-name 2..2> | 6, 7 |
Responsible for the device | var(*LIST).UNIT(*LIST).ASS-BY | S | *VM-ADMIN / *GUEST | 6, 7 |
Assignment as pubset device? | var(*LIST).UNIT(*LIST).ASS-VIA-PUBSET | B | TRUE / FALSE | 6, 7 |
Assignment as pubres device? | var(*LIST).UNIT(*LIST).PUBRES-FOR-ASS | B | TRUE / FALSE | 6, 7 |
Usage mode of the device | var(*LIST).UNIT(*LIST).USAGE | S | *EXCL / *SHARED | 6, 7 |
Is the device a virtual console? | var(*LIST).UNIT(*LIST).VC | B | TRUE / FALSE | 6, 7 |
| 1 | When the VM definition is not active, only the envisaged, explicit assignments by the VM2000 administrator (*VM-ADMIN) are displayed. |
Output format for INFORMATION = *STD
CPU-POOL(P) VM-ID ACT PER HA VM-GROUP(G) PROC MEM-SIZE MAX-IO 5 G4IVJ YES NO NO *STDPOOL(P) 2 512 100
Meaning of the output columns
VM-ID
Identifies the VM by means of VM index and VM name.
If the index *ANY is entered in the VM definition of a persistent VM, a hyphen (–) is output.
ACT
Displays whether the VM definition is active, i.e. whether the VM is initialized (YES/NO).
PER
Displays whether the VM has the PERSISTENT attribute (YES/NO).
HA
Displays whether the VM has the high-availability (HA) attribute (YES/NO).
CPU-POOL(P)VM-GROUP(G)
Displays the assignment to a VM group.
If the VM is not assigned or is not to be assigned to a VM group, the CPU pool to which the VM is assigned or is to be assigned is shown.
Whether the VM is assigned or is to be assigned to a VM group is indicated by a suffix:
<vm-group-name>(G) The VM is assigned to a VM group or is to be assigned to a VM group. Under CPU-Q the member CPU quota of the VM is output (SU /390).
<cpu-pool-name>(P) The VM is not assigned to any VM group, or is not to be assigned to any VM group. Under CPU-Q the CPU quota of the (individual) VM is output.
PROC
Entered virtual CPUs of the VM in the form:
m | Number of virtual normal CPUs of the VM (multiprocessor level of the VM) |
| Number of real normal CPUs which are available on the Server Unit for VM2000 operation. The VM was or will be created with |
| Number of real normal and extra CPUs which are available on the Server Unit for VM2000 operation. The VM was or will be created with |
Entered main memory size of the VM in Mbytes.
MAX-IO
Entered maximum I/O utilization of the VM.
Output format for INFORMATION = *CPU
CPU-POOL(P) VM-ID ACT VM-GROUP(G) CPU-Q MAX-U PROC ACT-I 5 G4IVJ YES *STDPOOL(P) 70.00 100.00 2 NO
Meaning of the output columns
VM-ID / ACT / CPU-POOL(P) VM-GROUP(G) / PROC
Corresponds to INFORMATION=*STD.
CPU-Q
Entered CPU quota of the VM.
MAX-U
Entered maximum CPU utilization of the VM.
ACT-I
Entered setting for controlling the real CPU in the case of fixed CPU assignment:
NO | The VM leaves control over the real CPU if the VM’s virtual CPU which runs on this is inactive (interruptible wait state, "Idle"). |
AT–DC | The VM retains control over the real CPU even if the VM’s virtual CPU which runs on this is inactive (interruptible wait state, "Idle", SU /390). |
Output format for INFORMATION = *MEMORY
VM-ID ACT MEM-SIZE MIN-MEM-S MAX-MEM-S 5 G4IVJ YES 512 512
Meaning of the output columns
VM-ID / ACT
Corresponds to INFORMATION=*STD.
MEM-SIZE
Entered main memory size of the VM in Mbytes.
MIN-MEM-S
Entered minimum size of the VM’s main memory in Mbytes (for main memory reconfiguration).
MAX-MEM-S
Entered maximum size of the VM’s main memory in Mbytes (SU x86 for main memory reconfiguration). No output for SU /390.
Output format for INFORMATION = *PRIVILEGES
VM-ID ACT PRIV DETAILS 5 G4IVJ YES AS
Meaning of the output columns
VM-ID / ACT
Corresponds to INFORMATION=*STD.
PRIV
Entered privileges of the VM.
NO PRIVILEGE | |
| No privileges. | |
ADM | Command/function scope for VM2000 administrator (monitor VM) or VM administrator, see DETAILS. |
AG | The VM has the ASSIGN-BY-GUEST privilege. The list of the assignment sets assigned is output in DETAILS. |
AS | AUTO-SNAP-ASSIGNMENT=*YES (default). |
IO–P | IO-PRIORITY=*YES. |
IO–R | IO-RESET=*YES. |
DETAILS
Supplementary information on the privileges:
For PRIV=ADM: | |
*VM2000-MIN | ADMIN-PRIVILEGES=*MIN for the monitor VM |
*VM-MAX | ADMIN-PRIVILEGES=*MAX for a VM other than the monitor VM |
For | |
*ALL | ASSIGN-BY-GUEST=*YES(SET-NAME=*ALL) |
*EXCEPT: set1, set2, ... | |
ASSIGN-BY-GUEST=*YES(SET-NAME=*EXCEPT(...)) | |
set1, set2, ... | |
ASSIGN-BY-GUEST=*YES(SET-NAME=<list>) | |
Output format for INFORMATION = *IPL
VM-ID ACT TYPE EFF IPL-U IPL-C MODE SYSNAME
5 G4IVJ YES AUTO NO
LAST YES FC17 CC FAST
Meaning of the output columns
VM-ID / ACT
Corresponds to INFORMATION=*STD.
TYPE
Type of subsequent IPL parameters.
AUTO | The IPL parameters specified using a command are displayed (AUTO-IPL parameters). |
LAST | If there are any, the IPL parameters are displayed with which the VM was most recently started. |
EFF
Shows whether the IPL parameters are effective (YES / NO).
TYPE and EFF.A VM definition can contain both IPL parameters for
TYPE=AUTOand forTYPE=LAST.EFFshows which entries are currently effective.After a VM has been initialized with
/CREATE-VM,EFF=NOalways applies forTYPE=AUTO.When a persistent VM definition is created using
/CREATE-VM-DEFINITION, the values forTYPE=AUTOdepend on the specifications in theAUTO-IPL=*YES/*NOparameter.The line with
TYPE=LASTis displayed only after the first successful start of the guest system.The combination
TYPE=AUTOandEFF=YESdisplays the IPL parameters for an automatic startup of the guest system on the persistent VM when its VM definition is activated next time.With the combination
TYPE=AUTOandEFF=NO, IPL parameters for an automatic startup can already be entered in the VM definition (by a former command withAUTO-IPL=*YES). However, they are currently deactivated (by a subsequent command withAUTO-IPL=*NO). In this case, the guest system is not started automatically the next time the VM definition is activated.- The values of the IPL parameters for
TYPE=AUTO, which are entered in the VM definition, can be modified with/MODIFY-VM-ATTRIBUTES(VM definition active) or/MODIFY-VM-DEFINITION(VM definition not active) using parameterPERSISTENT=*YES(AUTO-IPL=*YES(...)/*NO)orPERSISTENT=*NO. - With
TYPE=LAST, the value forEFFcannot be controlled directly by the VM2000 administrator. In this case, the IPL parameters become effective through a successful start of the guest system (EFF=YES). They become ineffective through a normal shutdown of the guest system (EFF=NO).
IPL-U
Mnemonic device name of the disk device used for the initial program loading (IPL) of the guest system.
IPL-C
Mnemonic device name of the KVP output device or of the virtual console (only with TYPE=LAST on SU /390).
MODE
Type of system initialization (AUTO / FAST / DIALOG).
SYSNAME
System name of the guest system (SU x86). No output for SU /390.
Output format for INFORMATION = *UNITS
VM-ID ACT UNITS
5 G4IVJ YES ASSIGNED BY VM-ADMIN
EXCL: CC(VC),CC48,CC49,CC88,CC89,CD48,CD49,
FC17(PR),FC18(PD),FC19(PD)
SHARED: 990F
Meaning of the output columns
VM-ID / ACT
Corresponds to INFORMATION=*STD.
UNITS
Entered mnemonic device names in blocks: first the explicitly assigned devices (ASSIGNED BY VM-ADMIN), then the implicitly assigned devices (ASSIGNED BY GUEST). The output is grouped in accordance with the usage mode (EXCL/SHARED). Empty blocks or groups are omitted.
When no devices are to be assigned, NO DEVICE ASSIGNED is output.
The device list is arranged within a group in ascending order of the value range (two- or four-digit). The two-digit device names are output first, followed by the four-digit device names.
The suffix (PR) indicates the pubres device of a pubset whose devices have been assigned to the VM or are to be assigned when the VM definition is activated.
The suffix (PD) indicates a pubres device which has been assigned to a VM with an active VM definition (i.e. the VM is initialized) via the pubset.
/DELETE-VM, entries for such devices and also the entries for implicitly assigned devices (ASSIGNED BY GUEST) are removed from the VM definition.The suffix (VC) identifies a virtual console (see "Operating the guest systems (VC dialog via $VMCONS)"). |
Example (SU /390)
/show-vm-definition vm-name=g4ivj,information=*all ———————————————————— (1) CPU-POOL(P)VM-ID ACT PER HA VM-GROUP(G) PROC MEM-SIZE MAX-IO 5 G4IVJ YES NO NO *STDPOOL(P) 2 512 100 CPU-POOL(P)VM-ID ACT VM-GROUP(G) CPU-Q MAX-U PROC ACT-I 5 G4IVJ YES *STDPOOL(P) 70.00 100.00 2 NOVM-ID ACT MEM-SIZE MIN-MEM-S MAX-MEM-S 5 G4IVJ YES 512 512VM-ID ACT PRIV DETAILS 5 G4IVJ YES ASVM-ID ACT TYPE EFF IPL-U IPL-C MODE SYSNAME 5 G4IVJ YES AUTO NO LAST YES FC17 CC FASTVM-ID ACT UNITS 5 G4IVJ YES ASSIGNED BY VM-ADMIN EXCL: CC(VC),CC48,CC49,CC88,CC89,CD48,CD49, FC17(PR),FC18(PD),FC19(PD) SHARED: 990F
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(1) | The VM2000 administrator inquires the settings for the VM entered in the VM definition. |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------